(Press-News.org) Distrust of health experts and credulity towards misinformation can kill. For example, during the Covid-19 crisis, high-profile health experts received death threats while misinformation went viral on social media. And already long before the pandemic, easily preventable but potentially serious diseases had been making a comeback around the world due to vaccine hesitancy – often powered by conspiracy theories.
But what feeds this lack in trust in reliable sources of health information? Can it perhaps be mitigated? Those are the subjects of a new study in Frontiers in Medicine by researchers from the US.
“Here we show that individuals who perceive conflict among experts about health recommendations, and who perceive that recommendations are constantly changing, have significantly lower trust in health information provided by government health agencies,” said Dr Arch Mainous, a professor at the University of Florida at Gainesville, and the paper’s senior author.
Nationally representative sample
Mainous and colleagues analyzed replies from 5,842 women and men over the age of 18 to the Health Information National Trends Survey, which gathers information on how the American public uses different communication channels to obtain cancer-related health information. Due to stratification, clustering, and weighting of subgroups within the wider population, this sample is believed to represent approximately 242 million people, or 93% of the adult US population.
The survey gauged trust in different kinds of medical experts with the question: “How much would you trust information about cancer from a doctor, government health agency, or scientist?” Answers for this and follow-up questions were on a four-point Likert scale.
It measured perceived uncertainty with two questions, "How often do health recommendations from experts seem to change over time?”, and, “how often do health recommendations from experts seem to conflict or contradict one another?”
A final question, “How much of the health information that you see on social media do you think is false or misleading?” focused on the respondents’ trust in social media as a source.
High trust in doctors
The results revealed that doctors were the most trusted source of information: 95% of respondents reported high trust in them. High trust was less frequently felt towards scientists (84%) and government health agencies (70%), and least towards social media (18%).
The minority who found social media trustworthy seemed to be a somewhat special group: for example, they expressed slightly but significantly less trust in doctors (92%) than their peers in terms of age, sex, race, total annual income, and education.
Importantly, people who perceived that recommendations often changed or conflicted indicated significantly less trust in scientists and health agencies compared to their peers. In contrast, their trust in doctors wasn’t impacted by their perception of uncertainty. These results imply that the process of scientific discovery, with its inevitable disagreements and changes in consensus among experts, seems to be confusing to the general public.
“Because our scientific and medical knowledge is always changing, this leads the public to question the expertise of government health agencies and brings up perceptions of political considerations in the crafting of the recommendations,” concluded Mainous.
Restoring trust
Fortunately, given that doctors continue to be well trusted, the results immediately suggested a way forward: to leverage the power and trust inherent in the patient-physician relationship, to ensure better health and restore trust in governmental health agencies.
“Government agencies need to continue to provide patient education, which is an integral part of public health. However, they need to focus more on letting individual physicians, rather than the agency director, for example, be the ones to disseminate agency recommendations to patients,” advised Mainous.
END
Conflicting health advice from agencies drives confusion, study finds, but doctors remain most trusted
Uncertainty inherent in scientific process confuses public and reduces trust in health agencies, finds study
2024-07-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
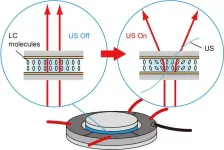
Towards next-gen indoor lighting: novel tunable ultrasonic liquid crystal light diffuser
2024-07-26
It is no mystery that light is essential to human life. Since the discovery of fire, humans have developed various artificial light sources, such as incandescent lamps, gaslights, discharge lamps, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The distribution and intensity of artificial lights indoors are important factors that affect our ability to study and work effectively and influence our physical and mental health. Consequently, modern artificial light sources are designed with these psychological elements to achieve the best aesthetics. ...
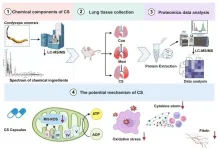
Chinese medicinal fungus shows promise in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
2024-07-26
A recent study from China has reported that Cordyceps sinensis (CS), a traditional Chinese medicinal fungus, can ameliorate idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in mice by inhibiting mitochondrion-mediated oxidative stress. The research, conducted by a team led by Huan Tang and Jigang Wang from the Institute of Chinese Materia Medica at the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, was published in Wiley's MedComm-Future Medicine.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic and progressive lung disease characterized by a decline in lung function, ultimately leading to respiratory failure and a significantly reduced quality of life for patients. With a median ...
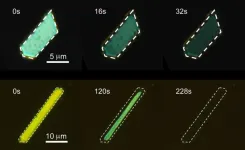
Shining light on similar crystals reveals photoreactions can differ
2024-07-26
A rose by any other name is a rose, but what of a crystal? Osaka Metropolitan University-led researchers have found that single crystals of four anthracene derivatives with different substituents react differently when irradiated with light, perhaps holding clues to how we can use such materials in functional ways.
Graduate student Sogo Kataoka, Dr. Daichi Kitagawa, a lecturer, and Professor Seiya Kobatake of the Graduate School of Engineering and colleagues compared the photoreactions of the single crystals when the entire anthracene crystal was irradiated with light.
For two ...
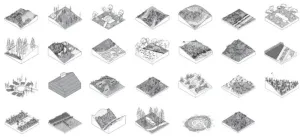
Innovative fire stewardship techniques to reshape landscape design to better adapt to and coexist with wildfire-prone environments
2024-07-26
Over the past few decades, many parts of the world have experienced record-breaking wildfire events—a trend that is, unfortunately, expected to rise. These extreme events not only result in mass evacuations, but also release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, pose risks to life, devastate buildings and essential infrastructure, and fundamentally disrupt and detrimentally transform native ecosystems. In response to the increased risk of catastrophic wildfires, many planning and site design practices have sought to protect the trends and status quo of land development. These measures strive to resist and, ...
Kepler’s 1607 pioneering sunspot sketches solve solar mysteries 400 years later
2024-07-26
Using modern techniques, researchers have re-examined Johannes Kepler's half-forgotten sunspot drawings and revealed previously hidden information about the solar cycles before the grand solar minimum. By recreating the conditions of the great astronomer’s observations and applying Spörer's law in the light of modern statistics, an international collaborative group led by Nagoya University in Japan has measured the position of Kepler’s sunspot group, placing it at the tail-end of the solar cycle before the cycle that Thomas Harriot, Galileo Galilei, and other ...
A new therapeutic target offers a promising pathway for multiple sclerosis treatment
2024-07-26
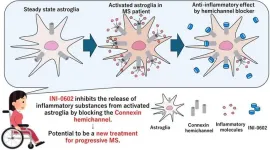
Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers from Kyushu University have identified a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of advanced multiple sclerosis (MS), a potentially disabling condition associated with the central nervous system. In their latest study, conducted using an experimental mouse model of MS, they explored the role of connexin 43 (Cx43), a protein involved in cellular communication and cardiac function, and examined whether targeting this protein with specific blockers could improve ...
Recent insights and advances in treatment and management show promise in stemming the growing prevalence of diabetes
2024-07-26
A new paper surveying advances in diabetes pathogenesis and treatment explores the complex factors contributing to the onset and progression of the disease, suggesting that an understanding of these dynamics is key to developing targeted interventions to reduce the risk of developing diabetes and managing its complications.
In a paper published July 25 in a special 50th anniversary issue of the peer-reviewed journal Cell, the authors surveyed hundreds of studies that have emerged over the years looking at the causes underpinning types 1 (T1D) and 2 (T2D) diabetes and new treatments for the disease. They examine the role that genes, environmental factors, and ...
Folded peptides are more electrically conductive than unfolded peptides
2024-07-26
What puts the electronic pep in peptides? A folded structure, according to a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Electron transport, the energy-generating process inside living cells that enables photosynthesis and respiration, is enhanced in peptides with a collapsed, folded structure. Interdisciplinary researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology combined single-molecule experiments, molecular dynamics simulations and quantum mechanics to validate their findings.
“This discovery provides a new understanding of how electrons flow through peptides ...
Biotechnology companies can sustain the pipeline of new drugs under the Inflation Reduction Act
2024-07-26
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
New research from the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University shows that differences between the financial structures of large pharmaceutical producers and smaller, emerging biotechnology companies creates synergies that contribute to the pipeline of new, innovative products in response to reductions in drug prices anticipated under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). While large pharmaceutical producers would likely reduce R&D spending in response to lower product revenues, R&D in smaller biotechnology companies is not likely to decrease and could sustain both corporate profits and new product ...
65 million Americans now own firearms for protection, suggests survey
2024-07-26
Some 65 million Americans now own firearms for protection—around 80% of the country’s estimated 81 million gun owners—suggest the results of a nationally representative survey carried out in 2023, and published online in the journal Injury Prevention.
This perceived need is changing the profile of gun owners, the findings indicate, with increasing numbers of women and those of minority ethnic backgrounds citing protection as the primary reason for owning a firearm.
In 2021, firearms caused the highest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Conflicting health advice from agencies drives confusion, study finds, but doctors remain most trustedUncertainty inherent in scientific process confuses public and reduces trust in health agencies, finds study