(Press-News.org) Through precision medicine, the University of Virginia is working toward a world in which no more pink ribbons are necessary. To that end, Susan G. Komen announced support this summer for the UVA School of Engineering and Applied Science’s efforts to apply systems biology research to defeat breast cancer.
Komen announced a collective $10 million in research awards , including a $100,000 grant over two years to support the work of doctoral student Catalina Alvarez Yela, who is studying “triple negative” breast cancer, an aggressive type of invasive breast cancer that is hard to selectively target.
UVA biomedical engineer Kevin Janes is her mentor on the project.
The pair will be focusing on how genes and proteins interact with each other within organelles. Those are the “little organs” such as mitochondria that reside within cells and perform specialized functions. Specifically, they are studying the regulation of a protein complex that forms its own mini-organelle when cells separate their chromosomes during division.
"Catalina is building computational models of chromosome segregation during cell division and how that process goes wrong in breast cancer," Janes said. "She is also testing model predictions in mouse experiments in the lab."
The ASPIRE Grant — an acronym for Supplement to Promote Inclusion for Research Excellence — encourages opportunity for students from diverse backgrounds. Alvarez Yela is a native of Colombia.
Janes, the John Marshall Money Professor of biomedical engineering, co-directs the Center for Systems Analysis of Stress-Adapted Cancer Organelles, where the research is being performed. The center previously received a $12 million grant from the National Institutes of Health.
Prior to the center’s founding in 2022, cancer research had largely focused on targeting specific genes or proteins involved with cell division and developing drugs for those targets, rather than taking a more systemic approach.
Alvarez Yela is co-advised by Todd Stukenberg in the UVA School of Medicine's Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics Group. Her breast cancer advocate is Ivy Hinton in the School of Nursing.
In all, “Komen’s 32 grants further cutting-edge breast cancer research being done at 27 prestigious institutions worldwide and continue Komen’s longstanding support of breast cancer researchers early in their careers, as well as the world’s leaders in the field,” the organization said in a news release.
END
Komen supports UVA Engineering researchers targeting ‘triple negative' breast cancer
2024-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Panel issues first guidelines to prevent anal cancer in people with HIV
2024-07-19
New recommendations for screening and treatment are based on the results of a major national study led at UCSF.
Results from a national study led by UC San Francisco informed the first guidelines at the federal level in the United States to detect and treat anal cancer precursor lesions in people with HIV to reduce the risk of developing anal cancer.
The guidelines were published on July 9 by a panel of experts in HIV care, utilizing findings from the Anal Cancer/HSIL Outcomes Research (ANCHOR) trial led by Joel ...
Estimating rainfall intensity using surveillance audio and deep-learning
2024-07-19
Surveillance cameras generate both video and audio outputs. Unlike video images recorded, the audio can be supplemented reliably as audio sources resist background interference and lighting variability. Creating a reliable way to use these audio sources to estimate the intensity of rainfall could open a new chapter in rainfall intensity estimation.
In a study published in Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers created an audio dataset of six real-world rainfall events, named the Surveillance Audio Rainfall Intensity Dataset (SARID). ...
Targeting factors for chemoprevention and cancer interception to tackle mesothelioma
2024-07-19
BUFFALO, NY- July 19, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on May 23, 2024, entitled, “Targeting inflammatory factors for chemoprevention and cancer interception to tackle malignant mesothelioma.”
In this perspective, researchers Joseph R. Testa, Yuwaraj Kadariya, and Joseph S. Friedberg from Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, identify potential targets for mesothelioma prevention. Mesothelioma, an incurable cancer of the mesothelial lining, ...
New snake discovery rewrites history, points to North America’s role in snake evolution
2024-07-19
A new species of fossil snake unearthed in Wyoming is rewriting our understanding of snake evolution. The discovery, based on four remarkably well-preserved specimens found curled together in a burrow, reveals a new species named Hibernophis breithaupti. This snake lived in North America 34 million years ago and sheds light on the origin and diversification of boas and pythons.
Hibernophis breithaupti has unique anatomical features, in part because the specimens are articulated—meaning they were found all in one piece with the bones still arranged in the proper order—which is unusual for fossil snakes. Researchers believe it may be ...
Large and unequal life expectancy declines in India during COVID-19
2024-07-19
The international study, co-authored by the Department of Sociology and the Leverhulme Centre for Demographic Science’s Dr Aashish Gupta and Professor Ridhi Kashyap, reveals that life expectancy in India suffered large and unequal declines during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Overall, mortality across India was 17% higher in 2020 compared to 2019, implying 1.19 million excess deaths in India. This extrapolated estimate is about eight times higher than the official number of COVID-19 deaths in India, and 1.5 times higher than the World Health Organization’s estimates.
Ridhi ...
A study of 156,000 UK residents found that urban residents score the lowest in social and economic satisfaction and well-being
2024-07-19
A new study conducted by the Centre for Urban Mental Health at the University of Amsterdam finds that, in a sample of 156,000 UK residents aged 40 and up, urban living is linked to lower levels of well-being, social satisfaction, and economic satisfaction. Urban residents also exhibit greater psychological inequality. The study identifies a ‘Goldilocks zone’ between cities and rural areas, where the highest satisfaction and most equal scores are observed.
The percentage of people living in cities has surged from 10% in the 1910s to a projected 68% by 2050. This shift means ...
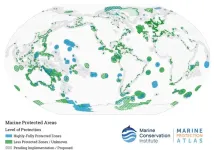
Global study by Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology demonstrates benefit of marine protected areas to recreational fisheries
2024-07-19
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are having a positive spillover effect, producing more “trophy-size” fish just outside of the fully protected areas, and the effect is growing stronger over time. That’s according to research led by University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa scientists at the Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) published today in Science Advances. The research provides the first global assessment of the benefits of MPAs. “Trophy-size” refers to fish that are exceptionally long or heavy and are considered a rare, ...
Researchers clarify how soft materials fail under stress
2024-07-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Understanding how soft materials fail under stress is critical for solving engineering challenges as disparate as pharmaceutical technology and landslide prevention. A new study linking a spectrum of soft material behaviors — previously thought to be unrelated — led researchers to identify a new parameter they call the brittility factor, which allows them to simplify soft material failure behavior. This will ultimately help engineers design better materials that meet future challenges.
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign chemical and biomolecular engineering professor Simon Rogers and graduate student Krutarth Kamani specialize ...
Revolutionizing the abilities of adaptive radar with AI
2024-07-19
DURHAM, N.C. – The world around us is constantly being flash photographed by adaptive radar systems. From salt flats to mountains and everything in between, adaptive radar is used to detect, locate and track moving objects. Just because human eyes can’t see these ultra-high frequency (UHF) ranges doesn’t mean they’re not taking pictures.
Although adaptive radar systems have been around since World War II, they’ve hit a fundamental performance wall in the past couple of decades. But with the help of modern AI approaches and lessons learned from computer vision, researchers at Duke University have broken through that wall, and they want to bring everyone ...
Plastic waste can now be converted to electronic devices
2024-07-19
University of Delaware and Argonne National Laboratory have come up with a chemical reaction that can convert Styrofoam into a high-value conducting polymer known as PEDOT:PSS. In a new paper published in JACS Au, the study demonstrates how upgraded plastic waste can be successfully incorporated into functional electronic devices, including silicon-based hybrid solar cells and organic electrochemical transistors.
The research group of corresponding author Laure Kayser, assistant professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in ...