(Press-News.org) Stockholm3, a prostate cancer test developed in Sweden, runs a combination of protein and genetic markers from a blood sample through an algorithm to find the probability of a patient having clinically significant cancer.
Studies in more than 90,000 men have shown that Stockholm3 produces significantly better results than the current PSA standard. The test improves prostate cancer diagnosis by reducing unnecessary MRI and biopsies and by identifying significant cancers in men with low or normal PSA values.
However, previous studies have been conducted primarily in Scandinavia on a mainly White population with uncertain generalisability to the rest of the world. A Swedish-American research group has now examined how well it works in an ethnically mixed group of men in the USA and Canada.
The study included over 2,000 men at 17 different clinics, 16 per cent of whom were Asian, 24 per cent African-American, 14 per cent Latin American and 46 per cent White American. All participants had a referral for a prostate biopsy on the basis of an elevated PSA score, abnormal rectal examination, MRI scan or other suspicious clinical finding.
Before the biopsy was performed, a blood test was taken along with clinical data pertinent to the Stockholm3 test, which was conducted blinded to the biopsy results.
The analysis shows that clinically relevant prostate cancer cases were found in a total of 29 per cent of the men, somewhat more in African Americans and slightly fewer in Asians. It also shows that the Stockholm3 test could almost halve the number of unnecessary biopsies (45 per cent fewer: 673 as opposed to 1,226) while being no less effective at detecting all clinically relevant cases. The results were similar across the different ethnic groups.
“The study demonstrates that the Stockholm3 test is just as effective on an ethnically mixed group as it is on a White, Swedish population,” says the study’s lead author Hari T. Vigneswaran, doctor and PhD student at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet.
According to him, the research answers several important questions and will lead to a more widespread use of the method:
“Colleagues in other countries are very interested in these data, which show that Stockholm3 works for a non-Swedish population and among minorities.”
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Society and A3P Biomedical, the company that holds the rights to the development of the Stockholm3 test. Hari T. Vigneswaran and Thorgerdur Palsdottir are employed at A3P Biomedical. Co-authors Henrik Grönberg, Martin Eklund and Tobias Nordström hold shares in A3P Biomedical AB. Henrik Grönberg and Martin Eklund are inventors of patents for the method. Other co-authors report research grants and fees from a number of pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the Stockholm3 method.
END
Prostate cancer blood test equally effective across ethnic groups
2024-07-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lehigh University team wins 2024 Alfred Noble Prize for work on optimizing bridge maintenance
2024-07-23
Lehigh University structural engineering alum Xu Han ’23 PhD and his doctoral advisor Professor Dan M. Frangopol have been awarded the 2024 Alfred Noble Prize, an esteemed interdisciplinary award from a consortium of professional societies, administered by the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE).
“I feel very humbled for receiving such a prestigious award and am very grateful to people nominating me,” says Han, who is now a postdoctoral research fellow at Texas A&M University.
Frangopol, Lehigh’s inaugural Fazlur R. Khan Endowed Chair of Structural Engineering and Architecture, is a world-renowned expert ...
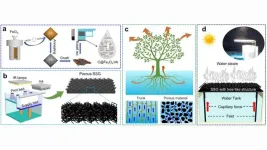
3D-printed microstructure forest facilitates solar steam generator desalination
2024-07-23
WASHINGTON, July 23, 2024 — Faced with the world’s impending freshwater scarcity, a team of researchers in Singapore turned to solar steam generators (SSGs), which are emerging as a promising device for seawater desalination. Desalination can be a costly, energy-intensive solution to water scarcity. This renewable-powered approach mimics the natural water cycle by using the sun’s energy to evaporate and isolate water. However, the technology is limited by the need to fabricate complex topologies to increase the surface area necessary to achieve high water evaporation efficiency.
To overcome this ...
Wearable sensors help athletes achieve greater performance
2024-07-23
WASHINGTON, July 23, 2024 – Today’s athletes are always on the lookout for new techniques and equipment to help them train more effectively. Modern coaches and sports trainers use intelligent data monitoring through videos and wearable sensors to help enhance athletic conditioning. However, traditional video analysis and wearable sensor technologies often fall short when tasked to produce a comprehensive picture of an athlete’s performance.
In APL Materials, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Lyuliang University developed ...
Gender differences in electronic health record usage among surgeons
2024-07-23
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of electronic health record (EHR) data found that female surgeons spent more time documenting patient encounters, wrote longer notes, and spent more time in the EHR system compared with male surgeons. These findings have important implications for understanding the differential burdens faced by female surgeons, including potential contributions to burnout and payment disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Corinna Zygourakis, ...
Injuries with electric vs conventional scooters and bicycles
2024-07-23
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of micromobility vehicles, an increased number of injuries and hospitalizations was observed with electric vehicles compared with conventional vehicles from 2017 to 2022. These findings suggest the need for change in educational policies, infrastructure, and law to recenter on safety with the use of micromobility vehicles.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Benjamin N. Breyer, M.D., M.A.S., email benjamin.breyer@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.24131)
Editor’s ...
Pioneering technique transforms genetic disorder diagnoses
2024-07-23
Despite rapid advances in genetic testing in recent decades, more than half of people worldwide with suspected Mendelian genetic disorders do not have an accurate molecular diagnosis. Others endure more than six years of tests before a diagnosis is given. Now, KAUST researchers and scientists across Saudi Arabia have developed NanoRanger, an accurate and rapid method for genetically diagnosing such diseases in a few hours[1].
“Precise, efficient genomic diagnosis is urgently needed to improve patient outcomes and facilitate carrier ...
Electric scooter and bike accidents are soaring across the US
2024-07-23
Electric Scooter and Bike Accidents Are Soaring Across the U.S.
National UCSF study finds some injuries and hospitalizations from popular micromobility vehicles have doubled.
In the crowded urban landscape, where small electric vehicles – primarily scooters and bicycles – have transformed short distance travel, UC San Francisco researchers are reporting a major national surge in accidents tied to “micromobility.”
E-bicycle injuries doubled every year from 2017 to 2022, while e-scooter injuries rose by 45 percent. Injured e-riders tended to be slightly older and wore helmets less often than conventional ...
Involvement of TAL1-microRNA axis in the progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
2024-07-23
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive form of leukemia that arises from the malignant transformation of T-cell progenitors. This disease is most commonly diagnosed in children, where it accounts for a significant portion of pediatric leukemia cases, but it also affects adults. The clinical presentation of T-ALL includes symptoms resulting from bone marrow failure, such as anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia, as well as symptoms due to extramedullary disease, including lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, ...
JMIR XR and Spatial Computing is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled “First Look: Early Research, Viewpoints, and Experiences with Apple Vision Pro in Health Care Settings”
2024-07-23
(Toronto, July 23, 2024) JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “First Look: Early Research, Viewpoints, and Experiences with Apple Vision Pro in Health Care Settings” in its new open access journal JMIR XR and Spatial Computing.
This theme issue aims to gather early research findings, diverse and critical viewpoints, and real-world experiences concerning the utilization of Apple Vision Pro in health care contexts. We invite contributions that explore the following topics:
Medical education ...
Decoding early Lyme disease
2024-07-23
Every year in the United States, an estimated 476,000 people are diagnosed and treated for Lyme disease. The estimate comes from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Lyme disease can be treated with antibiotics. The best health outcomes are most likely when diagnosis is made within the first weeks of infection. If left untreated, the effects of Lyme disease can linger for years and cause neurological problems, arthritis, and a host of other ailments. But because diagnosing ...