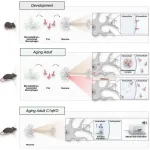
(Press-News.org) BOSTON, Mass. (July 15, 2024)—A groundbreaking study conducted at the lab of Beth Stevens, PhD, at Boston Children’s Hospital has revealed that an immune protein impacts neuronal protein synthesis in the aging brain. Previous work from the Stevens lab had uncovered that immune cells in the central nervous system, microglia, help prune synapses in the developing brain by tagging synapses with the immune protein C1q. New research led by Nicole Scott-Hewitt, published in Cell, shows that neurons can also internalize C1q. C1q seems to influence protein production inside neurons by interacting with ribosomal proteins, RNA-binding proteins, and RNA in the cell's cytoplasm. Additionally, C1q accumulates in neurons over time, suggesting it may play a role in age-related cognitive changes and neurodegenerative conditions.
The study, titled "Microglial C1q accumulates in neuronal ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes across aging," has been published in Cell, highlighting the following key findings:
Changes in Brain Protein Production with Age:
In adult mice lacking a protein called C1q, there is a significant increase in the production of proteins in neurons and a change in the balance of proteins in the brain, suggesting that C1q may be important for keeping the brain's proteins in check. These changes are specific to age, with noticeable differences in protein production in adult mice compared to younger ones.
How Neurons Take in C1q:
Neurons can take in C1q protein from outside the cell. This process depends on endocytosis, a way cells internalize molecules. The study found that a part of the C1q protein called the collagen-like domain is crucial for this uptake by neurons.
Impact on Learning and Memory:
Deleting C1q in microglia in adult mice affects their ability to forget fear memories, showing C1q's importance in learning and memory. This suggests that C1q helps with memory and brain flexibility, potentially by interacting with specific neuronal complexes that impact neuronal protein production.
C1q's Role in the Aging Brain:
Previous research showed that C1q levels increase significantly as the brain ages. While C1q is known for its roles on the surface of neurons and synapses in brain development and disease, its functions in the aging brain were unclear. This study used a broad approach to discover how C1q interacts with other proteins as the brain ages, discovering that C1q interacts with RNA-binding proteins in the aging brain. This was a surprising find, as it showed the presence of C1q inside neurons in older brains, indicating that immune proteins produced by brain macrophages, like microglia, can also impact internal neuronal functions.
Effects of Losing C1q on Protein Production and Memory:
The study examined if the absence of C1q affects protein production in the brain as it ages. They found an increase in protein production in the neurons of adult mice lacking C1q. Additionally, removing C1q affected the mice's ability to forget fearful experiences, indicating a unique role of C1q in the adult brain, independent of its previously described functions in synapse pruning.
For more insights into the intricate role of microglia in neuronal translation, check out this detailed piece from ALZFORUM: C1q: Microglia Meddles in Neuronal Translation
Media Contact:
media.relations@childrens.harvard.edu
END
New study reveals critical role of C1q protein in neuronal function and aging
Highlights how temporally regulated neuroimmune interactions can impact critical intraneuronal functions and raises questions about the additional roles of glial and immune interactions in brain health across aging
2024-07-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research demonstrates potential for increasing effectiveness of popular diabetes, weight-loss drugs
2024-07-15
A network of proteins found in the central nervous system could be harnessed to increase the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs, according to new research from the University of Michigan.
The study, appearing today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, focused on two proteins called melanocortin 3 and melanocortin 4 found primarily on the surface of neurons in the brain that play a central role in regulating feeding behavior and maintaining the body's energy balance.
Melanocortin ...
Understanding the 3D ice-printing process to create micro-scale structures
2024-07-15
Advances in 3D printing have enabled many applications across a variety of disciplines, including medicine, manufacturing, and energy. A range of different materials can be used to print both simple foundations and fine details, allowing for the creation of structures with tailored geometries.
However, creating structures with micro-scale, precise internal voids and channels still poses challenges. Scaffolds used in tissue engineering, for example, must contain a three-dimensional complex network of conduits that mimic the human vasculature. With traditional additive manufacturing, where the material is deposited layer ...
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers develop antioxidant strategy to address mitochondrial dysfunction caused by SARS-CoV-2 virus
2024-07-15
Philadelphia, July 15, 2024 – Building upon groundbreaking research demonstrating how the SARS-CoV-2 virus disrupts mitochondrial function in multiple organs, researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) demonstrated that mitochondrially-targeted antioxidants could reduce the effects of the virus while avoiding viral gene mutation resistance, a strategy that may be useful for treating other viruses. The preclinical findings were recently published in the journal Proceedings ...
How climate change is altering the Earth’s rotation
2024-07-15
Climate change is causing the ice masses in Greenland and Antarctica to melt. Water from the polar regions is flowing into the world’s oceans –and especially into the equatorial region. “This means that a shift in mass is taking place, and this is affecting the Earth’s rotation,” explains Benedikt Soja, Professor of Space Geodesy at the Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering at ETH Zurich.
“It’s like when a figure skater does a pirouette, first holding her arms close to her body and then stretching ...
Comparison of FDG-PET/CT and CT for treatment evaluation of patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma
2024-07-15
“FDG-PET is generally considered as a useful metabolic evaluation tool, while it is also thought to have an emerging role for assessment of systemic therapy response.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 15, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on June 20, 2024, entitled, “Comparison of FDG-PET/CT and CT for evaluation of tumor response to nivolumab plus ipilimumab combination therapy and prognosis prediction in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma.”
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive neoplasm and affected ...
New concept explains how tiny particles navigate water layers – with implications for marine conservation
2024-07-15
A new UBC study published recently in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) has unveiled insights into how microscopic organisms such as marine plankton move through water with different density layers.
Researchers Gwynn Elfring and Vaseem Shaik found that density layers, created by variations in temperature or salinity, influence the swimming direction and speed of tiny particles navigating a liquid.
Pushers and pullers
“There are two different types of microscopic swimmers – ...
New research shows a frictionless state can be achieved at macroscale
2024-07-15
UTICA, NY – The president of SUNY Polytechnic Institute (SUNY Poly), Dr. Winston “Wole” Soboyejo, and postdoctoral researcher, Dr. Tabiri Kwayie Asumadu, have published a revolutionary new paper titled, "Robust Macroscale Superlubricity on Carbon-Coated Metallic Surfaces." This paper explores an innovative approach to reducing friction on metallic surfaces – a significant advancement that could have major real-world impacts.
The study shows that superlubricity – a state with virtually no friction that was once believed to only be achievable at nanoscale – can now be maintained at macroscale for extended time ...
A novel and unique neural signature for depression revealed
2024-07-15
HOUSTON - (July 15, 2024) - As parents, teachers and pet owners can attest, rewards play a huge role in shaping behaviors in humans and animals. Rewards – whether as edible treats, gifts, words of appreciation or praise, fame or monetary benefits – act as positive reinforcement for the associated behavior. While this correlation between reward and future choice has been used as a well-established paradigm in neuroscience research for well over a century, not much is known about the neural process underlying it, namely how the brain encodes, ...
Academic psychiatry urged to collaborate with behavioral telehealth companies
2024-07-15
Waltham — July 15, 2024 — The strengths of academic psychiatry departments and the fast-growing private telehealth sector are complementary, according to a Perspective article published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer. Justin A. Chen, MD, MPH, a psychiatrist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City, and colleagues reviewed literature on provision of outpatient mental health care in the United States. They concluded that academic psychiatry departments and telehealth companies could mutually benefit from strategic collaboration.
Academic medical centers struggle to ...
NASA’s Webb investigates eternal sunrises, sunsets on distant world
2024-07-15
Researchers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have finally confirmed what models have previously predicted: An exoplanet has differences between its eternal morning and eternal evening atmosphere. WASP-39 b, a giant planet with a diameter 1.3 times greater than Jupiter, but similar mass to Saturn that orbits a star about 700 light-years away from Earth, is tidally locked to its parent star. This means it has a constant dayside and a constant nightside—one side of the planet is always exposed to its star, while the other is always shrouded in darkness.
Using Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
[Press-News.org] New study reveals critical role of C1q protein in neuronal function and agingHighlights how temporally regulated neuroimmune interactions can impact critical intraneuronal functions and raises questions about the additional roles of glial and immune interactions in brain health across aging