Understanding others: By age three, we can do this with mirror neurons
A study from the Università Cattolica, Milan Campus, in collaboration with Giacomo Rizzolatti of the University of Parma, published in the prestigious journal PNAS, captures the age when this complex ability appears.
2024-07-16
(Press-News.org)
Milan, July 15, 2024 – By the age of three, children are capable of understanding others, "mirroring" those they are with to imitate and anticipate their intentions. They are able to do it thanks to the sophisticated neurofunctional architecture that is necessary to understand others' intentions, the mirror neurons, that result already active at this age.
It’s the result of a study published in the prestigious journal PNAS, led by the collaboration between Giacomo Rizzolatti of the University of Parma, the scientist who discovered mirror neurons, and the research group composed of Cinzia Di Dio, Laura Miraglia, Giulia Peretti and coordinated by Antonella Marchetti, Director of the Department of Psychology at the Università Cattolica, Milan Campus. "This is a very important discovery," explains Professor Marchetti, "as it demonstrates that even at such a young age, children are equipped with the 'resonance' system constituted by mirror neurons, which are the building blocks upon which a more complex and articulated understanding of the social world will be built with development and experience."
Although preschoolers are capable of planning goal-directed motor action sequences, their understanding of the intentions of others engaged in motor tasks had not been thoroughly investigated until now. The group from Università Cattolica, along with Professor Rizzolatti, measured the ability of preschool children to organize a sequence of motor actions by understanding the intention behind another individual's chain of actions.
To verify this ability, the researchers measured the activation of the mylohyoid muscle, involved in opening the mouth, while the children grabbed a piece of food to eat or a piece of paper to put into a container. When grabbing the food, the mylohyoid muscle activation began several milliseconds before the action was completed. The muscle did not activate when grabbing the paper, suggesting a planned sequence of motor events focused on the action's goal. Even when the children observed an experimenter performing the same grabbing tasks, the mylohyoid muscle activated during the
observation of the eating task. However, as Professor Marchetti explains, "we discovered that the muscle activation occurs more slowly compared to older children, aged 6-9 years (examined in previous studies), who are supported by the emergence of more sophisticated cognitive processes." According to the authors, the results suggest that understanding others' motor intentions is a developing ability in preschool children.
"In conclusion," Professor Marchetti emphasizes, "the current data provide further support for the evidence regarding the various stages of child development in this domain, in continuity with research on infants that show early attunement to goal-directed motor acts.
Overall, these results are also relevant from the perspective of early diagnosis, for example, in the case of children with autism spectrum disorder, as they would make it possible to implement a psychophysical instrumental assessment of an eventual deficit in understanding intentions and a possible impairment of fundamental precursors for the development of social skills," she concludes.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-16
EMBARGO: THIS CONTENT IS UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 9 A.M. U.S. EASTERN STANDARD TIME ON JULY 16. INTERESTED MEDIA MAY RECIVE A PREVIEW COPY OF THE JOURNAL ARTICLE IN ADVANCE OF THAT DATE OR CONDUCT INTERVIEWS, BUT THE INFORMATION MAY NOT BE PUBLISHED, BROADCAST, OR POSTED ONLINE UNTIL AFTER THE RELEASE WINDOW.
New research shows that ozone concentrations at Carlsbad Caverns National Park frequently exceed Environmental Protection Agency health standards, likely due to oil and natural gas development in the Permian Basin and surrounding region.
The work was led through the Department of Atmospheric Science at Colorado State University and is part of ...
2024-07-16
ITHACA, N.Y. – Researchers studying antimicrobial-resistant E. coli – the leading cause of human death due to antimicrobial resistance worldwide – have identified a mechanism in dogs that may render multiple antibiotic classes ineffective.
The paper, which will publish July 16 in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology at 9:00am EST, opens up new avenues for therapies to treat both animals and humans – and establishes clinical infections in dogs as a surveillance approach for public health.
The research team analyzed more than 1,000 genomes of the resistant ...
2024-07-16
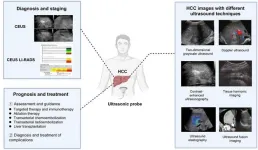
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a primary malignancy of the liver and one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective management and improved survival rates. Ultrasound (US) technology has significantly advanced and plays a pivotal role in the surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment of HCC. This paper delves into various ultrasound techniques and their clinical applications in HCC management.
Two-dimensional gray-scale ultrasound is a fundamental imaging technique for HCC surveillance. ...
2024-07-16
Democrats and Republicans overestimate the percentage of people in the opposing party who approve of widely agreed-upon moral wrongs, such as theft or animal abuse, according to a study. Today, Americans hate their opposing political party more than they love their own party, and political animosity and dehumanization of opposing party members have been on the rise for decades. Curtis Puryear and colleagues looked for a “basic morality bias” in social media posts from 5,806 political partisans by searching for words that referencd ...
2024-07-16
Mohammad Atari and colleagues explore the promise and peril of using large language models (LLMs) in psychological research, beginning by urging researchers to also ask themselves whether and why they should use LLMs—not just how they should use them. The authors caution against using LLMs as a replacement for human participants, noting that LLMs cannot capture the substantial cross-cultural variation in cognition and moral judgement known to exist. Most LLMs have been trained on data primarily from WEIRD (Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic) sources, disproportionately in English. Additionally, although ...
2024-07-16
Large language models (LMs) can complete abstract reasoning tasks, but they are susceptible to many of the same types of mistakes made by humans. Andrew Lampinen, Ishita Dasgupta, and colleagues tested state-of-the-art LMs and humans on three kinds of reasoning tasks: natural language inference, judging the logical validity of syllogisms, and the Wason selection task. The authors found the LMs to be prone to similar content effects as humans. Both humans and LMs are more likely to mistakenly label an invalid argument as valid when the semantic content is sensical and believable. LMs are also just as bad as humans at the Wason selection task, in which the participant ...
2024-07-16
A study combining history, economics, and fluvial geomorphology examines the causes of the adoption of coal power during the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. At the beginning of the mechanization of the textile industry in Britain, most machines were powered with waterpower. Eventually waterpower was replaced by using coal to make steam power and the causes of this shift have long been debated. One influential hypothesis has been that waterpower became scarce in the industrial heartland of northwest England during the early 19th century, as all available suitable sites were already fitted with ...
2024-07-16
Industrial emissions are one of the main sources of climate change-inducing carbon dioxide (CO2). While adopting renewable and clean energy alternatives is one option for mitigating these carbon emissions, carbon capture technology is another solution to control CO2 emissions. In big CO2-emitting industries, such as cement, oil refineries, and thermal power plants, carbon capture technology can be easily applied to remove CO2 emissions directly at the source at a feasible cost and with low energy consumption. Different materials have been explored for CO2 capture in factories, including zeolites, metal−organic frameworks, natural minerals, alkalis, ...
2024-07-16
The ELTE Eötvös Loránd University is home to the skulls of more than 150 dog breeds and other animals. To make this unique collection accessible to all, researchers digitised the skulls of 431 dogs, cats and wild relatives. The database can be used for educational and research purposes.
Tibor Csörgő, a researcher at ELTE, has been collecting animal skulls for decades to teach anatomy to biologists. The shape of the skull varies considerably between species and breeds, especially in dogs, where, for example, greyhounds have long skulls and the now popular French bulldogs have rounded skulls.
A skull biobank ...
2024-07-16
Overcoming Historical Barriers
Silicon, the cornerstone of modern electronics, photovoltaics, and photonics, has traditionally been limited to surface-level nanofabrication due to the challenges posed by existing lithographic techniques. Available methods either fail to penetrate the wafer surface without causing alterations or are limited by the micron-scale resolution of laser lithography within Si. In the spirit of Richard Feynman's famous dictum, 'There's plenty of room at the bottom', ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Understanding others: By age three, we can do this with mirror neurons
A study from the Università Cattolica, Milan Campus, in collaboration with Giacomo Rizzolatti of the University of Parma, published in the prestigious journal PNAS, captures the age when this complex ability appears.