(Press-News.org) The findings, published today in Nature Ecology & Evolution, sheds light on some core principles of the evolution of modern biodiversity.
In current oceans, molluscs such as clams, oysters, and snails are hugely diverse, with over 50,000 species, whereas brachiopods are rare by comparison with only 394 species known. But this was not always the case. The team have found that brachiopods were evolving new shell shapes and ecological behaviours following the end-Permian mass extinction which compromised their numbers.
“In the Palaeozoic, from 540 to 250 million years ago, brachiopods ruled the seabed,” said Dr Zhen Guo of the China University of Geosciences, who led the study. “Brachiopods are sometimes called lamp shells, and they generally sit on the sea floor, filtering tiny food particles from seawater. Most of them are quite small–you could hold twenty of them in your hands; but others were big and thick-shelled and lived a long time. Their shells were anything from circular to widely stretched and they had either smooth shells or carried deep ridges and troughs.”
“The brachiopods were hit very hard by the end-Permian mass extinction 252 million years ago,” said Professor Michael Benton of the University of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences, a collaborator. “The group could have disappeared completely, and indeed from that point, molluscs just became more and more successful. For a long time, it was thought that the brachiopods remained rare because the survivors were stuck in just a few modes of life.”
Dr Tom Stubbs of the Open University added: “In fact, the post-extinction brachiopods were innovating and trying new modes of life. One group, the terebratulids, were diversifying their body shapes and ecological functions from the end of the Permian to the present day, but their diversity did not increase.”
“This was quite unexpected,” said Professor Zhong-Qiang Chen of the China University of Geosciences. “Brachiopods were far from failures after the end-Permian extinction. They were evolving in new directions and exploring new modes of life, just as the molluscs were at the same time. But this did not turn into evolutionary success in terms of the numbers of species. Despite their bursts of evolution in form and function, they could not spread widely, and the exact reason remains unclear.”
The new study is based on analysis of a database of more than 1000 genera of brachiopods from the past 250 million years. For each genus, the analysts recorded dozens of measurements of the overall shape of the shells, their external sculpture, and internal anatomy. These features were analysed together to provide measurements of overall diversity of shapes for each major brachiopod group at each point in time. This measure of ‘diversity of shape’, usually called disparity, could then be compared from point to point in time to show a measure of shape innovation, and it can be compared with counts of the numbers of species or genera through the same time spans.
“Our study took a huge amount of effort,” concluded Zhen Guo. “But it’s important to understand modern biodiversity in terms of the processes that lie behind it.
“If we simply look at modern brachiopods, we have no understanding of their rich past history and how innovative they have been in evolutionary terms. But our discovery that disparity and diversity are decoupled in brachiopod history is new and unexpected. Brachiopods were pretty inventive in evolving new shell forms, but it did not translate into many new species.”
The paper:
‘Morphological innovation did not drive diversification in Mesozoic–Cenozoic brachiopods’ by Zhen Guo, Michael J. Benton, Thomas L. Stubbs, and Zhong-Qiang Chen. Nature Ecology & Evolution doi: 10.1038/s41559-024-02491-9. Read the paper here.
END
Ancient marine animal had inventive past despite being represented by few species, new study finds
2024-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Quantum sensor for the atomic world developed through international scientific collaboration
2024-07-25
In a scientific breakthrough, an international research team from Germany's Forschungszentrum Jülich and Korea's IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience (QNS) developed a quantum sensor capable of detecting minute magnetic fields at the atomic length scale. This pioneering work realizes a long-held dream of scientists: an MRI-like tool for quantum materials.
The research team utilized the expertise of bottom up single-molecule fabrication from the Jülich group while conducting experiments at QNS, utilizing the Korean team’s leading-edge ...
The research was wrong: study shows moderate drinking won’t lengthen your life
2024-07-25
PISCATAWAY, NJ – Probably everyone has heard the conventional wisdom that a glass of wine a day is good for you--or you’ve heard some variation of it. The problem is that it’s based on flawed scientific research, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Over the years, many studies have suggested that moderate drinkers enjoy longer lives with lower risks of heart disease and other chronic ills than abstainers do. That spurred the widespread belief that alcohol, in moderation, can be a health tonic. However, not all studies have painted such a rosy picture--and the ...
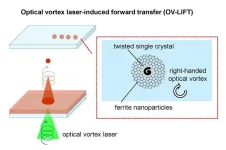
Save your data on printable magnetic devices? New laser technique’s twist might make this reality
2024-07-25
The proliferation of all things digital doesn’t mean that printing technology is no longer relevant. In fact, printing technology is required to make the semiconductors necessary for the digital world. And as an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has shown using a new printing technique, printable magnetic devices for high-density data storage might soon be realized.
Dr. Ken-ichi Yuyama, a lecturer at the Graduate School of Science, and his colleagues report in APL Materials on the development of a new type of laser-induced forward transfer ...
Early onset dementia more common than previously reported – the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease seems to be on the rise
2024-07-25
A new major study by the University of Eastern Finland, the University of Oulu and Neurocenter Finland explored early-onset dementia in the working-age population in Finland. The study cohort was one of the largest in the world to date, and the findings were published on 24th of July 2024 in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
Current epidemiological data on early-onset dementia is scarce and based on small study cohorts, with no recent data from Finland available. For the present ...
Pesticides potentially as bad as smoking for increased risk in certain cancers
2024-07-25
In modern day agriculture, pesticides are essential to ensure high enough crop yields and food security. These chemicals, however, can adversely affect plant and animal life as well as the people exposed to them.
Now, in a population-based, nation-wide study, researchers in the US have put increased cancer risk through agricultural pesticide use into context with smoking, a better understood cancer risk factor. The results were published in Frontiers in Cancer Control and Society.
“In our study we found that for some cancers, the effect of agricultural pesticide usage is comparable in magnitude to the effect of smoking,” said the study’s ...
NUS researchers develop new battery-free technology to power electronic devices using ambient radiofrequency signals
2024-07-25
Ubiquitous wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G rely on radio frequency (RF) signals to send and receive data. A new prototype of an energy harvesting module – developed by a team led by scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) – can now convert ambient or ‘waste’ RF signals into direct current (DC) voltage. This can be used to power small electronic devices without the use of batteries.
RF energy harvesting technologies, such as this, is essential as they reduce battery dependency, extend device lifetimes, minimise environmental impact, and enhance the feasibility of wireless sensor networks and IoT devices in remote ...
New protein discovery may influence future cancer treatment
2024-07-25
Researchers from the University of Otago, Christchurch, have spearheaded the discovery of a protein function which has the potential to guide the development of novel cancer treatment options and improve the diagnosis of various cancers.
The exciting research finding, carried out alongside Dr Vanessa Morris from the University of Canterbury’s School of Biological Sciences as well as researchers in Australia and Denmark, centres on the activity of a tumour- suppressing protein called p16.
The discovery, published in the British scientific journal Nature Communications and first authored by ...
Timing matters: Scripps Research study shows ways to improve health alerts
2024-07-25
LA JOLLA, CA—When seemingly healthy people receive an alert from a wearable sensor telling them they might have a respiratory virus—based on small changes in their unique heartrate, sleep and activity patterns—what do they do? According to a new study by Scripps Research scientists carried out at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, only a quarter of people follow up such an alert with an at-home viral test.
That is just one conclusion of the new study, published in The Lancet Digital Health on July 24, 2024, which tested the feasibility ...
New gene therapy approach shows promise for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
2024-07-25
INDIANAPOLIS - Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have made a significant breakthrough in developing a new gene therapy approach that restores full-length dystrophin protein, which could lead to new treatments for people with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
The study, recently published in Nature Communications, demonstrates the effectiveness of their novel gene therapy technology in improving muscle tissue and overall strength in mice models with Duchenne ...
Chemical analyses find hidden elements from renaissance astronomer Tycho Brahe’s alchemy laboratory
2024-07-25
In the Middle Ages, alchemists were notoriously secretive and didn’t share their knowledge with others. Danish Tycho Brahe was no exception. Consequently, we don’t know precisely what he did in the alchemical laboratory located beneath his combined residence and observatory, Uraniborg, on the now Swedish island of Ven.
Only a few of his alchemical recipes have survived, and today, there are very few remnants of his laboratory. Uraniborg was demolished after his death in 1601, and the building materials were scattered for reuse.
However, during an excavation ...