New type of “antibiotic” generated from the long pepper recommended
2024-07-30
(Press-News.org)
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, July 30, 2024 – Antibiotic resistant bacterial pathogens are on the rise, while fewer antibiotics are being developed. Prof. Ariel Kushmaro and his local and international colleagues tackled the need by focusing on the long pepper. Known in traditional medicine for its treatment of a variety of illnesses, the team created a derivative that disrupts bacterial chemical communication.
Their findings were just published in Biofilm (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioflm.2024.100215).
Many plants' secondary metabolites are essential for plant protection against microbial pathogens. These compounds have long been considered an important source for drug discovery. The synthesis of new derivatives of these metabolites increases the probability of finding new drugs for many therapeutic purposes.
In the study, sixteen derivatives of Piperlongumine (PL), an amide alkaloid from Piper longum L., were screened for Quorum Sensing Inhibition (QSI). Quorum Sensing (QS) uses auto-inducers to control bacterial concentration. PL-18 had the best QSI activity.
PL-18 both reduced bacterial virulence and disrupted the biofilms that protected their sample bacteria. Altogether, PL-18 inhibits QS, virulence, iron uptake, and biofilm formation. Thus, PL-18 should be further developed against bacterial infection, antibiotic resistance, and biofilm formation.
Additional researchers from Prof. Kushmaro's lab included: Yael Schlichter Kadosh and Marilou Shagan.
Additional researchers from BGU included: Khairun Nisaa, Prof. Anat Ben-Zvi, Danit Lisa Karsagi Byron and Prof. Jacob Gopas. They collaborated with Alexander Brandis and Tevie Mehlman, researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science, and Subramani Muthuraman and Rajendran Saravana Kumar of the Vellore Institute of Technology in India.
First author Yael Schlichter Kadosh was supported by the Israel Ministry of Science & Technology. The research was partially supported by the Avram and Stella Goldstein-Goren Fund.
Prof. Kushmaro is a member of the Avram and Stella Goldstein-Goren Department of Biotechnology Engineering, the Goldman Sonnenfeldt School of Sustainability and Climate Change, and the Ilse Katz Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-07-30
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Since the 1950s, researchers have used a famous method invented by Wallace Coulter known as “flow cytometry” to characterize different types of immune cells in research studies and in blood samples from human individuals. This has enabled a much deeper understanding of immune cell development as well as new ways to assess human health and diagnose various blood cancers. Later, flow cytometry was applied also to other cell types.
In traditional flow cytometry, cell surface and intracellular proteins are detected with antibody molecules that are linked to fluorescent probes. However, while providing single-cell ...
2024-07-30
Not all police misconduct is the same. Misconduct can range from offenses like homicide and sexual assault to seemingly minor infractions such as accepting free coffee from the public. Exactly what qualifies as police misconduct varies locally, and the response to this behavior is typically handled internally by law enforcement.
The absence of a commonly accepted framework to assess and interpret police misconduct remains a complex and contentious issue. Moreover, progress in researching this area is hindered by the limited ...
2024-07-30
Genetically engineered human skin bacteria can make mice less attractive to mosquitoes for 11 days. Mosquitoes transmit a host of deadly diseases, including malaria, West Nile, dengue, yellow fever, and Zika. Female mosquitoes on the hunt for a blood meal tune into scents released by skin microbes that live on their targets. Omar Akbari and colleagues engineered versions of the common human skin commensals Staphylococcus epidermidis and Corynebacterium amycolatum to produce much less of a form of lactic acid known to attract mosquitoes. The authors tested the microbes alone and found the engineered version of S. epidermidis attracted about half as ...
2024-07-30
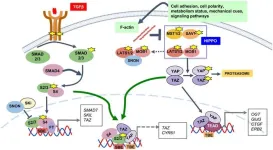
The liver's ability to communicate with other organs is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, particularly through signaling pathways. During liver regeneration, communication with organs such as the brain, pancreas, intestine, and heart is vital, mediated by chemical messengers like hormones, cytokines, and growth factors. Among these signals, the TGF-β and HIPPO pathways are critical, functioning as tumor suppressors and regulating liver development and regeneration. The review focuses on these pathways' interplay in maintaining liver homeostasis, facilitating regeneration, and contributing to diseases like hepatitis, fibrosis, ...
2024-07-30
A study explores the microbiome of keloids, which are treatment-resistant raised scars. Some wounds heal completely; some wounds leave a scar; and some wounds leave a noticeable raised and growing bump larger than the original wound called a keloid. These keloids can itch and cause psychological distress. Keloids are caused by hyperproliferation of cells called fibroblasts that produce collagen. Previous research had suggested that microbiota might be one of many factors influencing fibroblast production. Rui Chen, Tomasz Maj and colleagues looked for bacteria in clinical samples of keloid tissue and found higher concentrations ...
2024-07-30
Cancer is a complex, multifactorial disease with a substantial global burden. Recent years have seen a surge in research focusing on preventive measures, particularly through diet and supplements. The role of nutrition in cancer incidence and prevention is widely recognized, though the specifics of these relationships remain under investigation. This review expands on the findings of Anandu Chandra Khanashyam et al., exploring the nuanced links between diet, supplements, and cancer prevention.
The significance of diet and supplements in cancer prevention is well-documented, with nutrition ...
2024-07-30
Z-alkenes are organic compounds with a double bond between two carbon atoms and two substituents attached to the carbon atoms on the same side of the double bond. They are ubiquitous structural components of organic compounds in chemistry and biology. It is well known that many of the Z-alkenes cannot be prepared through conventional methods involving thermodynamic methods while photoisomerization can offer good yields. Photoisomerization is a process in which the structural arrangement of an isomer of a molecule is changed to another isomer by absorption of light. The photoisomerization of E-alkenes to produce Z-alkenes ...
2024-07-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Many studies have focused on falls among people who are ambulatory and have conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, but research to address falls among those who rely on wheelchairs or motorized scooters is rare, scientists report in a new study. The researchers found that full-time wheelchair or motorized-scooter users also experience falls and fall-related injuries, and many live with the fear of falling again.
The findings are detailed in the journal Disability and Rehabilitation.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, 5.5 million Americans ...
2024-07-30
North Sea oil and gas extraction can cause pollution to spike by more than 10,000% within half a kilometre around off-shore sites, a study has found for the first time.
The University of Essex, Natural History Museum and Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (CEFAS) research has uncovered the true impact on Britain’s seabed life - with the number of species plummeting nearly 30% near platforms.
The findings, published in Science of The Total Environment, come in the face of continued global fossil fuel exploration.
The study discovered pollutants like hydrocarbons were up to 10,613% higher within 500m ...
2024-07-30
PULLMAN, Wash. – Companies may unintentionally hurt their sales by including the words “artificial intelligence” when describing their offerings that use the technology, according to a study led by Washington State University researchers.
In the study, published in the Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, researchers conducted experimental surveys with more than 1,000 adults in the U.S. to evaluate the relationship between AI disclosure and consumer behavior.
The findings consistently showed products described as using artificial intelligence were less popular, according to Mesut Cicek, clinical assistant professor of marketing and lead author ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New type of “antibiotic” generated from the long pepper recommended