(Press-News.org) Limited impact of current movement restrictions highlights need for enhanced strategies, says study.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Dairy Science, researchers from the Complexity Science Hub (CSH), the University of Copenhagen, and SEGES have shown that despite stringent movement restrictions among Danish cattle farms Salmonella Dublin continues to propagate, indicating that current strategies are insufficient to curb the spread of the disease.
"We analyzed 11 years of data, including detailed information about infection outbreaks in farms and trading data between farms, and applied advanced social network and simulation modeling to study the movement patterns of cattle among farms," explain CSH Associate Faculty member Beate Conrady and CSH researcher Elma Dervic.
By mapping out these connections, the researchers aimed to assess how effectively movement restrictions were preventing the spread of Salmonella Dublin. "Surprisingly, we found that disease transmission between farms persists, with cattle movement activities in the previous month being the strongest predictor of farm infections," says Conrady, who is also an Associate Professor at the Department of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, University of Copenhagen.
Similar network trends were observed for infected and non-infected farms, indicating that the perceived strict movement restrictions had insufficient effect, likely because multi-site farm businesses are still allowed to move animals between their own farm properties. Local transmission, i.e., different transmission pathways in a short distance to neighboring farms, played a relatively minor role.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Given the limitations of current measures, the study calls for a multifaceted approach to managing Salmonella Dublin:
Pre- and Post-Movement Measures: Implementing stricter control measures before and after movement within a one-month period can reduce the spread of Salmonella Dublin.
Focused Control Strategies: Enhanced surveillance and targeted interventions based on cattle movement data and farm characteristics can improve the effectiveness of disease control programs. Analyzing the impact of multi-site businesses seems to be important to better understand the spread of Salmonella Dublin infections.
Policy Recommendations: Adapt control measures to emphasize within-herd biosecurity, and improve the diagnostics and testing before and after cattle movements.
A CLOSER LOOK AT SALMONELLA DUBLIN
Salmonella Dublin is a bacterial infection that poses a threat to cattle health, causing symptoms such as fever, diarrhea, and respiratory problems. The disease is also zoonotic, meaning it can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals or consumption of contaminated dairy products, potentially leading to severe health issues, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
IMPLICATIONS FOR SOCIETY
This study has profound implications for both farmers and policymakers. For farmers, it means that despite adhering to movement restrictions, their herds remain at risk of infection, which can lead to economic losses due to decreased productivity and increased veterinary costs. For policymakers, the study highlights the urgent need to develop more effective disease management strategies. Relying solely on movement restrictions is clearly not enough to combat the spread of Salmonella Dublin.
“Our study underscores the urgent need to revise existing policies of more dynamic and targeted approaches to control the spread of Salmonella Dublin to protect animal health and safeguard public health,” concludes Conrady.
ABOUT THE STUDY
The study “Social network analysis reveals the failure of between-farm movement restrictions to reduce Salmonella transmission,” by B. Conrady, E.H. Dervic, P. Klimek, L. Pedersen, M. Merhi Reimert, P. Rasmussen, O.O. Apenteng and L.R. Nielsen, was published in the Journal of Dairy Science (doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-24554).
About CSH
The Complexity Science Hub (CSH) is Europe’s research center for the study of complex systems. We derive meaning from data from a range of disciplines – economics, medicine, ecology, and the social sciences – as a basis for actionable solutions for a better world. Established in 2016, we have grown to over 70 researchers, driven by the increasing demand to gain a genuine understanding of the networks that underlie society, from healthcare to supply chains. Through our complexity science approaches linking physics, mathematics, and computational modeling with data and network science, we develop the capacity to address today’s and tomorrow’s challenges.
END
Current strategies ineffective in controlling Salmonella Dublin in Danish cattle
2024-07-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Military service's hidden health toll: servicewomen and their families endure increased chronic pain
2024-07-05
A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital reveals that military women and female family members face significantly higher risks of chronic pain
Active-duty servicewomen who served during periods of heightened combat deployments (2006-2013) face a significantly heightened risk of chronic pain compared to those serving at other times, according to a new study from researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. The study also found that female dependents of military personnel serving ...
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and 13 obesity-associated cancers in patients with type 2 diabetes
2024-07-05
About The Study: Glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) were associated with lower risks of specific types of obesity-associated cancers compared with insulins or metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes in this study. These findings provide preliminary evidence of the potential benefit of GLP-1RAs for cancer prevention in high-risk populations and support further preclinical and clinical studies for the prevention of certain obesity-associated cancers.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Nathan A. Berger, M.D. (nab@case.edu) and Rong Xu, Ph.D. (rxx@case.edu).
To access the embargoed ...
Medicare eligibility and changes in coverage, access to care, and health by sexual orientation and gender identity
2024-07-05
About The Study: The findings of this cross-sectional study indicate that Medicare eligibility was not associated with consistently greater improvements in health insurance coverage and access to care among LGBTQI+ individuals compared with heterosexual and/or cisgender individuals. However, among sexual minority individuals, Medicare may be associated with closing gaps in self-reported health status, and among states with the highest disparities, it may improve health insurance coverage, access to care, and self-reported health status.
Corresponding Author: To contact ...
TaSRT2 recognizes a viral protein to activate host immunity by increasing histone acetylation
2024-07-05
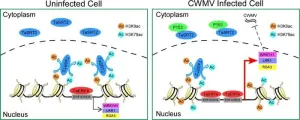
This study is led by Dr.Jian Yang and Dr. Kaili Zhong (State Key Laboratory for Managing Biotic and Chemical Threats to the Quality and Safety of Agro-products, Ningbo University). Their findings reveal a strategy that plants use to protect themselves from viral infection by regulating deacetylase function.
In this work, the team found CWMV infection induced H3K9ac and H3K79ac in wheat. Histone deacetylase TaSRT2 is demonstrated to deacetylate H3K9ac and H3K79ac since the levels of H3K9ac and H3K79ac were significantly reduced in TaSRT2 transgenic lines L6 and L8 plants but increased in virus-induced TaSRT2-silenced ...
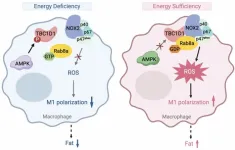
TBC1D1 is an energy-responsive polarization regulator of macrophages via governing ROS production in obesity
2024-07-05
This study is led by Dr. Shuai Chen (Model Animal Research Center, School of Medicine, Nanjing University, China) and Dr. Hong-Yu Wang (Model Animal Research Center, School of Medicine, Nanjing University, China).
Metabolic and immune pathways are highly regulated and interwoven by multiple mechanisms to govern metabolic health. Dysregulation of these pathways underlies the development of metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), which have become prevalent worldwide in recent years. Thus far, the molecular mechanisms ...
Gerhard Ertl Lecture Award 2024 goes to Graham Hutchings
2024-07-05
His journey from a technical officer at ICI Petrochemicals to becoming the Regius Professor of Chemistry at Cardiff University is marked by numerous achievements and accolades, including being elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 2009.
The Ertl Lecture Award, a tribute to the legacy of Gerhard Ertl, Nobel Laureate in Chemistry in 2007, is an annual accolade that highlights the exceptional work of researchers in the field of catalysis. Sponsored by BASF and established in 2008 by the three Berlin universities (Humboldt University, Technical ...
Migrating starlings are no copycats
2024-07-05
Young, naïve starlings are looking for their wintering grounds independently of experienced conspecifics. Starlings are highly social birds throughout the year, but this does not mean that they copy the migration route from each other. By revisiting a classic ‘displacement’ experiment and by adding new data, a team of researchers at the Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) and the Swiss Ornithological Institute (Vogelwarte Sempach) have settled a long-lasting debate. Their findings are now published in the scientific journal Biology Letters.
The question of how migratory birds locate their migration ...
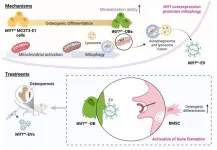
Osteoblast-derived extracellular vesicles exert bone formation effects by WIF1-mediated regulation of mitophagy
2024-07-05
Osteoporosis is a common disorder, especially in the elderly, characterized by bone loss and increased fracture risk. Treatments target abnormal osteoclast activity but face adherence issues. The disease disrupts the balance between bone resorption and formation. Key factors like Wnt signaling and mitochondrial health influence osteoblast differentiation. However, WIF1's role in regulating mitophagy and osteoblast differentiation remains unclear.
This research investigated the role of WIF1 in controlling the osteogenic differentiation stage of the OB precursor cell line (MC3T3-E1 cells) and assessed ...
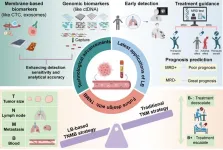
Based on the improvement of detection technology, a new summary is proposed for the application of liquid biopsy, future clinical trial design and patient management of NSCLC
2024-07-05
This study was led by Kezhong Chen (Department of Thoracic Surgery, Peking University People’s Hospital & Peking University People’s Hospital Thoracic Oncology Institute). In clinical practice, traditional tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging had difficulty achieving accuracy in prognosis stratification at the individual patient level. Researchers therefore proposed to introduce blood minimal residual disease (MRD) status and proposed a new tumor-node-metastasis-blood (TNMB) staging system to more accurately and individually define the postoperative status of lung cancer patients (Fig. 1).
LB, well known for its noninvasiveness, easy accessibility, ...
Experts show how resilience to Alzheimer’s differs by sex and gender
2024-07-05
An international panel of experts led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the “la Caixa” Foundation, under the umbrella of the Alzheimer's Association International Society to Advance Alzheimer's Research and Treatment, has produced a consensus statement on sex and gender disparities in resilience to Alzheimer's disease and call for incorporating these differences in future research. The work has been published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
Women make up the majority of people with Alzheimer's ...