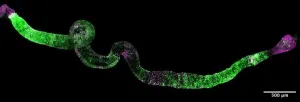
Advances in 3D organ bioprinting: A step towards personalized medicine and solving organ shortages
2024-08-01
(Press-News.org)
In a latest review published in Engineering, an international team of scientists from China and the United States has presented a comprehensive analysis of the latest advancements in 3D organ bioprinting. This innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize regenerative medicine and tackle some of the most pressing issues in organ transplantation.
Organ damage or failure, whether resulting from injury, disease, or aging, poses a significant challenge due to the body’s limited natural regenerative capabilities. Traditional organ transplantation, while lifesaving, is fraught with difficulties including donor shortages and the risk of immune rejection. This has spurred a quest for cutting-edge solutions, among which 3D bioprinting of organs on demand stands out as a promising avenue.
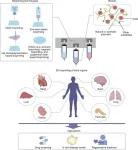
The review meticulously explores state-of-the-art bioprinting technologies, with a particular focus on bioinks and cell types crucial for successful organ fabrication. Bioinks, which are essential for constructing the complex structures of organs, and the selection of appropriate cells play a pivotal role in the bioprinting process. The scientists delve into the latest advancements in bioprinting various solid organs, including the heart, liver, kidney, and pancreas. They emphasize the critical importance of vascularization—creating the network of blood vessels necessary for organ function—and the integration of different cell types during the bioprinting process.
A key highlight of the review is the discussion on the challenges and future directions for the clinical translation of bioprinted organs. While the technology has shown great promise in preclinical studies, translating these successes into clinical applications involves overcoming significant hurdles. The review underscores the necessity for rigorous testing and regulatory validation to ensure the safety and reliability of bioprinted organs. Ensuring that these organs are not only functionally effective but also safe for patients is paramount.
In addition to technical challenges, the review also addresses ethical considerations surrounding organ bioprinting. Issues such as cell sourcing and the implications of modifying human biology are examined. Balancing the transformative potential of bioprinting with these ethical concerns presents a complex challenge that demands careful consideration.
Despite these challenges, the review paints an optimistic picture of the future. Bioprinting technology is seen as a major leap forward in biomedical sciences, with the potential to create replacement organs tailored to individual patients. This includes not only replicating the external anatomy of organs but also integrating the internal blood vessels and complex networks essential for their function. Such advancements could significantly mitigate organ shortages and provide personalized treatment options, fundamentally transforming organ transplantation and personalized medicine.
The review concludes with a forward-looking perspective on the potential of bioprinting to expand healthcare opportunities. By addressing both technical and ethical challenges, the field of bioprinting is poised to make significant strides toward meeting the needs of patients more effectively. The promise of this technology holds the potential to revolutionize the way we approach organ transplantation and personalized medicine, opening up new possibilities for patient care and treatment.
As the field continues to advance, the insights provided by this review will be instrumental in guiding future research and development in organ bioprinting. The excitement surrounding this technology reflects a shared vision of a future where organ shortages are alleviated and personalized treatments become a reality for patients around the world.
The paper “Progress in Organ Bioprinting for Regenerative Medicine,” authored by Xiang Wang, Di Zhang, Yogendra Pratap Singh, Miji Yeo, Guotao Deng, Jiaqi Lai, Fei Chen, Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, Yin Yu. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.04.023. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-01
The field of bridge engineering is witnessing a transformative era, as China leads the way with its recent advancements in constructing large-span arch bridges. Jielian Zheng, the member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering from Guangxi University, has authored a research article in Engineering, titled “Recent Construction Technology Innovations and Practices for Large-Span Arch Bridges in China.” The article elucidates the significant strides made in the construction of concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) and steel-reinforced concrete (SRC) ...
2024-08-01
(WASHINGTON, August 1, 2024) — In a year-long pilot program, external mentorship increased confidence, furthered career development, and facilitated networking opportunities for trainees in classical hematology, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
Classical hematology, the study of non-cancerous blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia and thrombotic and hemorrhagic disorders, is projected to face a significant workforce shortage in the coming years. The American Society of Hematology’s (ASH) previous surveys of hematology/oncology program ...
2024-08-01
Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers from Kyushu University have discovered that blowflies, a family of flies strongly attracted to decaying flesh and feces, are carrying the bird flu virus in southern Japan. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, introduce a potential new route of transmission for bird flu and highlight the need to develop new countermeasures to prevent and control the disease in poultry farms.
Since 2020, bird flu has been spreading rapidly around the globe, leading to the death of millions of wild birds and the culling ...
2024-08-01
In a recent study published in Engineering, a team of Chinese researchers has uncovered a startling correlation between stock market volatility and the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and suicide. The research, which analyzed over 12 million deaths across China from 2013 to 2019, provides compelling evidence that the psychological stress induced by stock market fluctuations has severe and immediate health implications.
The study, titled “Stock Volatility Increases the Mortality Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Suicide: A Case-Crossover Study of 12 Million Deaths,” is a wake-up call for investors, ...
2024-08-01
Judging how happy you are could backfire and negatively impact life satisfaction and psychological well-being, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
In three experiments comprising more than 1,800 participants, researchers found that having concerns or judgments about one’s own level of happiness were associated with lower well-being, due in part to greater negativity and disappointment about positive events.
The research was published in the journal Emotion.
Thinking too much about one’s own level of happiness could be related to fears about not measuring up or not being as happy as other people, said lead researcher Felicia ...
2024-08-01
In the United States and worldwide, cardiovascular disease is the leading avoidable cause of premature death and disability. Primarily heart attacks and stroke, cardiovascular disease accounts for more than 900,000 annual deaths nationally and about 10 million deaths globally.
Uncontrolled hypertension or high blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke and heart attacks. Prevention and management of cardiovascular disease involves therapeutic lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise and adjunctive drug therapies of proven benefit.
In a commentary published in The American ...
2024-08-01
Researchers including those from the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences transferred genes from simple organisms capable of regenerating their bodies into common fruit flies, more complex animals that cannot. They found the transferred gene suppressed an age-related intestinal issue in the flies. Their results suggest studying genes specific to animals with high regenerative capability may uncover new mechanisms for rejuvenating stem cell function and extending the healthy lifespan ...
2024-08-01
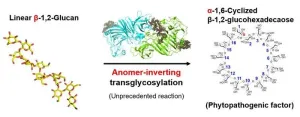
Plant diseases pose significant challenges to agricultural productivity, presenting formidable hurdles that require urgent attention. Left unchecked, these diseases can spread rapidly, inflicting widespread damage on crops and leading to reduced yields and substantial economic losses. Therefore, accurately identifying the pathogens responsible for these diseases is crucial. This identification allows for targeted interventions that minimize risks and effectively mitigate the agricultural impacts.
Xanthomonas species are notorious plant pathogens that affect a broad spectrum of hosts, including key crops like rice, wheat, and tomatoes. These pathogens augment ...
2024-08-01
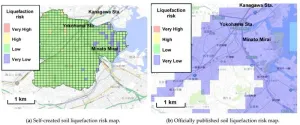
The development of human societies is concurrent with infrastructural changes, evidenced by rapid urbanization in recent years. We are moving towards the era of 'smart cities' powered by advanced technology—such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things, and big data analytics—for sustainable urban development. However, climate change has been hampering this growth—earthquakes and other natural hazards negatively impact buildings and other structures in their wake.
Soil liquefaction is an example of a natural ...
2024-08-01
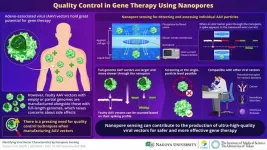
Over the past few decades, there has been remarkable progress in genetic manipulation technologies, bringing us closer to the point where genes can be modified in vivo. Such tools would open up the way to gene therapy, ushering in a new era in medicine. Thus far, the most promising strategies for gene therapy involve leveraging the existing molecular machinery found in viruses.
In particular, adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have recently garnered significant attention from the scientific community, given their potential to serve as nucleic acid vaccines ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Advances in 3D organ bioprinting: A step towards personalized medicine and solving organ shortages