(Press-News.org) HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and collaborators are initiating a research project that will send T cells to the International Space Station (ISS) to study the effects of prolonged microgravity on cell differentiation, activation, memory and exhaustion. These results will be further analyzed on Earth to uncover signaling pathways and identify potential immune targets that can improve treatment strategies for patients with cancer and other diseases.
To accomplish this work, MD Anderson researchers led by Cassian Yee, M.D., and Kunal Rai, Ph.D., will collaborate with Axiom Space, BioServe Space Technologies, Deep Space Biology and Mongoose Bio.
“We are excited to join with talented collaborators who are experienced in biological research and in delivering payloads to deep space in order to leverage the unique research environment of sustained microgravity on the ISS National Laboratory,” said Yee, professor of Melanoma Medical Oncology. “We look forward to this opportunity to study how T cells are affected by microgravity, identify novel targets and translate these findings into meaningful therapeutic strategies that can improve cellular therapies and enhance life here on Earth.”
Axiom Space and BioServe Space Technologies will act as hardware implementation partners, building upon multiple years of experience delivering and supporting biological payloads in space. The multi-flight solicitation will include two missions to the ISS, allowing for discovery research that may lead to translational phases on Axiom Space’s next-generation commercial space station, Axiom Station.
The Rai and Yee labs will use single-cell sequencing on samples cryopreserved in flight and returned to Earth to evaluate in vivo temporal and dynamic epigenetic changes and develop models for the different cell states. Their work will be facilitated using Deep Space Biology’s Yotta technology, the first artificial intelligence (AI) platform using space biology research for health discoveries on Earth. Mongoose Bio, a biopharmaceutical cell therapy company, is leveraging technology licensed from MD Anderson to translate and scale discoveries identified through this collaboration for use in future cell therapy projects and potential novel cancer treatments.
Cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that modifies or expands immune cells so they are better able to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. Approved cell therapies include chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies, which are T cells engineered to recognize a specific cancer target. Yet these therapies do not work for all patients, since infused T cells can become exhausted, or the cancer can evolve to escape the immune system.
Previous studies both on Earth and in space have shown that microgravity can impact T cell biology by modifying the cytoskeleton, chromatin structure, activation and other gravity-sensitive elements, leading researchers to believe that it could also affect how these cells differentiate.
A deeper understanding of immune differentiation pathways could also spur the advancement of other cell therapies currently being developed at MD Anderson, such as endogenous T cell (ETC) therapies, T cell receptor (TCR)-based therapies and CAR natural killer (NK) cell therapies.
This research project is designed to identify transcriptional and epigenetic signatures for microgravity-induced T cell memory, effector and exhaustion states; to validate individual effects of target overexpression or knockdown on T cell states; and to optimize combinations of targets for desired T cell states on Earth.
“This multidisciplinary project bridges the intersection of space science and immunology to uncover potential breakthroughs in cell therapy research,” said Rai, associate professor of Genomic Medicine. “This work will provide new insights into immune cell epigenetic pathways that will allow us to identify targets, simulate models and develop techniques to enhance T cell memory and prevent cell exhaustion so we can improve patient outcomes.”
This project is supported by a grant awarded by the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, Inc. (CASIS), which manages the ISS National Laboratory. CASIS and the Biological and Physical Sciences division of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) intend to select and fund spaceflight projects that lead to defined milestones in technological innovation that are in alignment with national research and technology development priorities and with the ISS National Lab mission to benefit humanity and the U.S. economy.
Read this press release in the MD Anderson Newsroom.
Disclosure
Yee is a co-founder of Mongoose Bio, and his financial relationship with the company is managed and monitored by the MD Anderson Conflict of Interest Committee. MD Anderson has an institutional conflict of interest with Mongoose Bio and has implemented an Institutional Conflict of Interest Management and Monitoring Plan to manage this relationship.
- 30 -
END
Chameleon, led by Senior Scientist Kate Keahey from Argonne National Laboratory, has been a cornerstone of CS research and education for nearly a decade. The platform has served over 10,000 users, contributing to more than 700 research publications. Chameleon has now secured an additional $12 million in funding from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) to roll out its next four-year phase. With this new funding, Chameleon will continue to innovate and support its growing community, enabling groundbreaking discoveries in CS systems research.
ABOUT CHAMELEON: A PLATFORM FOR INNOVATION
Chameleon is a large-scale, deeply reconfigurable experimental ...
When performing resistance training such as lifting weights, there’s a lot of interest in how close you push yourself to failure – the point where you can’t do another rep – and how it affects your results.
While research has looked at this concept in different ways, to date, no meta-analysis has explored the pattern (i.e., linear or non-linear) of how the distance from failure (measured by repetitions in reserve) affects changes in muscle strength and size.
As such, it’s ...
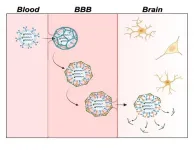
Neurotransmitter levels in the brain can indicate brain health and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. However, the protective blood-brain barrier (BBB) makes delivering fluorescent sensors that can detect these small molecules to the brain difficult. Now, researchers in ACS Central Science demonstrate a way of packaging these sensors for easy passage across the BBB in mice, allowing for improved brain imaging. With further development, the technology could help advance Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and treatment.
It is common for neurotransmitter levels ...
Millions of Americans take anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners. These medications work to prevent blood clots that cause heart attack and stroke.
More than two-thirds of those people take a type of blood thinner called a direct oral anticoagulant. DOACs, such as rivaroxaban (brand name Xarelto) and apixaban (brand name Eliquis), are under- or over-prescribed in up to one in eight patents.
These prescribing issues can have life threatening consequences, and they most often occur after a provider writes the initial prescription, according to a study led by Michigan Medicine.
“Direct oral anticoagulants may be viewed ...
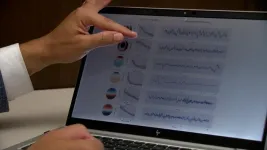
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic scientists are using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze electroencephalogram (EEG) tests more quickly and precisely, enabling neurologists to find early signs of dementia among data that typically go unexamined.
The century-old EEG, during which a dozen or more electrodes are stuck to the scalp to monitor brain activity, is often used to detect epilepsy. Its results are interpreted by neurologists and other experts trained to spot patterns among the test's squiggly waves.
In new research published in Brain Communications, scientists at the Mayo Clinic Neurology AI Program (NAIP) demonstrate ...
According to a World Health Organization (WHO) study (2017), about half of all infertility is due to men. Semen analysis is considered essential for diagnosis of male infertility, but is not readily available at medical institutions other than those specializing in infertility treatment, and there is a high threshold for receiving it.
In this study, a group led by Associate Professor Hideyuki Kobayashi of the Department of Urology, Toho University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan developed an AI model that can predict the risk ...
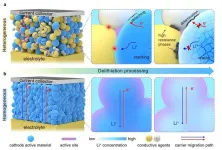
Researchers at the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with collaborators from leading international institutions, have introduced an innovative cathode homogenization strategy for all-solid-state lithium batteries (ASLBs).
This new approach, detailed in their recent publication in Nature Energy on July 31, significantly improves the cycle life and energy density of ASLBs, representing an important advancement in energy storage technology.
Current ASLBs face challenges due to heterogeneous composite cathodes, which require ...
Glioblastomas are highly aggressive, usually incurable brain tumors. If all therapeutic options are exhausted, patients have an average life expectancy of less than two years. Now researchers from the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK) at the West German Tumor Center Essen have made a surprising discovery: in the vicinity of glioblastomas, they found islands of highly potent immune cells in the neighboring bone marrow of the skull, which play a central role in defending against cancer. The new data may open up prospects ...
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease-related changes in Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies could be made possible by monitoring the amyloid-β (Aβ) and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) proteins. Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan also discovered the blood levels of neurofilament light chain (NfL) protein is elevated at an early stage of Parkinson's disease (PD) and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). This discovery may provide a method to identify potential patients and to make early interventions. The findings were published in npj Parkinson’s Disease.
The two forms of Lewy body disease are PD and DLB. ...
TORONTO, ON – A recent study of more than 2,700 older Canadians reported older adults with diabetes faced a heightened risk of depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this cohort, almost 50% of those who had a pre-pandemic history of depression experienced depression during the pandemic.
Those who experienced loneliness were among the most impacted.
“During the pandemic, loneliness almost tripled the risk of depression in older adults with diabetes,” says clinical pharmacist and first author ZhiDi Deng. “This not only highlights ...