(Press-News.org) Despite rapid advances in genetic testing in recent decades, more than half of people worldwide with suspected Mendelian genetic disorders do not have an accurate molecular diagnosis. Others endure more than six years of tests before a diagnosis is given. Now, KAUST researchers and scientists across Saudi Arabia have developed NanoRanger, an accurate and rapid method for genetically diagnosing such diseases in a few hours[1].
“Precise, efficient genomic diagnosis is urgently needed to improve patient outcomes and facilitate carrier screening,” says Yingzi Zhang, a Ph.D. candidate at KAUST, supervised by Mo Li. “This study aligns with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 — advancing healthcare through innovation to improve quality of life for all citizens.”
Mendelian disorders — including nervous system and intellectual developmental conditions — are caused by either an alteration in one particular gene or an abnormal rearrangement in one segment of the genome. Each disease has a specific “breakpoint”— the genomic location of a structural variant where DNA is deleted, rearranged or inverted.
While these variants may be identified using traditional screening techniques, the sheer complexity of the rearrangements means they are often missed. Mendelian diseases are inheritable, particularly if both parents are carriers of the same faulty segment. Such diseases are more prevalent in regions where it is common for marriage between related individuals (consanguinity).
“NanoRanger uses simple molecular biology strategies to ‘fish out’ genomic regions that are suspected of harboring complex mutations, deletions or rearrangements,” says Li.
The technique is cost-effective and requires only a tiny amount of DNA from a patient or suspected carrier. NanoRanger takes a sample of genomic DNA and uses molecular scissors called restriction enzymes to fragment the DNA into pieces with the same end sequences. These pieces are then self-joined into circles and amplified, which makes it easier to target and sequence the genomic regions of interest using Oxford Nanopore Tecnologies’ long-read sequencing technology.
“Using our custom-developed data analysis tool, NanoRanger accurately maps breakpoints at single base-pair resolution, providing a detailed picture that helps diagnose the genetic disorder,” says Zhang. “Diagnosis can be as fast as 12 minutes after initial sequencing, which is a game-changer.”
In trials done in collaboration with a group of Saudi clinicians led by Fowzan Alkuraya at King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Center, NanoRanger successfully identified precise breakpoints in 13 familial cases of genomic disorders that were missed by conventional genetic tests. Using these breakpoints, the researchers then screened the carrier status of related family members and 1,000 healthy Saudi individuals.
The testing method prompted one Saudi couple in the trial to opt for in vitro fertilization after they were both found to carry the genomic deletion for an inherited Mendelian disease.
“We have filed for a patent, and plan to integrate NanoRanger into standard diagnostic routines to provide a comprehensive toolkit for clinical settings, both here in Saudi Arabia and across the world,” concludes Li.
END
Pioneering technique transforms genetic disorder diagnoses
2024-07-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Electric scooter and bike accidents are soaring across the US
2024-07-23
Electric Scooter and Bike Accidents Are Soaring Across the U.S.
National UCSF study finds some injuries and hospitalizations from popular micromobility vehicles have doubled.
In the crowded urban landscape, where small electric vehicles – primarily scooters and bicycles – have transformed short distance travel, UC San Francisco researchers are reporting a major national surge in accidents tied to “micromobility.”
E-bicycle injuries doubled every year from 2017 to 2022, while e-scooter injuries rose by 45 percent. Injured e-riders tended to be slightly older and wore helmets less often than conventional ...
Involvement of TAL1-microRNA axis in the progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
2024-07-23
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive form of leukemia that arises from the malignant transformation of T-cell progenitors. This disease is most commonly diagnosed in children, where it accounts for a significant portion of pediatric leukemia cases, but it also affects adults. The clinical presentation of T-ALL includes symptoms resulting from bone marrow failure, such as anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia, as well as symptoms due to extramedullary disease, including lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, ...
JMIR XR and Spatial Computing is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled “First Look: Early Research, Viewpoints, and Experiences with Apple Vision Pro in Health Care Settings”
2024-07-23
(Toronto, July 23, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “First Look: Early Research, Viewpoints, and Experiences with Apple Vision Pro in Health Care Settings” in its new open access journal JMIR XR and Spatial Computing.
This theme issue aims to gather early research findings, diverse and critical viewpoints, and real-world experiences concerning the utilization of Apple Vision Pro in health care contexts. We invite contributions that explore the following topics:
Medical education ...
Decoding early Lyme disease
2024-07-23
Every year in the United States, an estimated 476,000 people are diagnosed and treated for Lyme disease. The estimate comes from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Lyme disease can be treated with antibiotics. The best health outcomes are most likely when diagnosis is made within the first weeks of infection. If left untreated, the effects of Lyme disease can linger for years and cause neurological problems, arthritis, and a host of other ailments. But because diagnosing ...
Non-coding RNAs affect breast cancer development through the notch signaling pathway
2024-07-23
Breast cancer (BC) remains one of the most challenging cancers to treat, primarily due to its heterogeneity and propensity for metastasis. The Notch signaling pathway is integral to various cellular processes and has been implicated in the development and progression of BC. NcRNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), have emerged as pivotal regulators of gene expression, affecting cancer biology through their interactions with the Notch pathway.
Non-coding ...
Is a gamma-ray laser possible?
2024-07-23
Since the laser was invented in the 1960s, scientists have been working to increase lasers’ peak power and to design machines producing coherent light at progressively shorter wavelengths that can improve image resolution and enable probing of quantum nuclear states.
Progress has been made with regard to peak power, most notably with the invention of chirped pulse amplification by University of Rochester researchers in the 1980s, a breakthrough that garnered the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2018. However, developing ...
Dual action antibiotic could make bacterial resistance nearly impossible
2024-07-23
A new antibiotic that works by disrupting two different cellular targets would make it 100 million times more difficult for bacteria to evolve resistance, according to new research from the University of Illinois Chicago.
For a new paper in Nature Chemical Biology, researchers probed how a class of synthetic drugs called macrolones disrupt bacterial cell function to fight infectious diseases. Their experiments demonstrate that macrolones can work two different ways – either by interfering with protein production or corrupting DNA structure.
Because bacteria would need to implement ...
Salk Professor Janelle Ayres named Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator
2024-07-23
LA JOLLA (July 23, 2024)—Salk Professor Janelle Ayres has been selected as a 2024 Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Investigator. The HHMI Investigators program awards established scientists with approximately $9 million in funding over seven years to pursue boundary-breaking research in their field. The honor recognizes her influential work in immunology and microbiology and its applications to the global crisis of antibiotic resistance.
Ayres is among 26 other 2024 selectees, who will join more than 250 standing Investigators—including Salk Professors ...
NLM extends commitment to LOINC with $5 million award
2024-07-23
INDIANAPOLIS -- The National Library of Medicine has awarded Regenstrief Institute a five-year, $5 million contract extension to ensure the continued maintenance, expansion and public distribution of LOINC®, a global standard for health terminology. The NLM issued its initial contract to support the creation and development of LOINC in 1999. With this extension, NLM's commitment to LOINC will reach 30 years by the time the award expires in 2029.
“The NLM’s continued support of LOINC demonstrates the value the standard delivers to patients, care providers, health ...
Light emission from nanostructures, revealed using 3D printing method for the first time
2024-07-23
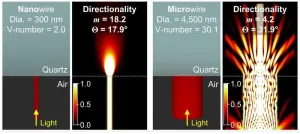
Dr. Jaeyeon Pyo’s team at the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) has become the first in the world to reveal light emission patterns from 3D-printed nanowires, which has been published as a cover article in the prestigious scientific journal ACS Nano.
The higher resolution in display devices signifies the more of pixels in a given screen size. As pixel density increases, movies and images are displayed with greater precision and detail. In this regard, ongoing research aims to fabricate ...