(Press-News.org) People can reduce their risk of age-related dementia by exercising their brains properly instead of Googling, according to a leading Canadian academic.
Professor Mohamed I. Elmasry says simple daily habits such as afternoon naps, memory ‘workouts’ and not reaching for a smartphone can increase the odds of healthy aging.
His new book, iMind: Artificial and Real Intelligence (with foreword by Canadian cell biologist Dr. Aileen Burford-Mason), says the focus has shifted too far away from RI (natural, or real) intelligence in favor of AI (machine, or artificial) intelligence. Elmasry instead calls us to nurture our human mind which, like smartphones, has ‘hardware’, ‘software’ and ‘apps’ but is many times more powerful – and will last much longer with the right care.
Professor Elmasry, an internationally recognized expert in microchip design and AI, was inspired to write the book after the death of his brother-in-law from Alzheimer’s and others very close to him, including his mother, from other forms of dementia.
Although he says that smart devices are ‘getting smarter all the time’, he argues in iMind that none comes close to ‘duplicating the capacity, storage, longevity, energy efficiency, or self-healing capabilities of the original human brain-mind’.
He writes that: “The useful life expectancy for current smartphones is around 10 years, while a healthy brain-mind inside a healthy human body can live for 100 years or longer.
“Your brain-mind is the highest-value asset you have, or will ever have. Increase its potential and longevity by caring for it early in life, keeping it and your body healthy so it can continue to develop.
“Humans can intentionally develop and test their memories by playing ‘brain games,’ or performing daily brain exercises. You can’t exercise your smartphone’s memory to make it last longer or encourage it to perform at a higher level.”
In iMind: Artificial and Real Intelligence Professor Elmasry shares an anecdote about his grandchildren having to use the search engine on their smartphones to name Cuba’s capital—they had just spent a week in the country with their parents.
The story illustrates how young people have come to rely on AI smartphone apps instead of using their real intelligence (RI), he says, adding: “A healthy memory goes hand-in-hand with real intelligence. Our memory simply can’t reach its full potential without RI.”
Published by Routledge, iMind: Artificial and Real Intelligence includes extensive background on the history of microchip design, machine learning and AI and their role in smartphones and other technology.
The book also explains how both AI and human intelligence really work, and how brain function links the mind and memory. It compares the human mind and brain function with that of smartphones, ChatGPT and other AI-based systems.
Drawing on comprehensive existing research, iMind aims to narrow the knowledge gap between real and artificial intelligence, to address the current controversy around AI, and to inspire researchers to find new treatments for Alzheimer’s, other neurodegenerative conditions and cancer.
It argues that current or even planned AI cannot match the capabilities of the human brain-mind for speed, accuracy, storage capacity and other functions. Healthy aging, Professor Elmasry notes, is as important as climate change but doesn’t attract a fraction of the publicity.
He calls for policymakers to adopt a series of key reforms to promote healthy aging. Among such changes, he suggests that bingo halls could transition from their sedentary entertainment function to become active and stimulating learning centers.
As well as napping to refresh our memories and other brain and body functions, he also outlines a series of practical tips to boost brain power and enhance our RI (Real Intelligence).
These include building up ‘associative’ memory – the brain’s ‘dictionary of meaning’ where it attaches new information to what it already knows. Try reading a book aloud, using all of your senses instead of going on autopilot and turning daily encounters into fully-lived experiences.
Other techniques include integrating a day for true rest into the week, reviewing your lifestyle as early as your 20s or 30s, adopting a healthy diet, and eliminating or radically moderating alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of dementia.
END
Quit Googling and take naps to cut dementia risk, says AI expert
Taking regular daytime naps can increase the odds of healthy aging, says a new book
2024-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Duke-NUS launches LIVE Ventures, a S$20 million incubator to accelerate research commercialisation
2024-07-22
New incubator aims to tap industry experts to bridge the knowledge and funding gap to enhance bench-to-bedside success
LIVE Ventures provides up to $500,000 for high-potential academic research projects
Duke-NUS Medical School today launched LIVE Ventures, a S$20 million incubation programme designed to catalyse the commercialisation of innovative academic research. Focused on translating scientific breakthroughs into clinical applications, LIVE Ventures will provide Duke-NUS scientists conducting ...
Samuel Pepys’ fashion prints reveal his guilty pleasure: Fancy French clothes
2024-07-22
University of Cambridge media release
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01AM (UK TIME) ON MONDAY 22ND JULY 2024
A collection of French fashion engravings offers precious new insights into the life of Samuel Pepys years after his premature final diary entry. The prints show the tailor’s son remained fascinated by the power of fashion long after he had secured wealth and status. But they also expose Pepys’ internal conflict over French style.
Most of what we know about Samuel ...
New genetic test will eliminate a form of inherited blindness in dogs
2024-07-22
Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is a group of inherited diseases that causes progressive degeneration of the light sensitive cells at the back of the eye. Dogs with PRA have normal sight at birth, but by the age of four or five they will be totally blind. There is no treatment.
Now a team led by the University of Cambridge has identified the genetic mutation that causes PRA in English Shepherd Dogs, and developed a DNA test for it. By identifying dogs carrying the disease before their eyesight starts to fail, this provides a tool to guide breeding decisions so the disease is not passed on to puppies.
Owners usually don’t realise their dog has PRA until it is ...
Cancer risk: Most Australian welders exposed to high levels of dangerous fumes
2024-07-21
New Curtin University research has revealed at least 46,000 Australian welders are exposed to high levels of dangerous, potentially cancer-causing fumes at work — and little is being done to protect them.
A joint Curtin School of Population Health and University of Sydney project funded through the Centre for Work Health and Safety, the Australian-first study was published today in the Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.
The research team surveyed 634 workers and employers involved in welding from across Australia ...
Two-in-one mapping of temperature and flow around microscale convective flows
2024-07-20
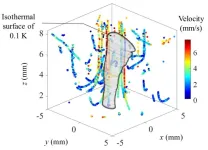
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have devised a way to measure both the temperature and velocity profiles of fluid in a convective plume at millimeter length scales in 3D. They combined near-infrared absorption imaging and image processing to separate the motion of tracer particles from snapshots of how light is absorbed, producing both a smooth velocity and temperature map. The technology promises new insights into optimizing the design of micro-heating and cooling devices.
Accurate maps of how heat and matter flow at the microscale are vital to the design of micro-heating and cooling devices. A classic example ...
Texas A&M engineers explore intelligence augmentation to improve safety
2024-07-20
Artificial intelligence (AI) has grown rapidly in the last few years, and with that increase, industries have been able to automate and improve their efficiency in operations.
A feature article published in AIChE Journal identifies the challenges and benefits of using Intelligence Augmentation (IA) in process safety systems.
Contributors to this work are Dr. Faisal Khan, professor and chemical engineering department head at Texas A&M University, Dr. Stratos Pistikopoulos, professor and director of the Energy Institute, Drs. Rajeevan Arunthavanathan, Tanjin Amin, and Zaman Sajid from the Mary Kay O’Connor Safety Center.
Additionally, Dr. Yuhe ...
ORNL economist honored at international hydropower conference
2024-07-19
Researcher Rocio Uria-Martinez was named one of four “Women with Hydro Vision” at this year’s HYDROVISION International 2024 conference taking place in Denver this week. Awarded by a committee of industry peers, the honor recognizes women who use their unique talents and vision to improve and advance the worldwide hydropower industry.
Uria is an energy and environmental economist and senior R&D staff member at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge ...
UCLA selected by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to test Medicare dementia care model
2024-07-19
UCLA has been selected by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to participate in a new Medicare alternative payment model designed to support people living with dementia and their caregivers.
UCLA is one of almost 400 participants building Dementia Care Programs (DCPs) across the country working under CMS’ Guiding an Improved Dementia Experience (GUIDE) Model to increase care coordination and improve access to services and supports, including respite care, for people living ...
Fish adjust reproduction in response to predators
2024-07-19
Some species of fish can evolve their egg-laying habits in response to predators in the area in order to survive, according to new research from The University of Texas at Arlington.
It has long been observed that organisms modify their traits, including reproductive patterns, in response to changes in their environment. This type of evolutionary plasticity has been observed in many types of animals in different habitats and with varying predators.
“We knew that fish who laid their eggs externally often adapted depending on the predators in the area, but we did not know how quickly species could change to these externals pressures,” said biology Professor Matthew Walsh, ...
DDX41 and its unique contribution to myeloid leukemogenesis
2024-07-19
“[...] myeloid neoplasms associated with DDX41 variants likely exhibit a unique pathogenesis that diverges from the conventional understanding of myeloid neoplasms.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 19, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 2, 2024, entitled, “DDX41 and its unique contribution to myeloid leukemogenesis.”
In this new editorial, researcher Hirotaka Matsui from the National Cancer Center Hospital in Tokyo, Japan, and Kumamoto University discusses myeloid neoplasms. Until ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] Quit Googling and take naps to cut dementia risk, says AI expertTaking regular daytime naps can increase the odds of healthy aging, says a new book