(Press-News.org) Many cat owners are familiar with torn cushions, carpets, and couches. The feline instinct to scratch is innate but is often perceived as a behavioral problem by cat owners and sometimes leads to interventions that are not cat friendly.
Now, an international team of researchers has investigated which factors influence undesired scratching behavior in domestic cats. They published their findings in Frontiers in Veterinary Science.
“Here we show that certain factors – such as the presence of children at home, personality traits of cats, and their activity levels – significantly impact the extent of scratching behavior,” said Dr Yasemin Salgirli Demi̇rbas, a veterinary researcher at Ankara University and first author of the study. “Our findings can help caregivers manage and redirect scratching to appropriate materials, which could help foster a more harmonious living environment for both cats and their caregivers.”
Kids, play, and personality
The researchers asked more than 1,200 cat owners in France about the daily lives and characteristics as well as undesired scratching behaviors of their feline companions. The study’s funder, Ceva Santé Animale, helped with collecting this data.
The researchers’ results showed that there are several factors that influence cats’ scratching behavior. “We see a clear link between certain environmental and behavioral factors and increased scratching behavior in cats,” Salgirli Demirbas explained. “Specifically, the presence of children in the home as well as high levels of play and nocturnal activity significantly contribute to increased scratching. Cats described as aggressive or disruptive also exhibited higher levels of scratching.”
Stress, the researchers said, was found to be a leading reason for unwanted scratching. For example, the presence of children, particularly while they are small, might amplify stress and be one of several causes that can make felines stress-scratch. The link between increased scratching and children in the home, however, is not fully understood and further study is needed. Another factor that could also be connected to stress is playfulness. When cats play for a long time, their stress levels can rise because of the uninterrupted stimulation.
Cat-friendly scratching interventions
While some factors that favor scratching – such as the cat’s personality or the presence of children – cannot be changed, others can, the researchers said. Placing scratch posts in areas the cat frequently passes or near to their preferred resting spot or the use of pheromones for example, can lessen cats’ scratching on furniture.
“Providing safe hiding places, elevated observation spots, and ample play opportunities can also help alleviate stress and engage the cat in more constructive activities,” Salgirli Demirbas pointed out. The key is to establish multiple short play sessions that mimic successful hunting scenarios. These play sessions are more likely to sustain cats’ interest and reduce stress, which ultimately can reduce excessive scratching on furniture. They can also foster the bond between cats and their caretakers, the researchers said.
“Understanding the underlying emotional motivations of scratching behavior, such as frustration, which seem to be linked to personality traits and environmental factors, allows caregivers to address these issues directly,” said Salgirli Demirbas. While the researchers had to rely on self-reported data, which is prone to subjectivity, they’ve gained unique insights into cats’ scratching behavior. The goal of this and future research is to develop more effective strategies to manage this behavior, ultimately enhancing the bond and harmony between cats and their caregivers, they said.
END
Scientists pinpoint strategies that could stop cats from scratching your furniture
Cats scratching on furniture can frustrate owners, but this normal feline behavior could be managed by adapting play sessions and offering scratch posts in the right spots, researchers found
2024-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
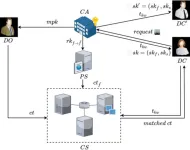
Offline/online attribute-based searchable encryption scheme from ideal lattices
2024-07-03
The security of traditional attribute-based searchable encryption schemes relies on traditional number-theoretic assumptions, and thus they are not able to resist the threat of quantum algorithms. Meanwhile, existing lattice-based searchable encryption schemes have two main problems: one is the low efficiency of the execution of encryption, key generation and search algorithms. The second is the large space required for storing search trapdoors.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Yang YANG published their new ...
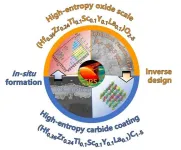
Theoretical design and experimental verification of high-entropy carbide ablative resistant coating
2024-07-03
The hot-end components of high-performance high-speed aircrafts need to meet performance requirements such as long service life, wide temperature range oxidation resistance and ablation resistance. This puts forward higher requirements for high-temperature service performance of thermal protection system (TPS).
With low density, low expansion and excellent high temperature mechanical properties, carbon-carbon (C/C) composites are expected to be the best choice for the new generation of TPS. However, the oxidation sensitivity of C/C composites severely limits their service life in high-temperature ablation environment. It ...
Cultural adaptation of behavioral interventions in health promises more effective results for the population
2024-07-03
Behavioral interventions are strategies designed to help people change their behaviors in a way that is positive for themselves and the community. These behaviors can relate to various topics, such as health, citizenship, ecology, and more. Interventions can be applied individually, like someone seeing a psychologist to quit smoking, or collectively, such as NGOs and public institutions investing in anti-smoking campaigns or raising awareness about the dangers of drunk driving.
Understanding how to adapt behavioral interventions to different cultures is essential for the success of health ...
New class of cancer mutations discovered in so-called ‘junk’ DNA
2024-07-03
New class of cancer mutations discovered in so-called ‘junk’ DNA
Using artificial intelligence, Garvan Institute researchers have found potential cancer drivers hidden in so-called ‘junk’ regions of DNA, opening up possibilities for a new approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Non-coding DNA – the 98% of our genome that doesn’t contain instructions for making proteins – could hold the key to a new approach for diagnosing and treating cancers, according to a new study from the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. The findings, ...
High ceilings linked to poorer exam results for uni students
2024-07-03
Ever wondered why you performed worse than expected in that final university exam that you sat in a cavernous gymnasium or massive hall, despite countless hours, days and weeks of study? Now you have a genuine reason – high ceilings.
New research from the University of South Australia and Deakin University has revealed a link between rooms with high ceilings and poorer examination results.
A study published in the Journal of Environmental Psychology, led by architecture and psychology-trained UniSA researcher Dr Isabella Bower in collaboration with educational psychology researcher Associate Professor Jaclyn Broadbent from Deakin University, demonstrates that building design impacts ...
Low-dose aspirin could help prevent pregnancy complications caused by flu infections
2024-07-03
A world-first study has found low-dose aspirin may treat flu-induced blood vessel inflammation, creating better blood flow to the placenta during pregnancy.
Animal studies examined whether the treatment for preeclampsia could be applied to flu infections – and the results, according to the research team, were very promising.
Lead researcher and RMIT Post-Doctoral Research Fellow, Dr Stella Liong, said flu infections during pregnancy can resemble preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication that causes inflammation to the aorta and blood vessels.
Low-dose aspirin is commonly taken to prevent preeclampsia, as it stops the body from creating chemicals that cause ...
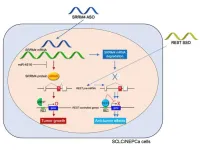
Splicing it all together in the fight against cancer
2024-07-03
Osaka, Japan – Neuroendocrine tumors, including small cell lung cancer and neuroendocrine prostate cancer, are very aggressive with high chances of spreading. However, many individuals develop resistance to few available treatment options, leading to poor patient outcomes. Researchers are therefore aiming to develop new therapeutic methods that focus on the disease-specific molecular mechanisms of these tumors.
In a recent article published in Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acids, a team of researchers at Osaka University describe a strategy targeting one such mechanism, called RNA splicing.
RNA splicing is the process ...
World’s first research journal dedicated to psychology and artificial intelligence announced
2024-07-03
Taylor & Francis has announced the launch of the Journal of Psychology and AI, an open access journal that aims to foster dialogue between technologists developing artificial intelligence (AI) systems and psychology researchers exploring human behavior, cognitions, and emotions.
As AI technology becomes increasingly integrated into our lives, the new journal will publish reports on direct human interaction with AI as well as exploring how it is influencing the way we interact with and think about the world.
Other research areas relevant to psychology and AI include using AI for the ...
Zayed to lead new Division of Surgical Sciences
2024-07-03
Mohamed A. Zayed, MD, PhD, a vascular surgeon known for his pioneering research in vascular diseases, has been appointed director of the newly established Division of Surgical Sciences in the Department of Surgery at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. He will assume his new role July 1.
Zayed, a professor of surgery, of radiology, of molecular cell biology, and of biomedical engineering, has more than 25 years of experience leading multifaceted research programs in biotech, medical startups ...
How dust pollution from shrinking Great Salt Lake affects communities disproportionately
2024-07-03
New research from the University of Utah demonstrates how wind-carried dust from the exposed bed of Great Salt Lake is disproportionately affecting disadvantaged communities in the Salt Lake metro area.
The findings suggest restoring the lake to a healthy water level would reduce disparities in harmful dust exposure experienced by different racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, along with delivering other ecological and economic benefits.
Exposure to particulate pollution arising from dry portions of the playa is highest among Pacific Islanders and Hispanics and lowest among white people compared to other racial/ethnic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Scientists pinpoint strategies that could stop cats from scratching your furnitureCats scratching on furniture can frustrate owners, but this normal feline behavior could be managed by adapting play sessions and offering scratch posts in the right spots, researchers found