(Press-News.org) A new study published in the International Journal of Sports Medicine, Inhalation of hydrogen-rich gas before acute exercise alleviates exercise fatigue, has found a possible novel intervention for exercise-induced fatigue. A cross-discipline international team of U.S. and Chinese researchers, including at Hebrew SeniorLife’s Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, found that inhaling hydrogen-rich gas (HRG) before engaging in acute exercise can significantly reduce fatigue and enhance performance.
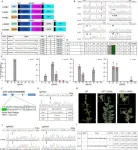
The research involved 24 healthy adult men who were tested for their maximum cycling power (Wmax) and maximum cycling time (Tmax). In a double-blind, counterbalanced, randomized, and crossover design, participants inhaled either HRG or placebo gas (air) for 60 minutes before cycling at 80% Wmax until exhaustion.
Key findings from the study include:
Reduced Perceived Fatigue: Participants who inhaled HRG reported significantly lower scores on the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for fatigue compared to those who inhaled placebo gas.
Improved Exercise Performance: HRG inhalation improved cycling frequency during the final 30 seconds of the exercise and reduced the rating of perceived exertion (RPE) at both the beginning and end of the ride.
Oxidative Stress Markers: HRG inhalation showed a significant improvement in the ability to inhibit hydroxyl radicals and lower serum lactate levels after exercise, indicating reduced oxidative stress.
Functional Performance: While HRG did not significantly impact counter-movement jump (CMJ) height or glutathione peroxidase activity, the overall benefits on fatigue and oxidative stress markers were notable.
“The study’s findings suggest that HRG inhalation prior to exercise could be a valuable strategy for athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking to enhance performance and recovery. By mitigating fatigue and improving markers of oxidative stress, HRG has the potential to support more effective training and better overall health outcomes,” said Junhong Zhou, PhD, assistant scientist II, Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife.
The study opens new avenues for exploring the benefits of hydrogen-rich gas in sports and exercise science. As further research continues, HRG inhalation may become a widely adopted practice for enhancing athletic performance and combating exercise-induced fatigue.
Co-authors include:
Gengxin Dong, School of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing
Jianxin Wu, Ministry of Sports, Tsinghua University, Beijing
Yinglu Hong, School of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing
Qian Li, Sports Coaching College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing
Meng Liu, Sports Coaching College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing
Guole Jiang, Sports Coaching College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing
Dapeng Bao, China Institute of Sport and Health Science, Beijing Sport University, Beijing
Brad Manor, PhD, Director of the Mobility and Brain Function Program at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research
Junhong Zhou, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
About Hebrew SeniorLife
Hebrew SeniorLife, an affiliate of Harvard Medical School, is a national senior services leader uniquely dedicated to rethinking, researching, and redefining the possibilities of aging. Hebrew SeniorLife cares for more than 4,500 seniors a day across seven campuses throughout Greater Boston. Locations include: Hebrew Rehabilitation Center-Boston and Hebrew Rehabilitation Center-NewBridge in Dedham; NewBridge on the Charles, Dedham; Orchard Cove, Canton; Simon C. Fireman Community, Randolph; Center Communities of Brookline, Brookline; Jack Satter House, Revere; and Leyland Community, Dorchester. Founded in 1903, Hebrew SeniorLife also conducts influential research into aging at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, which has a portfolio of more than $98 million, making it one of the largest gerontological research facilities in the U.S. in a clinical setting. It also trains more than 500 geriatric care providers each year. For more information about Hebrew SeniorLife, visit our website or follow us on our blog, Facebook, Instagram, Threads, and LinkedIn.
About the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research
Scientists at the Marcus Institute seek to transform the human experience of aging by conducting research that will ensure a life of health, dignity, and productivity into advanced age. The Marcus Institute carries out rigorous studies that discover the mechanisms of age-related disease and disability; lead to the prevention, treatment, and cure of disease; advance the standard of care for older people; and inform public decision-making.
END
Hydrogen-rich gas inhalation can alleviate exercise-induced fatigue
New study published in the International Journal of Sports Medicine
2024-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fruitful innovation: Transforming watermelon genetics with advanced base editors
2024-07-30
The development of new adenine base editors (ABE) and adenine-to-thymine/guanine base editors (AKBE) is transforming watermelon genetic engineering. These innovative tools enable precise A:T-to-G and A:T-to-T base substitutions, allowing for targeted genetic modifications. The research highlights the efficiency of these editors in generating specific mutations, such as a flowerless phenotype in ClFT (Y84H) mutant plants. This advancement not only enhances the understanding of gene function but also significantly improves molecular breeding, paving the way for more efficient watermelon crop improvement.
Traditional breeding methods for watermelon ...
SwRI’s Dr. Sergey Vinogradov to receive Ward Rummel Engineering Excellence Award
2024-07-30
SAN ANTONIO — July 30, 2024 —SwRI’s Dr. Sergey Vinogradov has been named the recipient of the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT) Ward Rummel Engineering Excellence Award, which recognizes outstanding sustained contributions in nondestructive testing (NDT) by a single individual. NDT, also known as nondestructive evaluation (NDE), uses technology to evaluate and inspect materials and components for safety and reliability without damaging them.
“Dr. Vinogradov pioneered using magnetostrictive transducer technology in NDE applications, developing the original designs as well as producing countless custom ...
Stem cell harmony: How solanaceae plants maintain homeostasis through receptor compensation
2024-07-30
A pivotal study sheds light on the evolutionary conservation of stem cell homeostasis in Solanaceae, revealing how receptor compensation mechanisms ensure the continuous and orderly formation of plant organs. This research uncovers the genetic interplay that maintains stem cell balance, offering new perspectives for crop improvement and resilience enhancement.
Stem cell homeostasis is vital for the continuous formation of plant organs. This process involves intricate interactions among peptide ligands and their receptor-like kinases. Due to the dynamic nature of plant genomes, understanding ...
Illicit fentanyl use linked to increased risk of hepatitis C among people who use drugs
2024-07-30
An international team of researchers from University of California San Diego and el Colegio de la Frontera Norte in Mexico have revealed a significant association between the use of illicit fentanyl and the transmission of hepatitis C virus (HCV) among people who inject drugs in San Diego, California and Tijuana, Mexico. The findings, published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, suggest that illicit fentanyl use could be driving recent increases in HCV incidence.
"Our study provides the first evidence that illicit fentanyl ...
Elusive predicted water structure created in the laboratory
2024-07-30
Clathrate hydrates are complex water structures that contain foreign guest molecules inside a host water-molecule shell. A predicted clathrate hydrate phase structure has been stably synthesized in the lab and may play an important role in future material science research.
Water molecules are made up of just three atoms: two hydrogen atoms bound to a single oxygen atom. Individual water molecules can weakly bind to one another and other molecules, changing their collective physicochemical properties.
Clathrate hydrates, in particular, are lattices of water molecules that self-assemble ...
Algorithm helps doctors identify more aggressive types of basal cell carcinoma
2024-07-30
An algorithm can help healthcare professionals recognize which patients have a highly aggressive form of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) of the face. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. If more BCCs are correctly identified as high-risk, the patients can directly receive the most effective treatment.
BCC is the most common form of skin cancer. The cancer type grows slowly and almost never spreads to other parts of the body. Most of the BCCs all are cured, but without treatment, highly ...
Mental health problems often go undetected in youth who die by suicide
2024-07-30
Three out of five youth who died by suicide in the U.S. did not have a prior mental health diagnosis, signaling missed opportunities to identify children and adolescents for suicide prevention strategies, including therapy or medications to treat depression. This finding comes from an analysis of over 40,000 suicides by youth of 10-24 years of age from 2010 to 2021, recorded in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Violent Death Reporting System. Results were published in the journal JAMA Network Open.
“We discovered that certain youth who died by suicide were less likely to have a documented ...
How spreading misinformation is like a nuclear reaction
2024-07-30
WASHINGTON, July 30, 2024 – It has never been easier to spread false or misleading information online. The anonymous, impersonal nature of the internet, combined with advanced tools like artificial intelligence, makes it trivial for bad actors to manipulate the truth and challenging for everyone else to separate reality from fiction. In this modern climate of disinformation, understanding how falsehoods and rumors spread is crucial for combating them.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Shandong Normal University developed a new type of rumor propagation model, taking inspiration from nuclear reactions. Their model can provide fresh insights ...
Suicide in US preteens ages 8 to 12, 2001 to 2022
2024-07-30
About The Study: The findings of this study revealed a significant increase in the suicide rate among U.S. preteens between the 2001-2007 and 2008-2022 periods. Results showing a disproportionate increase in female suicide rates relative to male expand on existing evidence depicting a narrowing of the historically large gap in youth suicide rates between sexes. Suicide was the 11th leading cause of death in female preteens between 2001 and 2007 and the 5th leading cause of death between 2008 and 2022, while suicide in male preteens ...
Youth suicide and preceding mental health diagnosis
2024-07-30
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, 3 of 5 youth suicide decedents did not have a documented preceding mental health diagnosis; the odds of having a mental health diagnosis were lower among racially and ethnically minoritized youths than white youths and among firearm suicides compared with other mechanisms. These findings underscore the need for equitable identification of mental health needs and universal lethal means counseling as strategies to prevent youth suicide.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Sofia Chaudhary, M.D., email sofia.s.chaudhary@emory.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
[Press-News.org] Hydrogen-rich gas inhalation can alleviate exercise-induced fatigueNew study published in the International Journal of Sports Medicine