(Press-News.org) The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has been awarded funding from DOE’s Office of Technology Transitions for four new projects that will help with commercialization of innovative clean-energy technology for a sustainable future.
Argonne scientists will work to turn their innovative ideas into next-generation technology necessary to build cleaner, more resilient energy systems. These projects build on Argonne’s decades-long role at the forefront of the quest to decarbonize the U.S. economy.
Argonne’s groundbreaking projects will focus on integrating next-generation power electronics into grid and solar power systems, designing and licensing molten salt nuclear reactors, decarbonizing and lowering the cost of organic waste treatment, and developing innovative solutions for water desalination.
Through collaborations with industry partners, these projects will advance the innovative technologies that will aid the transition to a clean energy economy.
Argonne researchers whose projects received 2024 funding are:
Moinuddin Ahmed: An In-situ Grid Dynamic Driven Failure Prediction Methodology for Integrating Next-generation Power Electronics into Grid and Solar Power Systems (in partnership with Kyma Technologies)
Thanh Hua: Advanced System Analysis Code Assessment and Enhancement to Support the Integral Molten Salt Reactor Design and Licensing (in partnership with Terrestrial Energy USA)
Yuepeng Zhang: rGO-Enhanced Nanocomposite Electromembrane Technology for Energy Efficient Water Desalination (in partnership with GOLeafe)
YuPo Lin: Decarbonizing and Improving the Profitability of Organic Waste Treatment through an Innovative Process and Value Chain (in partnership with Corumat, Inc.)
The awards are part of $41.4 million in funding toward 50 clean energy projects through DOE’s Technology Commercialization Fund Base Annual Appropriations Core Laboratory Infrastructure for Market Readiness award. Argonne scientists will help advance the nationwide goal to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050 and lower energy costs.
The 50 projects across 17 national laboratories will address commercialization challenges, accelerate the development of promising technologies and streamline processes to efficiently deliver clean-energy solutions to the marketplace. The 2024 awards are the largest amount of funding to date and represent coordinated investments from the largest set of DOE program offices.
END
Argonne receives U.S. Department of Energy funding for four next-generation clean-energy projects
Argonne innovations will advance U.S. goals to achieve net-zero carbon emissions
2024-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers develop general framework for designing quantum sensors
2024-07-30
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have designed a protocol for harnessing the power of quantum sensors. The protocol could give sensor designers the ability to fine-tune quantum systems to sense signals of interest, creating sensors that are vastly more sensitive than traditional sensors.
“Quantum sensing shows promise for more powerful sensing capability that can approach the fundamental limit set by the law of quantum mechanics, but the challenge lies in being able to direct ...
UBC super-black wood can improve telescopes, optical devices and consumer goods
2024-07-30
Thanks to an accidental discovery, researchers at the University of British Columbia have created a new super-black material that absorbs almost all light, opening potential applications in fine jewelry, solar cells and precision optical devices.
Professor Philip Evans and PhD student Kenny Cheng were experimenting with high-energy plasma to make wood more water-repellent. However, when they applied the technique to the cut ends of wood cells, the surfaces turned extremely black.
Measurements by Texas A&M University’s ...
Repair kit for NASA’s NICER mission heading to space station
2024-07-30
NASA will deliver a patch kit for NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer), an X-ray telescope on the International Space Station, on the agency’s Northrop Grumman 21st commercial resupply mission. Astronauts will conduct a spacewalk to complete the repair.
Located near the space station’s starboard solar array, NICER was damaged in May 2023. The mission team delivered the patch kit to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in May 2024 so it could be prepped and packed for the upcoming resupply mission.
“It’s ...
Mucus-based bioink could be used to print and grow lung tissue
2024-07-30
Lung diseases kill millions of people around the world each year. Treatment options are limited, and animal models for studying these illnesses and experimental medications are inadequate. Now, researchers describe in ACS Applied Bio Materials their success in creating a mucus-based bioink for 3D printing lung tissue. This advance could one day help study and treat chronic lung conditions.
While some people with lung diseases receive transplants, donor organs remain in short supply. As an alternative, medications and other treatments can be used to manage symptoms, but no cure is available for disorders such as chronic obstructive ...
Who is more polarized about AI—the tech community or the general public?
2024-07-30
The tech community is more strongly divided in how they feel about artificial intelligence (AI) than the general public according to a study of Reddit discourse following the launch of ChatGPT.
Researchers from the University of Rochester led by Jiebo Luo, a professor of computer science and the Albert Arendt Hopeman Professor of Engineering, used ChatGPT and natural language processing techniques to analyze the themes and sentiments of 33,912 comments in 388 unique subreddits in the roughly six months following the generative AI tool’s launch in November 2022. The findings appear in Telematics and Informatics.
Reddit is an online social ...
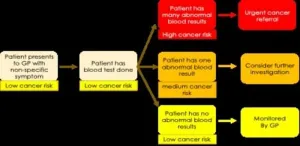
Routine blood test results can improve cancer risk assessment in patients with abdominal symptoms
2024-07-30
Incorporating information from common blood tests can enhance cancer risk assessment in patients with abdominal symptoms, according to a study publishing July 30th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Meena Rafiq from University College London, UK, and colleagues.
Early cancer detection is key to successful treatment. However, many undiagnosed cancer patients present to their primary care provider with non-specific symptoms that can be a result of several other benign causes, making it difficult ...
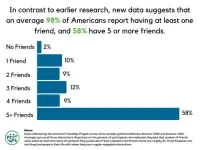
Friendships in America may be in less peril than previously thought
2024-07-30
American adults may typically have more friends than indicated by other recent surveys, with fewer Americans having no friends at all – though many would like closer friendships. Natalie Pennington of Colorado State University, US, and colleagues present these preliminary findings from the ongoing “American Friendship Project” in a study published July 30, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Having more and higher quality friendships is linked with greater happiness and life satisfaction. However, research suggests that ...
Common blood tests could improve cancer diagnosis for people with stomach pain or bloating
2024-07-30
The results of routine blood tests could be used to speed up cancer diagnosis among people with stomach pain or bloating, suggests a new study led by UCL researchers.
Most people who report these symptoms to their GP are referred for blood tests. However, it is not known how well these blood tests, used to explore a range of possible causes of ill health, can predict cancer risk.
The new study, published in PLOS Medicine, looked at data from more than 400,000 people aged 30 or older in the UK who had visited a GP due to stomach ...
Is that glass bottle of OJ better for the planet than a plastic container?
2024-07-30
Which packaging type for a 12-ounce, single-serve container of orange juice would you choose as the most sustainable option:
Aluminum/canned, made with recycled material;
Carton, described as biodegradable/compostable;
Glass, 100% recyclable; or
Plastic, described as biodegradable/compostable?
If you were like the U.S. consumers surveyed by food scientists in a University of Massachusetts Amherst study, you’d prefer glass and believe it was the most sustainable choice. And you all would be mistaken.
“Glass was ...
Hydrogen-rich gas inhalation can alleviate exercise-induced fatigue
2024-07-30
A new study published in the International Journal of Sports Medicine, Inhalation of hydrogen-rich gas before acute exercise alleviates exercise fatigue, has found a possible novel intervention for exercise-induced fatigue. A cross-discipline international team of U.S. and Chinese researchers, including at Hebrew SeniorLife’s Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, found that inhaling hydrogen-rich gas (HRG) before engaging in acute exercise can significantly reduce fatigue and enhance performance.
The research involved 24 healthy adult men who were tested for their maximum cycling ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Argonne receives U.S. Department of Energy funding for four next-generation clean-energy projectsArgonne innovations will advance U.S. goals to achieve net-zero carbon emissions