Comprehensive evaluation of large language models in mining gene relations and pathway knowledge
2024-07-11
(Press-News.org)
Understanding complex biological pathways, such as gene-gene interactions and gene regulatory networks, is crucial for exploring disease mechanisms and advancing drug development. However, manual literature curation of these pathways cannot keep pace with the exponential growth of discoveries. Large-scale language models (LLMs) trained on extensive text corpora contain rich biological information and can be leveraged as a biological knowledge graph for pathway curation.
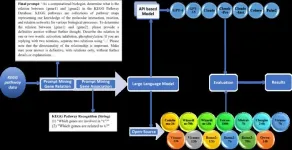
Recently, Quantitative Biology published a study titled "A Comprehensive Evaluation of Large Language Models in Mining Gene Relations and Pathway Knowledge." This research assesses 21 large language models (LLMs), including both API-based and open-source models, in their ability to retrieve biological knowledge. The evaluation focuses on predicting gene regulatory relations (activation, inhibition, and phosphorylation) and identifying gene components in pathways, using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway as the ground truth, as illustrated in Figure 1.
The results reveal a significant disparity in model performance, with API-based models outperforming their open-source counterparts. The findings suggest that while LLMs are informative in gene network analysis and pathway mapping, their effectiveness varies, necessitating careful model selection. GPT-4 and Claude-Pro emerged as top performers in predicting gene regulatory relations, achieving higher precision and recall rates than other models. This study underscores the importance of selecting appropriate computational tools for specific tasks in biological research. It also provides a case study illustrating the use of LLMs as knowledge graphs for data mining in general.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-11
LA JOLLA, CA—Do you grab a fork and take a first bite of cake, or say no and walk away? Our motivation to eat is driven by a complex web of cells in the brain that use signals from within the body, as well as sensory information about the food in front of us, to determine our behaviors. Now, Scripps Research scientists have identified a group of neurons in a small and understudied region of the brain—the parasubthalamic nucleus (PSTN)—that controls when an animal decides to take a first bite of food.
In the study, published in Molecular Psychiatry on July 4, 2024, the team of scientists set out to selectively manipulate a group of PSTN cells that dial up their ...
2024-07-11
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Quantum computing, which uses the laws of quantum mechanics, can solve pressing problems in a broad range of fields, from medicine to machine learning, that are too complex for classical computers. Quantum simulators are devices made of interacting quantum units that can be programmed to simulate complex models of the physical world. Scientists can then obtain information about these models, and, by extension, about the real world, by varying the interactions in a controlled way and measuring the resulting behavior of the quantum simulators.
In a paper published in Physical Review B, a UC Riverside-led research team ...
2024-07-11
U.S. Forest Service ecologists and partners published new findings on how planted mangroves can store up to 70% of carbon stock to that found in intact stands after only 20 years.
Researchers have long known that mangroves are superstars of carbon absorption and storage. But until now, limited information existed on how long it took for carbon stored in planted mangroves to reach levels found in intact mangroves.
“About ten years ago, Sahadev Sharma, then with the Institute of Pacific Islands Forestry, and I discovered that 20-year-old mangrove plantations in Cambodia had carbon stocks comparable to those of intact forests,” ...
2024-07-11
Immune system dysregulation and elevated inflammation contribute to the development of the fatal neurodegenerative condition amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease.
In new research published in The FASEB Journal, repeated infusions of certain immune cells delayed ALS onset and extended survival in mice, and also reduced markers of inflammation in an individual with the disease. The work was conducted by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General ...
2024-07-11
CAR-T cell therapy, which targets a specific protein on the surface of cancer cells, causes tumors to shrink or disappear in about half of patients with large B-cell lymphoma who haven’t experienced improvement with chemotherapy treatments.
But if this CAR-T treatment fails, or the cancer returns yet again — as happens in approximately half of people — the prognosis is dire. The median survival time after relapse is about six months.
Now, a phase 1 clinical trial at Stanford Medicine ...
2024-07-11
A major clinical trial, led by experts at the University of Nottingham, has shown the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT LOUD®) is more effective than the current speech and language therapy provided by the NHS, when treating patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
The results of the NIHR HTA funded trial, which are published today in the BMJ, showed that LSVT LOUD® was more effective at reducing the participant’s reported impact of voice problems than no speech and language therapy, as well as the NHS delivered speech and language therapy.
The trial was led by experts from the Universities of Nottingham and Birmingham, ...
2024-07-11
An intensive voice treatment developed in the USA and known as the Lee Silverman voice treatment (LSVT LOUD) is more effective than conventional NHS speech and language therapy or no therapy for people with Parkinson’s disease, finds a trial published in The BMJ today.
The researchers say the results emphasise the need to optimise the use of speech and language therapy resources for people with Parkinson’s disease.
Slurred or slow speech (known as dysarthria) is a common feature of Parkinson’s disease and can have a significant effect ...
2024-07-11
“The NHS’s relentless focus on finance and productivity is failing patient safety,” argues patient safety commissioner Henrietta Hughes in an interview for The BMJ today.
“The patient’s anecdote is the canary in the coal mine,” she says. It’s the thing that tells us there’s something going wrong. But too often we hear about patients who have raised concerns being gaslighted, dismissed, and fobbed off.”
Hughes, a GP and former medical director at NHS England, became England’s first independent patient safety commissioner in September 2022.
The job was created ...
2024-07-11
For the first time in the World Health Organization’s 76 year history, world leaders have unanimously committed to put social participation - people, communities and civil society - at the heart of health decision making processes.
This landmark pledge marks an important step forward in creating a healthy world, say experts in The BMJ today, and they urge everyone to seize their right to influence the decisions that affect their health and well-being.
Global challenges such as access to care, climate change, widening ...
2024-07-11
Artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots have frequently shown signs of an “empathy gap” that puts young users at risk of distress or harm, raising the urgent need for “child-safe AI”, according to a study.
The research, by a University of Cambridge academic, Dr Nomisha Kurian, urges developers and policy actors to prioritise approaches to AI design that take greater account of children’s needs. It provides evidence that children are particularly susceptible to treating chatbots as lifelike, quasi-human confidantes, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Comprehensive evaluation of large language models in mining gene relations and pathway knowledge