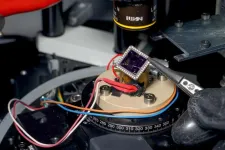
(Press-News.org) To perform quantum computations, quantum bits (qubits) must be cooled down to temperatures in the millikelvin range (close to -273 Celsius), to slow down atomic motion and minimize noise. However, the electronics used to manage these quantum circuits generate heat, which is difficult to remove at such low temperatures. Most current technologies must therefore separate quantum circuits from their electronic components, causing noise and inefficiencies that hinder the realization of larger quantum systems beyond the lab.
Researchers in EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES), led by Andras Kis, in the School of Engineering have now fabricated a device that not only operates at extremely low temperatures, but does so with efficiency comparable to current technologies at room temperature.
“We are the first to create a device that matches the conversion efficiency of current technologies, but that operates at the low magnetic fields and ultra-low temperatures required for quantum systems. This work is truly a step ahead,” says LANES PhD student Gabriele Pasquale.
The innovative device combines the excellent electrical conductivity of graphene with the semiconductor properties of indium selenide. Only a few atoms thick, it behaves as a two-dimensional object, and this novel combination of materials and structure yields its unprecedented performance. The achievement has been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
Harnessing the Nernst effect
The device exploits the Nernst effect: a complex thermoelectric phenomenon that generates an electrical voltage when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to an object with a varying temperature. The two-dimensional nature of the lab’s device allows the efficiency of this mechanism to be controlled electrically.
The 2D structure was fabricated at the EPFL Center for MicroNanoTechnology and the LANES lab. Experiments involved using a laser as a heat source, and a specialized dilution refrigerator to reach 100 millikelvin – a temperature even colder than outer space. Converting heat to voltage at such low temperatures is usually extremely challenging, but the novel device and its harnessing of the Nernst effect make this possible, filling a critical gap in quantum technology.
“If you think of a laptop in a cold office, the laptop will still heat up as it operates, causing the temperature of the room to increase as well. In quantum computing systems, there is currently no mechanism to prevent this heat from disturbing the qubits. Our device could provide this necessary cooling,” Pasquale says.
A physicist by training, Pasquale emphasizes that this research is significant because it sheds light on thermopower conversion at low temperatures – an underexplored phenomenon until now. Given the high conversion efficiency and the use of potentially manufacturable electronic components, the LANES team also believes their device could already be integrated into existing low-temperature quantum circuits.
“These findings represent a major advancement in nanotechnology and hold promise for developing advanced cooling technologies essential for quantum computing at millikelvin temperatures,” Pasquale says. “We believe this achievement could revolutionize cooling systems for future technologies.”
END
A 2D device for quantum cooling
EPFL engineers have created a device that can efficiently convert heat into electrical voltage at temperatures lower than that of outer space. The innovation could help overcome a significant obstacle to the advancement of quantum computing technologies.
2024-07-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MIT engineers find a way to protect microbes from extreme conditions
2024-07-05
Microbes that are used for health, agricultural, or other applications need to be able to withstand extreme conditions, and ideally the manufacturing processes used to make tablets for long-term storage. MIT researchers have now developed a new way to make microbes hardy enough to withstand these extreme conditions.
Their method involves mixing bacteria with food and drug additives from a list of compounds that the FDA classifies as “generally regarded as safe.” The researchers identified formulations that help to stabilize several different types ...
Why the U.S. food system needs agroecology
2024-07-05
Agroecology—a science, practice, and movement which seeks social, political, economic, and environmental sustainability in the global food system—is gaining momentum in the U.S., according to a new Dartmouth-led commentary in Nature Food. As the co-authors report, the approach requires coordination between scientists, farmers, and activists.
"When it comes to sustainable food and agriculture, people in the U.S. tend to be more familiar with organic farming, the production of food without synthetic inputs, and regenerative agriculture, which primarily strives to restore soil health," says lead author Theresa Ong, an assistant professor of environmental studies ...
Fresh wind blows from historical supernova
2024-07-05
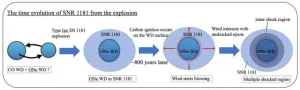
A mysterious remnant from a rare type of supernova recorded in 1181 has been explained for the first time. Two white dwarf stars collided, creating a temporary “guest star,” now labeled supernova (SN) 1181, which was recorded in historical documents in Japan and elsewhere in Asia. However, after the star dimmed, its location and structure remained a mystery until a team pinpointed its location in 2021. Now, through computer modeling and observational analysis, researchers have recreated the structure of the remnant white dwarf, a rare occurrence, explaining its ...
Desert-loving fungi and lichens pose deadly threat to 5,000-year-old rock art
2024-07-05
The Negev desert of southern Israel is renowned for its unique rock art. Since at least the third millennium BCE, the hunters, shepherds, and merchants who roamed the Negev have left thousands of carvings (‘petroglyphs’) on the rocks. These figures are mostly cut into ‘desert varnish’: a thin black coating on limestone rock, which forms naturally. Many represent animals such as ibexes, goats, horses, donkeys, and domestic camels, but abstract forms also occur.
Now, a study published in Frontiers in Fungal ...
Scientists map how deadly bacteria evolved to become epidemic
2024-07-04
Pseudomonas aeruginosa – an environmental bacteria that can cause devastating multidrug-resistant infections, particularly in people with underlying lung conditions – evolved rapidly and then spread globally over the last 200 years, probably driven by changes in human behaviour, a new study has found.
P. aeruginosa is responsible for over 500,000 deaths per year around the world, of which over 300,000 are associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR). People with conditions such as COPD (smoking-related lung damage), cystic fibrosis (CF), and non-CF bronchiectasis, are particularly susceptible.
How P. aeruginosa evolved from an environmental organism into a ...
Biodegradable biomass-based aerogel for sustainable radiative cooling
2024-07-04
An aerogel made from gelatin and DNA surpasses 100% solar reflectance, yielding exceptional radiative cooling, a new study reports. It is also biodegradable. The novel approach paves the way for high-performance next-generation radiative cooling materials, promoting environmentally friendly advancements in the field. Sustainable, energy-efficient, and environmentally conscious cooling technologies are crucial for adapting to our rapidly warming world. Compared to traditional refrigeration systems, passive radiative cooling technologies consume less energy and emit fewer greenhouse gasses, making them ...
New brain-to-nerve signaling mechanism reveals potential path to migraine pain
2024-07-04
The rapid influx of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and protein solutes released during cortical spreading depression (CSD) in the brain activates neurons to trigger aural migraine headaches, according to a new mouse study. The findings identify a novel non-synaptic signaling mechanism between the brain and peripheral sensory system important for migraine. They also suggest potential pharmacological targets for treating the painful disorder. Migraine with aura, or an aural migraine, is a distinct headache disorder that can include sensory disturbances, such as hearing- or vision-related symptoms that precede onset of ...
Federal grid reforms alone are not enough to solve clean energy interconnection problem
2024-07-04
Although energy production from wind and solar has grown rapidly in the United States, its integration into the national electric grid has been impeded by poor grid interconnection policies, leaving thousands of new facilities for generating renewable energy waiting to be connected to the grid. In a Policy Forum, Les Armstrong and colleagues highlight the interconnection problem and discuss whether federal grid policy reforms alone are enough to address it. Armstrong et al. argue that while the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s (FERC) recent orders to improve this bottleneck are a step in the right direction, fundamental issues remain unaddressed. In the ...
Uncovering “blockbuster T cells” in the gut wins NOSTER & Science Microbiome Prize
2024-07-04
In the gut, dozens of strains of bacteria exert different effects on the immune system that in turn impact our health – fending off pathogens, helping digest food and maybe even influencing behavior. But pinpointing which bacteria exert which effects has been challenging. Better understanding this process could lead to a powerful way to treat a host of diseases. For developing a method by which to zero in on individual gut bacterium’s impacts on T cells, Kazuki Nagashima, a senior research scientist at Stanford University, is the winner of this year’s NOSTER & Science Microbiome ...
Study reveals brain fluid dynamics as key to migraine mysteries, new therapies
2024-07-04
New research describes for the first time how a spreading wave of disruption and the flow of fluid in the brain triggers headaches, detailing the connection between the neurological symptoms associated with aura and the migraine that follows. The study also identifies new proteins that could be responsible for headaches and may serve as foundation for new migraine drugs.
“In this study, we describe the interaction between the central and peripheral nervous system brought about by increased concentrations of proteins released ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] A 2D device for quantum coolingEPFL engineers have created a device that can efficiently convert heat into electrical voltage at temperatures lower than that of outer space. The innovation could help overcome a significant obstacle to the advancement of quantum computing technologies.