(Press-News.org) The largest animals do not have proportionally bigger brains - with humans bucking this trend - a new study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution has revealed.
Researchers at the University of Reading and Durham University collected an enormous dataset of brain and body sizes from around 1,500 species to clarify centuries of controversy surrounding brain size evolution.
Bigger brains relative to body size are linked to intelligence, sociality, and behavioural complexity – with humans having evolved exceptionally large brains. The new research, published today (Monday, 8 July), reveals the largest animals do not have proportionally bigger brains, challenging long-held beliefs about brain evolution.
Professor Chris Venditti, lead author of the study from the University of Reading, said: “For more than a century, scientists have assumed that this relationship was linear – meaning that brain size gets proportionally bigger, the larger an animal is. We now know this is not true. The relationship between brain and body size is a curve, essentially meaning very large animals have smaller brains than expected."
Professor Rob Barton, co-author of the study from Durham University, said: “Our results help resolve the puzzling complexity in the brain-body mass relationship. Our model has a simplicity that means previously elaborate explanations are no longer necessary – relative brain size can be studied using a single underlying model.”
Beyond the ordinary
The research reveals a simple association between brain and body size across all mammals which allowed the researchers to identify the rule-breakers – species which challenge the norm.
Among these outliers includes our own species, Homo sapiens, which has evolved more than 20 times faster than all other mammal species, resulting in the massive brains that characterise humanity today. But humans are not the only species to buck this trend.
All groups of mammals demonstrated rapid bursts of change – both towards smaller and larger brain sizes. For example, bats very rapidly reduced their brain size when they first arose, but then showed very slow rates of change in relative brain size, suggesting there may be evolutionary constraints related to the demands of flight.
There are three groups of animals that showed the most pronounced rapid change in brain size: primates, rodents, and carnivores. In these three groups, there is a tendency for relative brain size to increase in time (the “Marsh-Lartet rule”). This is not a trend universal across all mammals, as previously believed.
Dr Joanna Baker, co-author of the study also from the University of Reading, said: “Our results reveal a mystery. In the largest animals, there is something preventing brains from getting too big. Whether this is because big brains beyond a certain size are simply too costly to maintain remains to be seen. But as we also observe similar curvature in birds, the pattern seems to be a general phenomenon – what causes this ‘curious ceiling’ applies to animals with very different biology.”
END
Brain size riddle solved as humans exceed evolution trend
2024-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
GeneMAP discovery platform will help define functions for ‘orphan’ metabolic proteins
2024-07-08
A multidisciplinary research team has developed a discovery platform to probe the function of genes involved in metabolism — the sum of all life-sustaining chemical reactions.
The investigators used the new platform, called GeneMAP (Gene-Metabolite Association Prediction), to identify a gene necessary for mitochondrial choline transport. The resource and derived findings were published July 8 in the journal Nature Genetics.
“We sought to gain insight into a fundamental question: ‘How does genetic variation determine our “chemical individuality” — the inherited differences that make us biochemically unique?” said Eric Gamazon, ...
Zero-emissions trucks alone won't cut it: Early retirement of polluters key to California's emission goals
2024-07-08
California must implement early retirement for existing heavy-duty vehicles as well as introducing zero-emissions vehicles (ZEVs) to protect Black, Latino and vulnerable communities and hit net zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions targets by 2045. This is the outcome of a new study published in Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability by researchers from Stanford University and Arizona State University.
Stringent policies for mandating both ZEVs and early vehicle retirement could reduce cumulative emissions by two-thirds (64%) and reduce half of pollution-related mortality, particularly among disadvantaged communities.
California is the world’s 5th largest ...
Hexagonal perovskite oxides: Electrolytes for next-generation protonic ceramic fuel cells
2024-07-08
This study presents a significant advancement in fuel cell technology. Researchers from Tokyo Tech identified hexagonal perovskite-related Ba5R2Al2SnO13 oxides (R = rare earth metal) as materials with exceptionally high proton conductivity and thermal stability. Their unique crystal structure and large number of oxygen vacancies enable full hydration and high proton diffusion, making these materials ideal candidates as electrolytes for next-generation protonic ceramic fuel cells that can operate at intermediate temperatures without degradation.
Fuel cells offer a promising solution for clean energy by combining hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity, ...
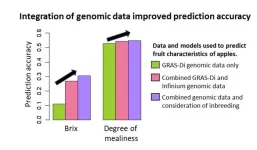
Genomic data integration improves prediction accuracy of apple fruit traits!
2024-07-08
Over the past few decades, the world has witnessed tremendous progress in the tools used for genomic analysis. While it’s usually more common to associate these tools with the fields of biology and medicine, they have proven to be very valuable in agriculture as well. Using numerous DNA markers obtained from next-generation sequencing technologies, breeders can make genomic predictions and select promising individuals based on based on their predicted trait values.
Various systems and methodologies aimed at improving the ...
Visualizing short-lived intermediate compounds produced during chemical reactions
2024-07-08
Immobilizing small synthetic molecules inside protein crystals proves to be a promising avenue for studying intermediate compounds formed during chemical reactions, report scientists from Tokyo Tech. By integrating this method with time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography, they successfully visualized reaction dynamics and rapid structural changes occurring within reaction centers immobilized inside protein crystals. This innovative strategy holds significant potential for the intelligent design of drugs, catalysts, and functional materials.
Most complex chemical reactions, whether synthetic or biological, do not involve ...
It’s time to rethink our attitude to fatness, academic argues
2024-07-08
Prejudice against fat people is endemic in our society and public health initiatives aimed at reducing obesity have only worsened the problem, according to a U.S. academic.
In her new book Why It’s OK To Be Fat, Rekha Nath, an Associate Professor of Philosophy at the University of Alabama, argues for a paradigm shift in how society approaches fatness.
According to Nath, society must stop approaching fatness as a trait to rid the population of, and instead fatness should be approached through the lens of social equality, attending to the systematic ways that society penalizes fat people for their body size.
Nath explains: “Being fat is seen as unattractive, as gross even. ...
Braiding community values with science is key to ecosystem restoration
2024-07-08
Up on the “roof of the world”, one of the world’s largest ecosystem restoration projects is taking place. The Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP) in western China is the world’s highest plateau and covers a land area roughly five times the size of France.
Home to thousands of rare plants and wildlife and the source of water for more than 2.5 billion people, this vital ecosystem is under threat.
The region’s grassland is degrading due to climate change and intense livestock grazing. Government ...
Study of key characteristics of politicians reveals ‘ambition, narcissism, genuine idealism’ among common traits
2024-07-08
In a new study of politicians’ personalities, humour, charm and raw courage are listed among the most important character traits for successful leaders.
Bill Jones, Honorary Professor of Political Studies at Liverpool Hope University, has combed through biographies and interviewed key political figures to understand the kind of people who enter politics, and strengths and frailties of those who occupy positions of power.
Jones explains: “Why do aspiring politicians embark on such a perilous journey, involving hugely long hours, no real job security and, on occasions, high degrees ...
Air pollution linked to a decrease in IVF birth rate success, new study shows
2024-07-08
A pioneering study, presented today at the ESHRE 40th Annual Meeting in Amsterdam, has revealed that exposure to fine particulate matter (PM) prior to the retrieval of oocytes (eggs) during in vitro fertilisation (IVF) can reduce the odds of achieving a live birth by almost 40% [1].
The study analysed PM10 exposure in the two weeks leading up to oocyte collection, finding that the odds of a live birth decreased by 38% (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.43-0.89, p=0.010) when comparing the highest quartile of exposure (18.63 to 35.42 µg/m3) to the lowest quartile (7.08 to 12.92 µg/m3).
Conducted ...
Gestational carriers face higher health risks during pregnancy compared to IVF and natural conceptions, new study shows
2024-07-08
Gestational carriers, also known as surrogates, experience an elevated risk of severe maternal morbidity and adverse pregnancy outcomes compared to women who conceive naturally or through in vitro fertilisation (IVF), according to new research presented today at the ESHRE 40th Annual Meeting in Amsterdam [1].
The population-based study analysed 937,938 singleton births in Ontario, Canada between 2012 and 2021, comparing outcomes among unassisted conceptions, IVF conceptions and gestational carriers.
The findings uncovered marked variations in outcomes across the different conception methods. Gestational carriers faced a severe maternal morbidity rate ...