(Press-News.org) Astronauts on spacewalks famously have to relieve themselves inside their spacesuits. Not only is this uncomfortable for the wearer and unhygienic, it is also wasteful, as – unlike wastewater on board the International Space Station (ISS) – the water in urine from spacewalks is not recycled.
A solution for these challenges would be full-body ‘stillsuits’ like those in the blockbuster Dune franchise, which absorbed and purified water lost through sweating and urination, and recycled it into drinkable water. Now, this sci-fi is about to become reality, with a prototype novel urine collection and filtration system for spacesuits. The design, by researchers from Cornell University, is published in Frontiers in Space Technology.
“The design includes a vacuum-based external catheter leading to a combined forward-reverse osmosis unit, providing a continuous supply of potable water with multiple safety mechanisms to ensure astronaut wellbeing,” said Sofia Etlin, a research staff member at Weill Cornell Medicine and Cornell University, and the study’s first author.
Designed for upcoming Moon and Mars missions
In 2025 and 2026, NASA is planning for the Artemis II and III missions, where a crew will orbit the Moon and land on its south pole, respectively. These missions are expected to be followed by crewed missions to Mars by the early 2030s. However, astronauts have long complained about a lack of comfort and hygiene of the existing maximum absorbency garment (MAG) – the waste management system of traditional NASA spacesuits –in use since the late 1970s – which functions like a multi-layered adult diaper made of superabsorbent polymer.
“The MAG has reportedly leaked and caused health issues such as urinary tract infections and gastrointestinal distress. Additionally, astronauts currently have only one liter of water available in their in-suit drink bags. This is insufficient for the planned, longer-lasting lunar spacewalks, which can last ten hours, and even up to 24 hours in an emergency,” said Etlin.
Astronauts have also requested that the time needed to fill and de-gas the in-suit drink bags be reduced in future spacesuits, and that a separate supply of non-caffeinated high-energy drink be added.
With all these objectives in mind, Etlin and colleagues have now designed a urine collection device, including an undergarment made of multiple layers of flexible fabric. This connects to a collection cup (with a different shape and size for women and men) of molded silicone, to fit around the genitalia.
The inner face of the collection cup is lined with polyester microfiber or a nylon-spandex blend, to draw urine away from the body and towards the inner cup’s inner face, from where it is sucked by a vacuum pump. A RFID tag, linked to an absorbent hydrogel, reacts to moisture by activating the pump.
High-tech backpack
Once collected, the urine is diverted to the urine filtration system, where it gets recycled with an efficiency of 87% through a two-step, integrated forward and reverse osmosis filtration system. This uses a concentration gradient to remove water from urine, plus a pump to separate water from salt. The purified water is then enriched in electrolytes and pumped into the in-suit drink bag, again available for consumption. Collecting and purifying 500ml of urine takes only five minutes.
The system, which integrates control pumps, sensors, and a liquid-crystal display screen, is powered by a 20.5V battery with a capacity of 40 amp-hours. Its total size is 38 by 23 by 23 cm, with a weight of approximately eight kilograms: sufficiently compact and light to be carried on the back of a spacesuit.
Now that the prototype is available, the new design can be tested under simulated conditions, and subsequently during real spacewalks.
“Our system can be tested in simulated microgravity conditions, as microgravity is the primary space factor we must account for. These tests will ensure the system’s functionality and safety before it is deployed in actual space missions,” concluded Dr Christopher E Mason, a professor at the same institute as Etlin and the study’s lead author.
END
Real-life ‘stillsuit’: Dune-inspired upgrade for spacesuits allow astronauts to recycle urine into water
Where do you go to the bathroom in outer space? Scientists solve the problem with a sci-fi-like recycling suit
2024-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A comprehensive derivative synthesis method for development of new antimicrobial drugs
2024-07-12
A method to screen a wide variety of drug candidates without laborious purification steps could advance the fight against drug-resistant bacteria.
Efforts to combat the increasing threat of drug-resistant bacteria are being assisted by a new approach for streamlining the search for antimicrobial drug candidates, pioneered by researchers at Hokkaido University, led by Assistant Professor Kazuki Yamamoto and Professor Satoshi Ichikawa of the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences. Their methods, developed together with researchers elsewhere in Japan and in the USA, are discussed ...
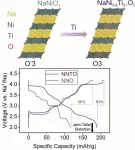
Improving cycling performance of sodium-ion batteries through titanium substitution
2024-07-12
Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have made significant advances in sodium-ion battery (SIB) technology by improving cycling performance of the NaNiO2 cathode. They successfully synthesized, for the first time, the cathode active material NaNi0.9Ti0.1O2, which delivers a specific capacity of 190 mAh/g, thus positioning it as a potential candidate for application in high-energy-density SIBs. This innovative approach not only improves battery stability but also propels us toward advanced energy-storage solutions beyond.
With its high theoretical ...
Hatcheries can boost wild salmon numbers but reduce diversity
2024-07-12
The ability of salmon hatcheries to increase wild salmon abundance may come at the cost of reduced diversity among wild salmon, according to a new University of Alaska Fairbanks–led study.
The number of juvenile salmon released into the North Pacific Ocean by hatcheries increased rapidly in the second half of the last century and remains at over 5 billion each year. Salmon hatcheries have helped push annual pink salmon harvests in Prince William Sound from about 4 million fish prior to hatchery programs to roughly 50 million in recent years.
Using data collected from pink salmon streams ...
Artificial intelligence speeds up heart scans, saving doctors’ time, and could lead to better treatment for heart conditions
2024-07-12
Researchers created a computer model that uses AI to examine heart images from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Results were comparable to those worked out by doctors manually, but instead of taking 45 minutes or more, the AI model takes just a few seconds
The AI model could lead to more efficient diagnoses, better treatment decisions and improved outcomes for patients
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking method for analysing heart MRI scans with the help of artificial ...
How the 'heart and lungs' of a galaxy extend its life
2024-07-12
Galaxies avoid an early death because they have a "heart and lungs" which effectively regulate their "breathing" and prevent them growing out of control, a new study suggests.
If they didn't, the Universe would have aged much faster than it has and all we would see today is huge "zombie" galaxies teeming with dead and dying stars.
That’s according to a new study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, which investigates one of the great mysteries of the Universe – why galaxies are not ...
Light-induced Meissner effect in optically driven YBa2Cu3O6.48
2024-07-12
Superconductivity is a fascinating phenomenon, which allows a material to sustain an electrical current without any loss. This collective quantum behavior of matter only appears in certain conductors at temperatures far below ambient.
A number of modern studies have investigated this behavior in so-called non-equilibrium states, that is in situations in which the material is pushed away from thermal equilibrium. In these conditions, it appears that at least some of the features of superconductivity can be recreated even at ambient temperatures. Such non-equilibrium high temperature superconductivity, shown to exist under irradiation ...
Study finds short and long sleep duration associated with blood vessel damage in those recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
2024-07-12
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September) shows that people recently diagnosed with diabetes who experience short or long sleep duration are more likely to experience microvascular disease (damage to the small blood vessels), which could ultimately lead to more serious complications. The study is by Mette Johansen and Thomas Olesen, Steno Diabetes Center Odense, Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark, and colleagues.
Microvascular complications, such as retinopathy and nephropathy, are major contributors ...
IoT sensors tattle on stores that neglect promo displays
2024-07-11
Whether it’s a pharmacy, a supermarket, or a clothier, when you walk into a retail store in the U.S., you are sure to encounter a flashy promotional display featuring products from a specific brand.
It’s a marketing strategy that’s been proved to be highly effective at boosting sales. Brands carefully plan display campaigns, signing contracts with retailers that specify when to install the exhibits and for how long. They often provide financial incentives to encourage compliance.
But a new study from Ashish ...
A stealth fungus has decimated North American bats but scientists may be a step closer to treating white-nose syndrome
2024-07-11
An invasive fungus that colonizes the skin of hibernating bats with deadly consequences is a stealthy invader that uses multiple strategies to slip into the small mammals' skin cells and quietly manipulate them to aid its own survival. The fungus, which causes the disease white-nose syndrome, has devastated several North American species over the last 18 years.
Scientists have learned much about the fungus, Pseudogymnoascus destructans, since it was first documented in a New York cave in 2006, including where it thrives, its distribution, and clinical features. But exactly ...
Menstrual cramps can be worse in normal-length cycles without ovulation
2024-07-11
According to current understanding, menstrual cramps only happen in cycles in which an egg is released, or an ovulatory cycle. But new research from the University of British Columbia (UBC) is challenging this notion.
The findings, published in the Journal of Pain Research, reveal that some women not only experience cramps when no egg is released, but that cramps can be more severe and last longer during these anovulatory cycles.
“I was surprised to see significant cramps in menstrual cycles with or without ovulation, which challenges current thinking” said co-author, Dr. Paul Yong, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at UBC and Canada Research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
[Press-News.org] Real-life ‘stillsuit’: Dune-inspired upgrade for spacesuits allow astronauts to recycle urine into waterWhere do you go to the bathroom in outer space? Scientists solve the problem with a sci-fi-like recycling suit