(Press-News.org) How do people like to interact with robots when navigating a crowded environment? And what algorithms should roboticists use to program robots to interact with humans?
These are the questions that a team of mechanical engineers and computer scientists at the University of California San Diego sought to answer in a study presented recently at the ICRA 2024 conference in Japan.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating robots that infer human perception of risk for intelligent decision-making in everyday settings,” said Aamodh Suresh, first author of the study, who earned his Ph.D. in the research group of Professor Sonia Martinez Diaz in the UC San Diego Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. He is now a postdoctoral researcher for the U.S. Army Research Lab.
“We wanted to create a framework that would help us understand how risk-averse humans are–or not–when interacting with robots,” said Angelique Taylor, second author of the study, who earned her Ph.D. in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at UC San Diego in the research group of Professor Laurel Riek. Taylor is now on faculty at Cornell Tech in New York.
The team turned to models from behavioral economics. But they wanted to know which ones to use. The study took place during the pandemic, so the researchers had to design an online experiment to get their answer.
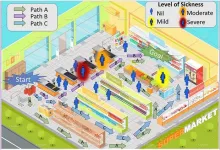
Subjects–largely STEM undergraduate and graduate students–played a game, in which they acted as Instacart shoppers. They had a choice between three different paths to reach the milk aisle in a grocery store. Each path could take anywhere from five to 20 minutes. Some paths would take them near people with COVID, including one with a severe case. The paths also had different risk levels for getting coughed on by someone with COVID. The shortest path put subjects in contact with the most sick people. But the shoppers were rewarded for reaching their goal quickly.
The researchers were surprised to see that people consistently underestimated in their survey answers indicating their willingness to take risks of being in close proximity to shoppers infected with COVID-19. “If there is a reward in it, people don’t mind taking risks,” said Suresh.
As a result, to program robots to interact with humans, researchers decided to rely on prospect theory, a behavioral economics model developed by Daniel Kahneman, who won the Nobel Prize in economics for his work in 2002. The theory holds that people weigh losses and gains compared to a point of reference. In this framework, people feel losses more than they feel gains. So for example, people will choose to get $450 rather than betting on something that has a 50% chance of winning them $1100. So subjects in the study focused on getting the reward for completing the task quickly, which was certain, instead of weighing the potential risk of contracting COVID.
Researchers also asked people how they would like robots to communicate their intentions. The responses included speech, gestures, and touch screens.
Next, researchers hope to conduct an in-person study with a more diverse group of subjects.
Robot Navigation in Risky, Crowded Environments:Understanding Human Preferences
Aamodh Suresh, Angelique Taylor, Laurel D. Riek, Sonia Martinez Diaz, University of California San Diego
END
How risk-averse are humans when interacting with robots?
Online experiment shows that humans underestimate how much risk they’re willing to take
2024-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An unequal toll of financial stress: Poll of older adults shows different impacts related to health and age
2024-07-11
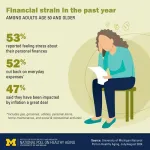
Inflation rates may have cooled off recently, but a new poll shows many older adults are experiencing financial stress – especially those who say they’re in fair or poor physical health or mental health.
Women and those age 50 to 64 are more likely than men or people over age 65 to report feeling a lot of stress related to their personal finances. So are people age 50 and older who say they’re in fair or poor physical or mental health.
In all, 47% of people age 50 and older said inflation had impacted them a great deal in the past year, and 52% said they ...
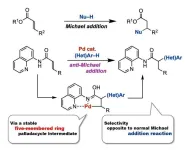
One-step synthesis of pharmaceutical building blocks: new method for anti-Michael reaction
2024-07-11
In 1887, chemist Sir Arthur Michael reported a nucleophilic addition reaction to the β-position of α,β- unsaturated carbonyl compounds. These reactions, named Michael addition reactions, have been extensively studied to date. In contrast, the anti-Michael addition reaction, referring to the nucleophilic addition reaction to the α-position, has been difficult to achieve. This is due to the higher electrophilicity of the β-position compared to the α-position. Previous attempts to overcome these difficulties have involved two main methods. The first is restricting the addition position via intramolecular reactions, ...
Urban seagulls still prefer seafood
2024-07-11
Seagull chicks raised on an “urban” diet still prefer seafood, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists studied herring gull chicks that had been rescued after falling off roofs in towns across Cornwall, UK.
Raised in captivity (before being released), they were given either a “marine” diet consisting mainly of fish and mussels, or an “urban” diet containing mostly bread and cat food.
Every few days the gull chicks were presented with a choice of all four foods in different bowls, to test which they preferred – and all gulls strongly favoured fish.
“Our results suggest that, even when reared on an ‘urban’ ...
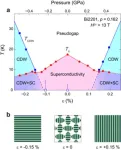
Understanding the origin of superconductivity in high-temperature copper oxide superconductors
2024-07-11
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity with zero resistance when cooled to a certain temperature, called the critical temperature. They have applications in many fields, including power grids, maglev trains, and medical imaging. High-temperature superconductors, which have critical temperatures higher than normal superconductors have significant potential for advancing these technologies. However, the mechanisms behind their superconductivity remain unclear.
Copper oxides or cuprates, a class of high-temperature superconductors, exhibit superconductivity ...
Shaping the future of polymer nanocarriers
2024-07-11
Scientists have taken a significant step towards the development of tailor-made chiral nanocarriers with controllable release properties. These nanocarriers, inspired by nature's helical molecules like DNA and proteins, hold immense potential for targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
The study, led by Professors Emilio Quiñoá and Félix Freire at the Center for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS), highlights the intricate relationship between the structure of helical polymers and their self-assembly into nanospheres. By carefully designing ...
2000th ERC Proof of Concept grant awarded
2024-07-11
The grants – each worth €150,000 – help researchers to bridge the gap between the discoveries stemming from their frontier research and the practical application of the findings, including early phases of their commercialisation.
Nanda Rea’s new project, called DeepSpacePULSE, aims to facilitate deep space exploration. Currently, to find their way, spacecraft and satellites use up a lot of energy exchanging vital navigation information with mission coordinators on Earth. Using ERC Proof of Concept funding, Prof. Nanda Rea ...
Wild plants and crops don’t make great neighbors
2024-07-11
Native plants and non-native crops do not fare well in proximity to one another, attracting pests that spread diseases in both directions, according to two new UC Riverside studies.
“We have changed the landscape, and it’s created opportunities for pathogens to thrive,” said UCR entomologist Kerry Mauck, who co-authored the studies. “We have introduced pathogens that damage native plants, and on the other side of the coin we have endemic pathogens that mutate to infect ...
Movement sensors show promise in identifying horses at injury risk
2024-07-11
PULLMAN, Wash. – A small 3-ounce sensor capable of recording 2,400 data points of movement in just one second being tested and refined by researchers at Washington State University could be key in reducing the number of injuries to racehorses.
Led by Dr. Warwick Bayly in WSU’s College of Veterinary Medicine, researchers used the biometric sensors, developed by the company StrideSAFE, to track thoroughbreds as they raced and trained at some of the top racetracks in the country. Using collected data, the team was able to identify miniscule stride changes associated with increased risk ...
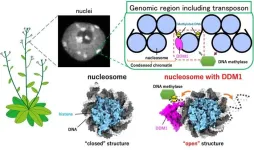
Opening the right doors: “jumping gene” control mechanisms revealed
2024-07-11
International joint research led by Akihisa Osakabe and Yoshimasa Takizawa of the University of Tokyo has clarified the molecular mechanisms in thale cresses (Arabidopsis thaliana) by which the DDM1 (Decreased in DNA Methylation 1) protein prevents the transcription of “jumping genes.” DDM1 makes “jumping genes” more accessible for transcription-suppressing chemical marks to be deposited. Because a variant of this protein exists in humans, the discovery provides insight into genetic conditions caused by such “jumping gene” mutations. The findings ...
Blood fat profiles confirm health benefits of replacing butter with high-quality plant oils
2024-07-11
Switching from a diet high in saturated animal fats to one rich in plant-based unsaturated fats affects the fat composition in the blood, which in turn influences long-term disease risk. A recent study published in Nature Medicine, conducted by a team of researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Germany and several other universities, shows that it is possible to accurately measure diet-related fat changes in the blood and directly link them to the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
“Our study confirms with even more certainty the health benefits of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] How risk-averse are humans when interacting with robots?Online experiment shows that humans underestimate how much risk they’re willing to take