(Press-News.org) An ongoing research project into the impact of offshore windfarm electromagnetic fields on shark development reveals that the alternating electric currents produced by underwater windfarm cables seems not to disrupt the growth or survival of sharks.
Offshore windfarms are one of the most common marine renewable energy (MRE) producers, and are seen as a pivotal technology in the global transition towards renewable energy and away from fossil fuels that contribute to climate change.
However, their proliferation in marine environments raises new questions about their impacts on wildlife. Energy operators and researchers are working together to understand the effects of these increasingly prevalent technologies.
“Wind farms can induce noise, vibrations, interruptions to ecological continuity and generate electromagnetic fields at the level of submarine electric cable,” says Dr Julie Lucas, a research associate at France's National Museum of Natural History. “They can affect behaviour of electro-sensitive species which use natural electromagnetic fields to move and feed, such as sharks.”
These offshore windfarms rely on submarine electric cables (CES) that use either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) depending on their function, power output and cable length. “Currently, wind farms located less than 50km from the coast use AC current, whereas more powerful future wind farms are planned to be located more than 50 km away and will use DC current,” says Dr Lucas.
Both AC and DC currents produce strong magnetic fields into the water surrounding them. “These magnetic fields can affect the behaviour of electro- and magneto-sensitive species such as elasmobranchs, which use natural electromagnetic fields to move and feed,” says Dr Lucas. “The increasing number of offshore wind farms is likely to amplify these effects, while existing information on their impact on marine communities remains patchy.”
Dr Lucas’ study aims to identify the effects of the magnetic fields caused by AC and DC currents on the survival, development and behaviour of sharks and other electro-sensitive elasmobranchs. “The results will enable us to understand how elasmobranchs react to electromagnetic fields,” says Dr Lucas.
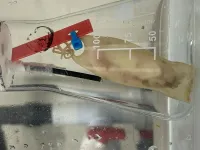
Dr Lucas and her team studied two key life stages of the small-spotted catshark (Scyliorhinus canicular), embryo and juvenile, under either control or windfarm-impacted conditions using AC or DC currents. They recorded daily survival, weekly development and growth and metabolic rate through respirometry for both life stages.
“Thankfully, preliminary results suggest that the impact of alternating electromagnetic fields seem to be limited on the factors that we have measured,” says Dr Lucas. However, the full results are still being analysed and the effects of DC current will be investigated later this year.
“The results of this project will make it possible to understand more precisely how sharks react to electromagnetic fields depending on their intensity and the type of current,” says Dr Lucas. “They will also improve our knowledge of the impacts of MREs on marine species.”
Dr Lucas hopes that this research can help inform policy to protect marine species and determine what improvements can be made to CES to continue limiting their impact. “This project will provide essential information for managers and decision-makers to meet the challenges of developing MREs without harming marine biodiversity,” says Dr Lucas.
This research is being presented at the Society for Experimental Biology Annual Conference in Prague on the 2-5th July 2024.
END
Offshore windfarms – A threat for electro-sensitive sharks?
2024-07-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A 2D device for quantum cooling
2024-07-05
To perform quantum computations, quantum bits (qubits) must be cooled down to temperatures in the millikelvin range (close to -273 Celsius), to slow down atomic motion and minimize noise. However, the electronics used to manage these quantum circuits generate heat, which is difficult to remove at such low temperatures. Most current technologies must therefore separate quantum circuits from their electronic components, causing noise and inefficiencies that hinder the realization of larger quantum systems beyond the lab.
Researchers in EPFL’s Laboratory of ...
MIT engineers find a way to protect microbes from extreme conditions
2024-07-05
Microbes that are used for health, agricultural, or other applications need to be able to withstand extreme conditions, and ideally the manufacturing processes used to make tablets for long-term storage. MIT researchers have now developed a new way to make microbes hardy enough to withstand these extreme conditions.
Their method involves mixing bacteria with food and drug additives from a list of compounds that the FDA classifies as “generally regarded as safe.” The researchers identified formulations that help to stabilize several different types ...
Why the U.S. food system needs agroecology
2024-07-05
Agroecology—a science, practice, and movement which seeks social, political, economic, and environmental sustainability in the global food system—is gaining momentum in the U.S., according to a new Dartmouth-led commentary in Nature Food. As the co-authors report, the approach requires coordination between scientists, farmers, and activists.
"When it comes to sustainable food and agriculture, people in the U.S. tend to be more familiar with organic farming, the production of food without synthetic inputs, and regenerative agriculture, which primarily strives to restore soil health," says lead author Theresa Ong, an assistant professor of environmental studies ...
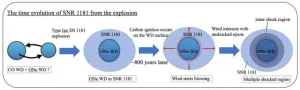
Fresh wind blows from historical supernova
2024-07-05
A mysterious remnant from a rare type of supernova recorded in 1181 has been explained for the first time. Two white dwarf stars collided, creating a temporary “guest star,” now labeled supernova (SN) 1181, which was recorded in historical documents in Japan and elsewhere in Asia. However, after the star dimmed, its location and structure remained a mystery until a team pinpointed its location in 2021. Now, through computer modeling and observational analysis, researchers have recreated the structure of the remnant white dwarf, a rare occurrence, explaining its ...
Desert-loving fungi and lichens pose deadly threat to 5,000-year-old rock art
2024-07-05
The Negev desert of southern Israel is renowned for its unique rock art. Since at least the third millennium BCE, the hunters, shepherds, and merchants who roamed the Negev have left thousands of carvings (‘petroglyphs’) on the rocks. These figures are mostly cut into ‘desert varnish’: a thin black coating on limestone rock, which forms naturally. Many represent animals such as ibexes, goats, horses, donkeys, and domestic camels, but abstract forms also occur.
Now, a study published in Frontiers in Fungal ...
Scientists map how deadly bacteria evolved to become epidemic
2024-07-04
Pseudomonas aeruginosa – an environmental bacteria that can cause devastating multidrug-resistant infections, particularly in people with underlying lung conditions – evolved rapidly and then spread globally over the last 200 years, probably driven by changes in human behaviour, a new study has found.
P. aeruginosa is responsible for over 500,000 deaths per year around the world, of which over 300,000 are associated with antimicrobial resistance (AMR). People with conditions such as COPD (smoking-related lung damage), cystic fibrosis (CF), and non-CF bronchiectasis, are particularly susceptible.
How P. aeruginosa evolved from an environmental organism into a ...
Biodegradable biomass-based aerogel for sustainable radiative cooling
2024-07-04
An aerogel made from gelatin and DNA surpasses 100% solar reflectance, yielding exceptional radiative cooling, a new study reports. It is also biodegradable. The novel approach paves the way for high-performance next-generation radiative cooling materials, promoting environmentally friendly advancements in the field. Sustainable, energy-efficient, and environmentally conscious cooling technologies are crucial for adapting to our rapidly warming world. Compared to traditional refrigeration systems, passive radiative cooling technologies consume less energy and emit fewer greenhouse gasses, making them ...
New brain-to-nerve signaling mechanism reveals potential path to migraine pain
2024-07-04
The rapid influx of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and protein solutes released during cortical spreading depression (CSD) in the brain activates neurons to trigger aural migraine headaches, according to a new mouse study. The findings identify a novel non-synaptic signaling mechanism between the brain and peripheral sensory system important for migraine. They also suggest potential pharmacological targets for treating the painful disorder. Migraine with aura, or an aural migraine, is a distinct headache disorder that can include sensory disturbances, such as hearing- or vision-related symptoms that precede onset of ...
Federal grid reforms alone are not enough to solve clean energy interconnection problem
2024-07-04
Although energy production from wind and solar has grown rapidly in the United States, its integration into the national electric grid has been impeded by poor grid interconnection policies, leaving thousands of new facilities for generating renewable energy waiting to be connected to the grid. In a Policy Forum, Les Armstrong and colleagues highlight the interconnection problem and discuss whether federal grid policy reforms alone are enough to address it. Armstrong et al. argue that while the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s (FERC) recent orders to improve this bottleneck are a step in the right direction, fundamental issues remain unaddressed. In the ...
Uncovering “blockbuster T cells” in the gut wins NOSTER & Science Microbiome Prize
2024-07-04
In the gut, dozens of strains of bacteria exert different effects on the immune system that in turn impact our health – fending off pathogens, helping digest food and maybe even influencing behavior. But pinpointing which bacteria exert which effects has been challenging. Better understanding this process could lead to a powerful way to treat a host of diseases. For developing a method by which to zero in on individual gut bacterium’s impacts on T cells, Kazuki Nagashima, a senior research scientist at Stanford University, is the winner of this year’s NOSTER & Science Microbiome ...