Chronic allergic disorder EoE’s rising incidence in Japan confirmed by large-scale data analysis
First epidemiological study on incidence of EoE in Japan
2024-07-10
(Press-News.org)
Osaka, Japan — In one of the first studies of its kind in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University-led researchers uncovered the incidence and prevalence of the chronic allergic disorder eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE.
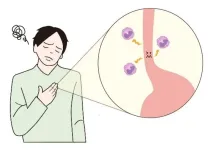
EoE can cause difficulty in swallowing with tissue inflammation and fibrosis as eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, build up in the esophagus. EoE cases have been increasing in North America and Western Europe since the 1990s, but little has been known about the situation in Asia including Japan.
Dr. Akinari Sawada, Associate Professor Fumio Tanaka, and Professor Yasuhiro Fujiwara of OMU’s Graduate School of Medicine and colleagues analyzed a health insurance claims database spanning January 2005 to September 2022 of 15,200,895 anonymous individuals. These individuals were company employees and their dependents, all under the age of 75. From this data, the research team found 1,010 cases of EoE.
In results published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the researchers assessed the EoE incidence in 2022 as 2.82 per 100,000 person-years and the prevalence as 10.68 per 100,000 people. Compared to 2017 data, the incidence was three times higher and the prevalence was eight times higher.
“In clinical practice, I thought that the number of patients with EoE was likely to increase in Japan. By using large-scale data, we were able to confirm the actual increase in the incidence and prevalence of EoE in this study. We hope that this will lead to raising awareness of EoE in Japan,” said Dr. Sawada.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-10
HERNDON, Va., July 10, 2024 -- One of the privileges the wealthiest Americans enjoy is living wherever they want. But new research published in Risk Analysis suggests they should be cautious when choosing their Shangri-La.
In their nationwide analysis, Rutgers University geographers Michael Greenberg and Dona Schneider compared the concentration of hazards and associated risks impacting the richest and poorest counties and the richest and poorest municipalities in all 50 states (200 locations).
When ...
2024-07-10
Auroras have inspired myths and portents for millennia — but only now, with modern technology dependent on electricity, are we appreciating their true power. The same forces which cause auroras also cause currents that can damage infrastructure which conducts electricity, like pipelines. Now scientists writing in Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences have demonstrated that the impact angle of interplanetary shocks is key to the currents’ strength, offering an opportunity to forecast dangerous shocks and shield critical infrastructure.
“Auroras and geomagnetically induced currents are ...
2024-07-10
Face attribute classification (FAC) is a high-profile problem in biometric verification and face retrieval. Although recent research has been devoted to extracting more delicate image attribute features and exploiting the inter-attribute correlations, significant challenges still remain.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Na LIU published their new research on 15 June 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a scattering-based hybrid block, termed WS-SE, to incorporate frequency-domain (WST) and image-domain (CNN) features in a channel attention manner. Compared with CNN, WS-SE achieved ...
2024-07-10
10 July 2024
Risky drinkers most at risk: Ads from sports broadcasts significantly increase alcohol urges
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research shows exposure to alcohol advertisements during national sports broadcasts, particularly those that feature a preferred beverage, significantly increases cravings in people with risky drinking behaviours.
The ECU study, led by Dr Ross Hollett, analysed nationally televised finals matches from the Australian Football League (AFL) and the National Rugby League (NRL) ...
2024-07-10
Quality is the core characteristic of cultivated land and is crucial for ensuring sustainable resource utilization and national food security. To meet the increasing demand for food driven by rapid population growth and the continual optimization of dietary structures, the intensity of cultivated land utilization has been steadily increasing. This trend has resulted in degradation issues such as deterioration of black soil, thinning of the cultivated land layer, reduction in organic matter content, soil salinization, acidification, and contamination by heavy metals, all of which threaten national food security. Currently, China has entered a critical period of agricultural ...
2024-07-10
New research led by UCLA Health revealed that Black patients with Huntington's disease in the U.S. and Canada received their diagnoses, on average, one year later compared to White patients after symptoms first appear.
Huntington’s disease is a rare, incurable genetic disease that causes a gradual death of nerve cells, resulting in a variety of symptoms affecting movement, emotions and cognition. About 41,000 Americans have the disease and 200,000 are at risk of inheriting it, according to the Huntington’s Disease Society of America. Children of a parent with ...
2024-07-10
A trove of ancient plant remains excavated in Kenya helps explain the history of plant farming in equatorial eastern Africa, a region long thought to be important for early farming but where scant evidence from actual physical crops has been previously uncovered.
In a new study published July 10 in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, archaeologists from Washington University in St. Louis, the University of Pittsburgh and their colleagues report the largest and most extensively dated archaeobotanical record from interior east Africa.
Up until now, scientists have ...
2024-07-10
A longitudinal study by University of Queensland researchers has found high-intensity interval exercise improves brain function in older adults for up to 5 years.
Emeritus Professor Perry Bartlett and Dr Daniel Blackmore from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute led the study in which volunteers did physical exercise and had brain scans.
Emeritus Professor Perry Bartlett and Dr Daniel Blackmore have shown high intensity exercise boosts cognition in healthy older adults and the improvement was retained for up to 5 years.
Emeritus Professor Bartlett said it is the first ...
2024-07-10
LA JOLLA, CA—Even years after they have recovered, a person who once struggled with alcohol or opioid addiction can relapse—and that relapse is more likely to occur during particularly stressful times. Now, Scripps Research scientists have identified an area of the brain that plays a key role in stress-induced oxycodone relapse. Their findings explain why the drug suvorexant, which they previously found to reduce alcohol and oxycodone relapse when administered orally, works so well.
“Having a better understanding of the region(s) in the brain responsible for this kind of relapse is incredibly important as we develop treatments for alcohol use disorder and opioid ...
2024-07-10
Daily sugar intake fell by around 5 g in children and by around 11 g in adults in the 12 months following the introduction of the UK’s ‘sugar tax’, formally known as the Soft Drinks Industry Levy, finds an analysis of 11 years of survey data, published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
The sugar from soft drinks alone made up over half this total, the estimates suggest. But overall daily energy intake from free sugars levels are still higher than the updated recommendation from the World Health Organisation (WHO) of 5%---equivalent to 30 g/day for adults, 24 g for 7–10 year olds, and 19 g for 4–6 year olds—point ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Chronic allergic disorder EoE’s rising incidence in Japan confirmed by large-scale data analysis
First epidemiological study on incidence of EoE in Japan