(Press-News.org) There has been a mixed response to primary education reforms in Mexico which have created widespread uncertainty among teachers, children and parents, new research shows.
Those affected have expressed concerns about lack of training to help them prepare for the major changes, but also enthusiasm about many of the aims.
The new Nueva Escuela Mexicana (NEM) in Basic Education represents a large shift in curriculum, pedagogy and assessment.
Subjects such as maths and science have been combined into integrated “formative fields”. There is a focus on education that places more value on local communities and an emphasis on active and interactive learning through projects.
Children also learn more about topics related to inclusion and diversity. Teachers have increased autonomy to adapt their work to local contexts.
The NEM has been met with both enthusiasm and scepticism. This research is one of the first to comprehensively gather people’s experiences and perspectives of the NEM in its first full year of implementation.
The study was carried out by Dr Nozomi Sakata, from Hiroshima University and Dr Nicholas Bremner, from the University of Exeter. They carried out 79 interviews with students, teachers, parents, head teachers, teacher trainers and supervisors in 12 primary schools in Nuevo León, Hidalgo and Chiapas.
The study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Dr Bremner said: “We found a mixture of positive and negative perspectives, but overall there was widespread uncertainty about the NEM reform. Although teachers, head teachers and teacher trainers were getting used to the changes over time, they were frustrated with inconsistent policy messages and a general lack of explicit training.”
Researchers recommend more concrete training and support is needed, especially in terms of supporting teachers to manage increased autonomy. They say there also needs to be a more consistent, unambiguous communication strategy.
The research suggests that the Mexican Ministry of Education needs to address concerns the changes could lead to gaps in foundational knowledge. They should consider the extent to which students may need basic knowledge in order to develop higher order skills.
Communication with parents and the wider public should also be strengthened to make it clear what NEM does and what it does not do.
Dr Bremner said: “More emphasis seems to have been placed on the “what” - the content of the reform itself - and much less on how to implement it.
“Those interviewed were very concerned about the lack of ‘foundational’ knowledge many of their students had, and there was a lot of scepticism regarding combining specific school subjects into ‘formative fields’.”
Teachers, pupils and parents were generally very supportive of content related to inclusion and diversity, but expressed doubts about certain topics, for example content relating to gender and sexuality.
Those affected by the reform were generally happy with the notion of ‘focusing on the local’, contextualisation and teacher autonomy. However, some teachers did not always know how to manage such autonomy, requesting more explicit guidance.
One local supervisor in rural Chiapas said: “There is a paradigm shift; there is a change in the approach to education. But there has been no real systematisation of teacher training.”
One local supervisor in rural Nuevo León said: “We started to be updated on a drip-feed basis. […] The information either arrived too quickly for us to transmit it, or it arrived late, or it didn’t arrive at all. You asked the corresponding educational authority, and they didn’t know either. […] I would say it is not consistent, and at many times it is not coherent.”
Download a Spanish and English version of the report at https://we.tl/t-7gC8BEkySz
END
Primary education reforms in Mexico greeted with both enthusiasm and scepticism, study shows
2024-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Little evidence to back widespread prescribing of mood-altering drugs to children for mental health issues
2024-07-30
There’s limited evidence to back up the widespread and increasing rates of prescribing mood-altering drugs (psychotropics) as the mainstay of mental health treatment for children and young people, warn experts in an editorial, published today in the August issue of Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin (dtb)
But first and foremost, current prescribing practice for these drugs, which include sedatives, anti-anxiolytics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, and melatonin, needs to be a lot safer, they insist.
The numbers of these ...
Inflammatory activity of rheumatoid arthritis linked to specific cognitive impairments
2024-07-30
The inflammatory activity in the body caused by rheumatoid arthritis is linked to specific cognitive impairments, finds a small comparative study, published in the open access journal RMD Open.
These are diminished visuospatial abilities, recall, abstract thinking, and the executive functions of working memory, concentration, and inhibition.
Inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis has been associated with various systemic effects, including on the brain, but it’s not clear which specific cognitive domains might be affected.
To try and find out, the researchers compared the cognitive ...
Lettuce may be just as good as dock leaf for easing nettle sting symptoms
2024-07-30
Rubbing a lettuce leaf on a nettle sting to ease the associated discomfort may be just as good as using the age-old folk remedy of a dock leaf, suggest the results of a small comparative study, published online in Emergency Medicine Journal.
It may simply be the cooling and soothing effect of sap evaporating from a crushed leaf that brings relief, and doing nothing might work just as well, although possibly not if you’re a small child, suggest the researchers.
Nettles are a common native plant in the British Isles. Their stems and leaves are covered in stinging hairs, or trichomes, with a brittle tip that snaps off when touched, ...
Wayne State University’s new assistant vice president for technology commercialization announced
2024-07-29
DETROIT – Taunya A. Phillips has been named the assistant vice president for Technology Commercialization in the Division of Research & Innovation at Wayne State University.
Phillips will lead revitalization efforts of the technology transfer and commercialization office that includes increasing the protection and commercialization of intellectual property developed at Wayne State, as well as promoting innovation and entrepreneurship efforts in support of the university’s strategic goals and Prosperity Agenda. Her guidance will aid the university’s efforts and commitment to propelling Michigan’s competitiveness in 21st century commerce and cultivating a campus ...
Scientists untangle interactions between the Earth’s early life forms and the environment over 500 million years
2024-07-29
The atmosphere, the ocean and life on Earth interacted over the past 500-plus million years in ways that improved conditions for early organisms to thrive. Now, an interdisciplinary team of scientists has produced a perspective article of this co-evolutionary history published in multidisciplinary open-access journal National Science Review (Oxford University Press, Impact Factor 20.7).
“One of our tasks was to summarize the most important discoveries about carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere and ocean over the past 500 million ...
UAB study reveals link between transthyretin levels and heart disease risk
2024-07-29
Physician-scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine have uncovered significant findings regarding the impact of transthyretin, or TTR, protein levels on heart disease risk. The study, recently published in Nature Communications, explores how variations in TTR levels are associated with adverse clinical outcomes, providing new insights into the prevention and management of amyloid heart disease. Transthyretin is a transport protein produced in the liver, and its misfolding is linked to the development of cardiac amyloidosis, a condition that leads to heart failure and increased mortality.
The study, led ...
MicroRNA study sets stage for crop improvements
2024-07-29
MEDIA INQUIRES
WRITTEN BY
Laura Muntean
Ashley Vargo
laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu
601-248-1891
FOR ...
Semaglutide may show promise for smoking cessation
2024-07-29
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 29 July 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
Self-powered ’bugs’ can skim across water to detect environmental data
2024-07-29
INGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York have developed a self-powered “bug” that can skim across the water, and they hope it will revolutionize aquatic robotics.
Futurists predict that more than one trillion autonomous nodes will be integrated into all human activities by 2035 as part of the “internet of things.” Soon, pretty much any object — big or small — will feed information to a central database without the need for human involvement.
Making this idea tricky is that 71% of the Earth’s ...
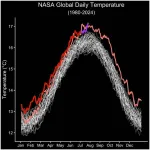
NASA data shows July 22 was Earth’s hottest day on record
2024-07-29
July 22, 2024, was the hottest day on record, according to a NASA analysis of global daily temperature data. July 21 and 23 of this year also exceeded the previous daily record, set in July 2023. These record-breaking temperatures are part of a long-term warming trend driven by human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. As part of its mission to expand our understanding of Earth, NASA collects critical long-term observations of our changing planet.
“In a year that has been the hottest on record to date, these past two weeks have ...