(Press-News.org) About The Study: The results of this study suggest that many common environmental toxicants are associated with depressive symptoms. This research provides insight into selecting environmental targets for mechanistic research into the causes of depression and facilitating efforts to reduce environmental exposures.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jing Li, Ph.D., email jing.li@hsc.pku.edu.cn.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.20259)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.20259?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=070324
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Environmental toxicant exposure and depressive symptoms
JAMA Network Open
2024-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Web-based cognitive behavioral treatment for bulimia nervosa
2024-07-03
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial, a web-based cognitive behavioral self-help intervention effectively decreased eating disorder symptoms and illness-related burden in individuals with bulimia nervosa, underlining the potential of digital interventions to complement established treatments.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Steffen Hartmann, M.S., email steffen.hartmann@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.19019)
Editor’s ...
States with highest COVID-19 vaccination rates showed steepest decline in pediatric asthma prevalence
2024-07-03
States with Highest COVID-19 Vaccination Rates Showed Steepest Decline in Pediatric Asthma Prevalence
Study suggests COVID-19 vaccination might have broader benefits for children living with asthma
WILMINGTON, Del. (July 3, 2024) — States with high rates of COVID-19 vaccination saw more pediatric asthma patients get a break from their symptoms, according to new research published today in JAMA Network Open by leaders from Nemours Children’s Health and Endeavor Health.
“Asthma is one of the most common chronic illnesses among children in the United States, with about 4.7 million ...
Scientists unravel life-saving effect of dexamethasone in COVID-19
2024-07-03
Dexamethasone is one of the most important drugs in the treatment of severe COVID-19, but patients respond very differently to the therapy. Researchers at the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have now discovered how the cortisone compound influences the impaired inflammatory response and which patients benefit from it. Their method uses so-called single-cell analyses and raises hopes for a precise prediction tool for other therapies and diseases as well. The findings have been published in the scientific journal Cell.
It has long been puzzling why certain drugs work so well for some people and fail ...
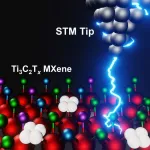
Mapping the surfaces of MXenes, atom by atom, reveals new potential for the 2D materials
2024-07-03
In the decade since their discovery at Drexel University, the family of two-dimensional materials called MXenes has shown a great deal of promise for applications ranging from water desalination and energy storage to electromagnetic shielding and telecommunications, among others. While researchers have long speculated about the genesis of their versatility, a recent study led by Drexel and the University of California, Los Angeles, has provided the first clear look at the surface chemical structure foundational to MXenes’ capabilities.
Using advanced imaging techniques, known as ...
Mobile phone data helps track pathogen spread and evolution of superbugs
2024-07-03
A new way to map the spread and evolution of pathogens, and their responses to vaccines and antibiotics, will provide key insights to help predict and prevent future outbreaks. The approach combines a pathogen’s genomic data with human travel patterns, taken from anonymised mobile phone data.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, University of the Witwatersrand and National Institute for Communicable Diseases in South Africa, the University of Cambridge, and partners across the Global Pneumococcal Sequencing project1, integrated genomic data from nearly 7,000 Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) samples collected in South Africa with detailed ...
Discovery of cellular mechanism to maintain brain’s energy could benefit late-life brain health
2024-07-03
A key mechanism which detects when the brain needs an additional energy boost to support its activity has been identified in a study in mice and cells led by UCL scientists.
The scientists say their findings, published in Nature, could inform new therapies to maintain brain health and longevity, as other studies have found that brain energy metabolism can become impaired late in life and contribute to cognitive decline and the development of neurodegenerative disease.
Lead author Professor Alexander Gourine (UCL Neuroscience, ...
Extinct humans survived on the Tibetan plateau for 160,000 years
2024-07-03
Bone remains found in a Tibetan cave 3,280 m above sea level indicate an ancient group of humans survived here for many millennia, according to a new study published in Nature.
The Denisovans are an extinct species of ancient human that lived at the same time and in the same places as Neanderthals and Homo sapiens. Only a handful Denisovan remains have ever been discovered by archaeologists. Little is known about the group, including when they became extinct, but evidence exists to ...
PolyU study reveals the mechanism of bio-inspired control of liquid flow, enlightening breakthroughs in fluid dynamics and nature-inspired materials technologies
2024-07-03
The more we discover about the natural world, the more we find that nature is the greatest engineer. Past research believed that liquids can only be transported in fixed direction on species with specific liquid communication properties and cannot switch the transport direction. Recently, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) researchers have shown that an African plant controls water movement in a previously unknown way – and this could inspire breakthroughs in a range of technologies in fluid dynamics and nature-inspired materials, including applications that require multistep and repeated reactions, such as microassays, medical ...
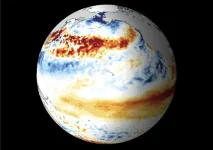
Early-onset El Niño means warmer winters in East Asia, and vice versa
2024-07-03
Fukuoka, Japan—The phenomenon known as El Niño can cause abnormal and extreme climate around the world due to it dramatically altering the normal flow of the atmosphere. In Japan, historical data has shown that El Niño years tend to lead to warmer winters. This case was exemplified recently with Japan’s warm 2023-2024 winter season. However, there have also been cases of cold winters in Japan during El Niño years, such as the one recorded in 2014-2015. Yet, it was unclear as to why this was occurring.
Publishing in the Journal of Climate, ...
How to avoid wasting huge amounts of energy
2024-07-03
Norway wastes huge amounts of energy. Surplus heat produced by industry is hardly exploited at all.
Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) have been looking at the possibilities for doing something about this.
“Surplus heat from industrial processes is a huge resource,” says Kim Kristiansen.
He has just completed his PhD on a technology that can harness some of the surplus heat that currently goes to waste. Almost all the heat generated by industrial processes is currently released directly into the air or the ocean, and we are not talking about small amounts. In Norway alone, industry produces ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Environmental toxicant exposure and depressive symptomsJAMA Network Open