Sexual and gender minorities are twice as likely to report active epilepsy
NIH-funded study highlights importance of health disparities research
2024-07-22
(Press-News.org) What:
Sexual and gender minorities (SGM)—individuals who identify as gay, lesbian, bisexual, queer, transgender, non-binary, or gender-diverse—are twice as likely to report active epilepsy compared to non-SGM individuals, based on a National Institutes of Health (NIH) analysis of data from the population-based National Health Information Survey. “Active epilepsy” means a person has been diagnosed with epilepsy and has had more than one seizure in the past year or is currently taking anti-seizure medication.
This study suggests that epilepsy could be added to the growing number of neurological health disparities experienced by SGM individuals and other minoritized communities. The potential causes of this increase in prevalence are unknown.
The authors note limitations of the study. The survey relies on self-reporting of SGM and epilepsy status, about which some may have been reluctant to report, even when responding anonymously. The survey data analyzed in this study are from 2022, the first year in which questions about current gender identity, sexual orientation, and sex assigned at birth were included.
These findings, along with the study limitations, highlight the importance of collecting information on SGM status and the need for further research into the health disparities seen within that population. The Office of Global Health and Health Disparities at NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) supports rigorous research aimed at better understanding and reducing these types of disparities to reduce the burden of neurological disease for all people.
This study was supported by the NINDS Intramural Research Program and the NIH’s National Institute on Aging (AG063899).
Who:
Richard Benson, M.D. Ph.D., director, Office of Global Health and Health Disparities, NINDS
Article:
Johnson, EL et al., “Prevalence of epilepsy in sexual and gender minorities.” JAMA Neurology. July 22, 2024
###
NINDS (http://www.ninds.nih.gov) is the nation’s leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-22
During the peak of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, there was an increase in maternal mortality in Chile. This is confirmed by a natural population experiment based on data from the Department of Health Statistics and Information (DEIS) of the Chilean Ministry of Health. The research was published in PLOS Global Public Health.
In a collaborative study, led by Professor Elard Koch, senior epidemiologist and founder of MELISA Institute (Chile), and conducted with a team of researchers from the Universidad Católica Sedes Sapientiae (Peru), the Pontificia Universidad ...
2024-07-22
A University of Virginia School of Medicine scientist and other top experts from around the world have developed the first comprehensive guidelines for reporting cutting-edge “precision medicine” research in a bid to improve patient care and health equity for people everywhere.
Precision medicine aims to tailor treatments to individual patients to get the best possible outcomes. It does this by considering many different factors specific to the patient, such as the patient’s genetics, environment, lifestyle and more. But until now there have been no standardized guidelines for reporting precision ...
2024-07-22
Research Highlights:
Two new, basic research studies in rodents (mice and rats) analyzed the impacts that alcohol may have on the heart.
In a mouse study, abnormal heart rhythms that can occur after a pattern of repeated simulation of binge drinking may be related to a spike in a stress protein found in the heart. Researchers tested a heart protective molecule to reduce the stress protein spike and the resulting irregular heart rhythms.
In a study using rats that lacked estrogen production to simulate human menopause, alcohol exposure resulted ...
2024-07-22
A technology has been developed to decompose refrigerants, a greenhouse gas 1,300 times more potent than carbon dioxide, using challenging-to-handle industrial waste.
Dr. Ryi, Shin-kun’s research team at the Hydrogen Convergence Materials Lab of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has successfully developed a catalyst from industrial waste known as 'red mud,' a byproduct of aluminum production. This catalyst can decompose HFC-134a refrigerant, commonly used in household appliances like air conditioners and refrigerators, with an efficiency of 99%.
* Red Mud: An industrial byproduct remaining after extracting aluminum ...
2024-07-22
Tim Rademacher is taking on a sweet new role at the University of Vermont—as the new Scientific Director of UVM’s Proctor Maple Research Center (PMRC). The PMRC is a field research station of the Department of Plant Biology at the University of Vermont, and is the oldest and most renowned maple science research centers in the world. Since 1947 it has produced cutting edge research on maple, supported maple sugar producers, and bolstered maple syrup production in Vermont—and globally.
“I'm very excited to join PMRC with its rich history and its excellent work that has really pushed the industry in the past, says Rademacher, who will start this fall. “I ...
2024-07-22
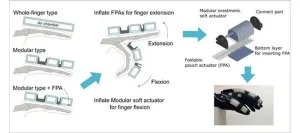
Soft rehabilitation gloves have become popular tools for helping patients with hand function-related disabilities recover finger movement. These gloves often use soft pneumatic actuators that employ air pressure to generate movements. Despite significant design improvements in recent years, many available soft actuators have drawbacks in achieving bidirectional motion typical of finger joints—such soft actuators facilitate finger bending (or flexion) but not finger straightening (or extension).
A group of biomedical researchers from Chiba University successfully ...
2024-07-22
The bull elephants gather in the evening coolness to drink. After a spell, a senior male lifts his head and turns from the waterhole. With ears flapping gently, he lets out a deep, resonant rumble.
One by one, the others respond, their voices overlapping in a sonorous, infrasonic chorus that whispers across the savanna. This elephant barbershop quartet conveys a clear message: It’s time to move on.
Gradually, the elephants shift, their massive bodies swaying as they follow their rumbling leader to the next stop on their nocturnal wanderings.
For the first time, scientists from Stanford University and other institutions have documented male elephants using “let’s ...
2024-07-22
Submarine canyons are crucial for the instability of the Antarctic ice sheet
Antarctic canyons play a crucial role in the instability of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, as they facilitate the transfer of relatively warm water (Circumpolar Deep Water) from the abyssal areas to the continental shelf and from there to the base of the ice sheet, thus contributing to its melting.
The new study, conducted by an international team of researchers led by the National Institute of Oceanography and Applied Geophysics (OGS) and including the University of Southampton, ...
2024-07-22
Research Highlights:
Adults in their 50s with peripheral artery disease or PAD — are more likely than adults older than 80 to undergo leg amputation one to five years after an emergency surgery to restore blood flow to the lower limbs.
This study analyzes outcomes among patients older than age 50 hospitalized with PAD, as noted in eight years of data collected in England.
Researchers say early diagnosis, risk factor modification and treatment are warranted to help prevent patients from developing severe forms of PAD.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, July 22, 2024
DALLAS, ...
2024-07-22
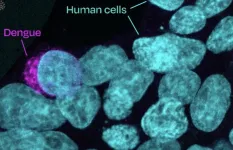
KANSAS CITY, MO—July 22, 2024—Mosquito-borne viral infections once confined to tropical regions are spreading. Dengue virus infects up to 400 million people worldwide each year according to World Health Organization estimates, and no available treatments exist for this disease. Now, research from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research has uncovered surprising strategies for how dengue and hundreds of other viruses replicate in their hosts, with the potential to aid in developing novel antiviral treatments and vaccines.
Led by Stowers Predoctoral Researcher Luciana ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sexual and gender minorities are twice as likely to report active epilepsy
NIH-funded study highlights importance of health disparities research