Exploring distress experiences of patients with sickle cell disease
Patients worry about going to emergency departments to manage their acute pain flares
2024-07-08
(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – While distress is well-documented in patients with sickle cell disease, sources of distress and how patients manage distress have not been well explored.
“Our study found that the most profound source of distress for patient with sickle cell disease in a home visit program was anticipating and going to acute care centers to manage their acute pain,” said senior study author Maryanna Klatt, PhD, director of the Center for Integrative Health at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center.
Study findings are published in the journal Qualitative Research in Health.
These findings bolster researchers’ earlier perspective published in the New England Journal of Medicine that cited a need for a biopsychosocial model to treat chronic pain in sickle cell disease.
Researchers recruited 11 patients with sickle cell from a home visit program at Ohio State Wexner Medical Center between February and July 2021. They wanted to identify sources of distress for persons with sickle cell.
A researcher conducted one-on-one semi-structured interviews with study participants. The research team coded and analyzed all interview transcripts.
Participants said the most profound source of distress was clinical encounters in the emergency department and intermediate care center to manage acute pain flares.
Key findings
“Pain performativity” is a strategy some patients use to try to show providers their pain.
Researchers should consider how clinical settings and practices foster distress.
Listening to patients may help clinicians to reduce distress.
“We found that there is often a performative element for persons with sickle cell in emergency and intermediate care center settings. They feel they have to present in a certain way for providers to see their pain as credible and treat it promptly. Yet often, patients are simply incapable of performing their pain, or ‘crying on cue,’ as one participant put it,” said study first author Janet Childerhose, PhD, a research assistant professor in the Department of Internal Medicine at the Ohio State’s College of Medicine.
“Our analysis also found stigma and racism surround the care of this neglected disease. Participants lack any sense of control over their pain management plan,” said Klatt, who also is a professor in the Department of Family and Community Medicine. “Researchers may wish to consider how these settings could better address patient distress, and providers may wish to adopt participant recommendations to reduce distress associated with seeking pain treatment in acute care settings.”
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-08
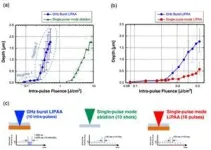
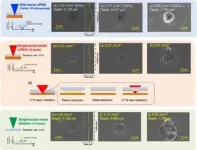
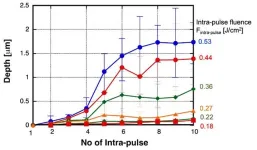
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240029 , discusses super-resolution machining of single crystalline sapphire by GHz burst mode femtosecond laser-induced plasma assisted ablation.
GHz burst-mode femtosecond (fs) laser, which emits a series of pulse trains (burst pulse) with extremely short intervals of several hundred ps, offers distinct characteristics in materials processing as compared with conventional fs laser (single-pulse mode). The authors of this article have demonstrated that the GHz burst mode fs laser greatly improves ablation efficiency, quality and speed. GHz burst mode fs laser was further applied ...
2024-07-08
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240002 , discusses boosting UV Light Absorption in 2D Semiconductor with quantum dot hybrids for enhanced light emission.
Two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have emerged as a promising class of materials due to their remarkable properties. These materials, such as monolayer tungsten disulfide (1L-WS2), are just a few atoms thick, yet they possess intriguing electronic and optical characteristics that make them highly attractive for various applications, from flexible electronics ...
2024-07-08
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.230053 , discusses forbidden propagation of hyperbolic phonon polaritons and applications in near-field energy transport.
Manipulating photons on the nanoscale to develop integrated and miniaturized optoelectronic devices as well as photonic chips has been a strong pursuit of the nanophotonics community. Among them, phonon polaritons supported by two-dimensional layered van der Waals (vdW) materials, which have emerged in recent years, have attracted much attention by virtue of their ultra-long lifetimes, ultr-low losses, and strong confinement capabilities, ...
2024-07-08
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
734-764-2220
For immediate release
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — To understand why some cancers successfully circumvent the immune system to grow unchecked, researchers turned to pregnancy.
“In pregnancy, the immune system does not reject the growing fetus, so we know there must be mechanisms active in the placenta. In cancer, it’s the same thing: the growing tumor is not rejected by the immune system. It means the cancer cells have developed strategies to suppress immune rejection, same as in pregnancy,” said Weiping ...
2024-07-08
UC San Diego Health is the first health system in San Diego County to offer a new bladder-saving gene therapy to treat localized bladder cancer.
The novel treatment is the first and only FDA-approved gene therapy delivered directly into the bladder for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Called nadofaragene firadenovec (Adstiladrin), the gene therapy addresses an unmet need for patients who are no longer responding to the longstanding first line of defense — bacillus calmette-guerin (BCG), a bacteria-based immunotherapy for cancer management. While BCG is a common first therapy, it can eventually stop working, ultimately leading to complete bladder removal.
The American ...
2024-07-08
July 8, 2024, Mountain View, CA – Today, the SETI Institute announced the first projects it will fund with a new program to Support Technology, Research, Innovation, Development, and Education programs – or STRIDE. The SETI Institute established the $500K STRIDE fund for SETI Institute researchers and EOC (Education, Outreach, and Communications) professionals to develop innovative research and education proposals. The first five grants awarded will support projects that:
analyze Earth’s colors and climate to create detectors for studying exoplanets
develop a multi-backend capability for ...
2024-07-08
The human body’s inability to break down sucralose, an artificial sweetener found in many zero-calorie food and drink products, is well established by scientific research. The compound is so stable that it escapes wastewater treatment processing and is in drinking water and aquatic environments.
“We can't break down sucralose, and a lot of microorganisms can't break it down, either, because it's a really tough molecule that doesn't degrade easily. So there are a lot of questions about how it is affecting the environment ...
2024-07-08
DNA from fossilised dingo remains going back 2746 years compared with modern dingoes’
Dingos arrived in Australia more than 3000 years ago
K’gari dingoes have no domestic dog ancestry – they are pure dingo
Co-lead author, paleogeneticist Dr Sally Wasef, from QUT’s School of Biomedical Sciences said this dataset gave a rare glimpse into the pre-colonial genetic landscape of dingoes, free from any mixing with modern dog breeds.
“Consequently, are behaviourally, genetically, and anatomically distinct from domestic dogs,” Dr Wasef said.
“Modern-day dingoes’ ancestors arrived in Australia more than 3000 years ...
2024-07-08
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Jefferson Science Associates, LLC, today announced that Kim Sawyer will become the new director of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, effective Aug. 2.
Sawyer will serve as the lab’s fifth director in its 40-year history. In this role, Sawyer will be responsible for leading all activities in support of the world’s premiere research institution for exploring the nature of matter.
“We are pleased that Kim has been selected to lead Jefferson Lab,” said ...
2024-07-08
Disparities in cardiovascular disease outcomes between urban and rural areas continue to widen, yet nearly half of U.S. counties do not have a practicing cardiologist. According to a new analysis published in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology, these counties tend to be more rural and socioeconomically disadvantaged, with a greater burden of cardiovascular disease, thus highlighting deep geographic disparity in access to cardiovascular care.
“While cardiologists are not the only determinants of cardiovascular outcomes, the lack of access to cardiologists in areas with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Exploring distress experiences of patients with sickle cell disease
Patients worry about going to emergency departments to manage their acute pain flares