Innovative, highly accurate AI model can estimate lung function just by using chest x-rays
Potential benefits of method include subjecting patients to fewer exams and reducing health care costs
2024-07-09
(Press-News.org)
If there is one medical exam that everyone in the world has taken, it’s a chest x-ray. Clinicians can use radiographs to tell if someone has tuberculosis, lung cancer, or other diseases, but they can’t use them to tell if the lungs are functioning well.
Until now, that is.
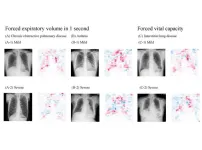
In findings published in The Lancet Digital Health, a research group led by Associate Professor Daiju Ueda and Professor Yukio Miki at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine has developed an artificial intelligence model that can estimate lung function from chest radiographs with high accuracy.
Conventionally, lung function is measured using a spirometer, which requires the cooperation of the patient, who is given specific instructions on how to inhale and exhale into the instrument. Accurate evaluation of the measurements is difficult if the patient has a hard time following instructions, which can occur with infants or persons with dementia, or if the person is prone.
Professor Ueda and the research group trained, validated, and tested the AI model using over 140,000 chest radiographs from a nearly 20-year period. They compared the actual spirometric data to the AI model’s estimates to fine-tune its performance. The results showed a remarkably high agreement rate, with a Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) of more than 0.90, indicating that the method is sufficiently promising for practical use.
The AI model developed in this study has the potential to expand the options for pulmonary function assessment for patients who have difficulty performing spirometry.
“Highly significant is the fact that just by using the static information from chest x-rays, our method suggests the possibility of accurately estimating lung function, which is normally evaluated through tests requiring the patients to exert physical energy,” Professor Ueda explained. “This AI model was built through the cooperation of many people, from physicians, researchers, and technicians to patients at several institutions. If it can help lessen the burden on patients while also reducing medical costs, that would be a wonderful thing.”
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-09
New research led by the University of Cincinnati and Swing Therapeutics found that a self-guided smartphone-based behavioral therapy led to significant improvements for patients with fibromyalgia.
The multicenter, randomized controlled trial tested Stanza, a smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy recommended by international clinical guidelines for fibromyalgia management, with the results of the study published July 8 in The Lancet.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition that affects an estimated 10 million Americans, a majority ...
2024-07-09
Cardiac arrests affect around 350,000 people in Europe each year with less than 20% surviving an out of hospital cardiac arrest. Research from Amsterdam UMC shows that women who survive consequently have greater rates of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, both men and women are affected by negative population-wide changes in socioeconomic status as they age. Suggesting more support is necessary for those who have suffered a cardiac arrest. These results are published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality & Outcomes.
"We looked at many factors to determine the five-year consequences of a cardiac arrest, here we saw, most significantly, a 50% ...
2024-07-09
Planes flying into one of the world's busiest airports are ingesting around 10kg of dust per 1,000 flights - with most of this dust ingested while they are waiting to land, new research has revealed.
Scientists used 17 years of ECMWF atmospheric data and data from the CALIPSO satellite to calculate the quantity of sand and dust swallowed by jet engines at ten major international airports located in desert regions or subject to seasonal dust storms.
The global study, published today (Tuesday, 9 July) in the journal Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, ...
2024-07-09
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Coral reefs, those vibrant underwater cities, stand on the precipice of collapse. While rising ocean temperatures and coral bleaching grab headlines, a new essay in Current Biology reveals a hidden layer of complexity in this fight for survival: the often-overlooked roles of the reefs’ smallest inhabitants.
Scientists have long understood the vital partnership between corals and their symbiotic algae, but work by researchers at UC Santa Barbara and University of Georgia highlights how the fate of entire reefs may hinge ...
2024-07-09
Even as the nation’s opioid epidemic continues to ravage families and communities nationwide — with more than 100,000 Americans dying of drug overdoses each year — stigma remains a barrier for many people accessing treatment for addiction.
A new study from Oregon Health & Science University suggests telehealth may be an important antidote to overcoming stigma and reducing barriers for people seeking out the treatment they need.
The study, published recently in the Harm Reduction Journal, compiled in-depth interviews with 30 people treated for substance use disorder ...
2024-07-09
A new way to store carbon captured from the atmosphere developed by researchers from The University of Texas at Austin works much faster than current methods without the harmful chemical accelerants they require.
In new research published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, the team developed a technique for ultrafast formation of carbon dioxide hydrates. These unique ice-like materials can bury carbon dioxide in the ocean, preventing it from being released into the atmosphere.
“We’re staring at a huge challenge — finding a way ...
2024-07-09
Novel research, presented today at the ESHRE 40th Annual Meeting in Amsterdam, reveals significant social disparities in achieving live births following assisted reproductive technology (ART) treatment. Women with a research education (PhD) were over three times more likely to achieve a live birth compared to those with a primary school education, while women in the highest income group were twice as likely than those in the lowest income group [1].
Conducted by researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Copenhagen University Hospital (Rigshospitalet), the national, register-based study analysed data from 68,738 women aged 18-45 who underwent ...
2024-07-09
Women in Europe are receiving more cycles of in vitro fertilisation (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI), according to data presented today at the ESHRE 40th Annual Meeting in Amsterdam [1].
Preliminary data from the ESHRE European IVF Monitoring (EIM) Consortium [2] reveals a steady and progressive rise in the use of Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART). In 2021, a total of 1 103,633 ART treatment cycles were reported by 1,382 clinics across 37 European countries – a 20% increase from the 919,364 cycles reported in 2020, keeping in mind that this was the year COVID affected the number ...
2024-07-09
Innovative research, presented today at the ESHRE 40th Annual Meeting in Amsterdam, has introduced a novel 3D imaging model designed to identify features of blastocysts – the early stage of development for an implanted embryo – associated with successful pregnancies. This new approach could transform current blastocyst selection methods, and open avenues for increased pregnancy rates [1].
The shape and structure of blastocysts can predict the success of a pregnancy, aiding blastocyst selection for in vitro fertilisation (IVF). However, selecting ...
2024-07-08
MINNEAPOLIS – The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) has named a new editor-in-chief of Brain & Life®, its free patient and caregiver magazine, website and podcast. Sarah Song, MD, MPH, FAAN, an associate professor in the department of neurological sciences at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, will succeed Editor-in-Chief Orly Avitzur, MD, MBA, FAAN, who will complete her 10-year term on December 31, 2024.
Song, a Fellow of the American Academy of Neurology, will be the third editor-in-chief of Brain & Life since the publication began in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Innovative, highly accurate AI model can estimate lung function just by using chest x-rays
Potential benefits of method include subjecting patients to fewer exams and reducing health care costs