(Press-News.org) The element actinium was first discovered at the turn of the 20th century, but even now, nearly 125 years later, researchers still don’t have a good grasp on the metal’s chemistry. That’s because actinium is only available in extremely small amounts and working with the radioactive material requires special facilities. But to improve emerging cancer treatments using actinium, researchers will need to better understand how the element binds with other molecules.
In a new study led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), researchers grew crystals containing actinium and studied the compound’s atomic structure. While elements often behave similarly to their lighter cousins on the periodic table, researchers were surprised to find that the actinium behaved differently than predicted by looking at its counterpart, lanthanum.
“There’s a breadth of applications for these elements, from nuclear energy to medicine to national security, but if we don’t know how they behave, that inhibits the progress we can make,” said Jen Wacker, first author of the paper published today in Nature Communications and a chemist at Berkeley Lab. “We’re seeing that this work is necessary to really understand the complexity of these radioactive elements, because in a lot of cases, using their surrogates is not sufficient to understand their chemistry.”
One area of interest is in using an isotope of actinium (actinium-225) in a cancer treatment method called targeted alpha therapy (TAT), which has shown promise in clinical trials. The TAT method uses biological delivery systems such as peptides or antibodies to move the radioactive element to the cancer site. When the actinium decays, it releases energetic particles that travel a short distance, destroying the nearby cancer cells but sparing healthy tissue further away.
“There’s a movement to design better delivery systems to get the actinium to particular cells and keep it there,” said Rebecca Abergel, a UC Berkeley associate professor of nuclear engineering and of chemistry who leads the Heavy Element Chemistry Group at Berkeley Lab. “If we can engineer proteins to bind the actinium with a really high affinity, and either be fused with an antibody or serve as the targeting protein, that would really enable new ways to develop radiopharmaceuticals.”
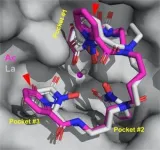
Researchers used a novel approach to grow the crystals using only 5 micrograms of pure actinium – roughly one tenth the weight of a grain of salt, and invisible to the naked eye. They first purified the actinium through a complex filtration process that removed other elements and chemical impurities. They then bound the actinium to a metal-trapping molecule called a ligand and enveloped the bundle inside of a protein isolated and purified by Roland Strong’s team at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, building a “macromolecular scaffold.” The crystals, grown over a week inside of the Heavy Element Research Laboratory, were then cryocooled in liquid nitrogen and illuminated with X-rays at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS). The X-rays revealed the compound’s 3D structure and showed how actinium interacted with surrounding atoms. It is the first single-crystal X-ray structure reported for actinium
“I’ve been working in crystallography for 40 years and seen a lot of things, and the method the team is using is unique and provides details we couldn’t get in the past,” said Marc Allaire, a scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Biophysics and Integrated Bioimaging Division and head of the Berkeley Center for Structural Biology team at the ALS. “To the best of my knowledge, Berkeley Lab is the only place in the world where we do this kind of study and measure radioactive protein crystals.”
In this work, scientists used actinium-227, the longest-lived isotope of the element. Future studies will explore actinium-225 (the preferred isotope for targeted alpha therapy) to look for other changes in how the metal binds. Researchers are also interested in pairing actinium with different proteins to learn more about the structures it forms.
“This is very fundamental science that is part of our core program in understanding the chemistry of heavy elements,” Abergel said. “We’ve achieved a really technically difficult experimental method that pushes the boundaries of isotope chemistry and lets us gain a better understanding of this element. It hopefully will enable us and others to develop better systems that are useful for targeted alpha therapy.”
The Advanced Light Source is a DOE Office of Science user facility.
###
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) is committed to delivering solutions for humankind through research in clean energy, a healthy planet, and discovery science. Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest problems are best addressed by teams, Berkeley Lab and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Researchers from around the world rely on the lab’s world-class scientific facilities for their own pioneering research. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
END
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening aims to identify men who may harbor potentially lethal prostate cancer, and those with high PSA results often require more extensive (and expensive) diagnostic testing to establish a diagnosis. New research reveals that the out-of-pocket costs for such additional tests are substantial, common, and rising. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Abnormal screening tests (i.e., elevated PSA) warrant ...
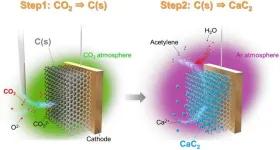
Since its discovery, in 1836, acetylene has emerged as an essential chemical compound in industry, widely used as a chemical building block and fuel. It has applications in the raw material for resins, such as vinyl chloride, welding gas, and illumination. Recent developments aimed at reducing the dependence on petroleum feedstocks have shown that acetylene is a promising platform molecule for producing various base chemicals. Additionally, polyacetylene, a crucial semiconducting material, is made from acetylene. Currently, acetylene is mainly produced through two methods: ...
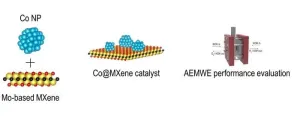
A research team led by Dr. Sung Mook Choi of the Korea Institute of Materials Science, a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, has developed a one-step electrode fabrication process for the first time in South Korea. This process produces electrodes, a key component of anion exchange membrane water electrolysis, directly from raw materials to a mass-producible level. The team successfully applied this process to a commercial-scale stack of anion exchange membrane water ...
137 countries around the world have signed a "net-zero" climate change agreement to end fossil fuel use and achieve zero carbon emissions by 2050. Hydrogen is being touted as the next green energy source because it emits only water and oxygen when utilized as an energy source. Hydrogen production methods are divided into gray hydrogen, blue hydrogen, and green hydrogen depending on the energy source and carbon emissions. Among them, green hydrogen production method is the most eco-friendly method that produces hydrogen without carbon emissions by electrolyzing water using green energy.
A research team led by Dr. ...
Orlando, Fla - A new national survey by the Orlando Health Advanced Rehabilitation Institute finds most Americans believe it’s normal for women to experience pain, pressure and incontinence after having children. But experts say these are actually signs of pelvic floor issues, and while they are extremely common, affecting about a third of women, they are not normal.
“When we say it's not normal, what we mean is it's not something you should have to live with. It's something ...
New research aims to help reduce the quantity of unused prescription opioids after emergency department visits and lessen the risk of opioid misuse and overdose. The study is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231640.
VIEW EMBARGOED ARTICLE
Overprescribing is linked to opioid misuse and overdose, with household supplies of opioids associated with an increased risk of overdose, as many people do not dispose of unused medications safely. In Canada, ...
Funding agencies in Canada need to review their policies for evaluating research proposals to ensure that South Asian research is conducted by South Asians, write authors in a commentary in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231189
VIEW EMBARGOED ARTICLE
Much of the health research conducted in Canada on South Asian diaspora communities has historically been marked by unequal power relations, rather than meaningfully engaging and benefitting these communities.
As the largest and fastest growing diverse ...
A study published in Genome Biology opens new possibilities to improve production efficiency in the cattle industry and potentially animal agriculture more broadly. A team of researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Cornell University and the USDA discovered that, like humans, cattle have CoRSIVs. CoRSIVs are regions of the genome carrying chemical markers on the DNA that provide information that may allow farmers to predict and select desirable cattle characteristics, such as milk production, female fertility and resistance to disease.
“Most people know that each person ...
Late detection biggest worry in relation to cancer diagnosis, with 55% of people wanting to see future advances in early cancer detection
Public overwhelmingly support use of AI to tackle cancer
43% of people recognise major impact universities can have on reducing deaths from cancer
Cambridge University partnering with NHS to build revolutionary new Cambridge Cancer Research Hospital
Two-thirds of the public say they are very or somewhat worried about being told they have the disease – higher than ...
Doctors, nurses and other healthcare staff suffering burnout should be shown compassion and not blamed for being unwell, according to a leading GP.
Clare Gerada says employers often treat physicians as ‘naughty schoolchildren’ when they go sick or suffer mental health problems. Professor Dame Gerada, past president of the Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP), is calling for more comprehensive guidance that focuses on ‘kindness’ and ‘sensitivity’.
The doctor, who helped found mental health charity, Doctors in Distress, addresses the need for major reform in a new book aimed at reforming care for doctors and nurses ...