(Press-News.org) Judging how happy you are could backfire and negatively impact life satisfaction and psychological well-being, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
In three experiments comprising more than 1,800 participants, researchers found that having concerns or judgments about one’s own level of happiness were associated with lower well-being, due in part to greater negativity and disappointment about positive events.
The research was published in the journal Emotion.
Thinking too much about one’s own level of happiness could be related to fears about not measuring up or not being as happy as other people, said lead researcher Felicia Zerwas, PhD, who was a doctoral student at the University of California-Berkeley during this research and is now a postdoctoral researcher at New York University.
“There are plenty of societal pressures, at least within the United States, which encourage the fallacy that people must feel happy all of the time to achieve greater well-being,” she said. “Overall, allowing yourself to experience your emotions, whether they are positive or negative, with an accepting attitude could be a useful tool for pursuing happiness and increasing well-being.”
Contrary to some previous studies, the current research found that the pursuit of happiness, or viewing happiness as a very important goal, didn’t have any detrimental impacts on well-being. However, judging one’s own level of happiness did. The research included various samples of participants, including Yale University students, community members from Denver and Berkeley, California, and online studies with participants from the United States and Canada.
The participants answered questions about their beliefs about happiness, as well as their psychological well-being and depressive symptoms. Being concerned about one’s own happiness was associated with lower overall life satisfaction and psychological well-being, as well as greater depressive symptoms.
The research also found that having concerns about one’s own happiness was associated with greater negativity about positive events.
“Having high expectations for one’s happiness can be detrimental because it makes it more difficult to achieve the level of happiness that we are expecting from a positive event,” Zerwas said.
Article: “Unpacking the Pursuit of Happiness: Being Concerned About Happiness but Not Aspiring to Happiness Is Linked with Negative Meta-Emotions and Worse Well-Being,” Felicia Zerwas, PhD, Oliver John, PhD, and Iris Mauss, PhD, University of California Berkeley, and Brett Ford, PhD, University of Toronto, Emotion, published online Aug. 1, 2024.
Contact: Felicia Zerwas, PhD, can be contacted at fz2338@nyu.edu.
The American Psychological Association, in Washington, D.C., is the largest scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the United States. APA’s membership includes over 157,000 researchers, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. Through its divisions in 54 subfields of psychology and affiliations with 60 state, territorial and Canadian provincial associations, APA works to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve lives.
END
Judging your own happiness could backfire
Experiencing emotions with acceptance is more useful, study finds
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Uncontrolled hypertension: The old ‘silent killer’ is alive and well
2024-08-01
In the United States and worldwide, cardiovascular disease is the leading avoidable cause of premature death and disability. Primarily heart attacks and stroke, cardiovascular disease accounts for more than 900,000 annual deaths nationally and about 10 million deaths globally.
Uncontrolled hypertension or high blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke and heart attacks. Prevention and management of cardiovascular disease involves therapeutic lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise and adjunctive drug therapies of proven benefit.
In a commentary published in The American ...
Talking about regeneration
2024-08-01
Researchers including those from the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences transferred genes from simple organisms capable of regenerating their bodies into common fruit flies, more complex animals that cannot. They found the transferred gene suppressed an age-related intestinal issue in the flies. Their results suggest studying genes specific to animals with high regenerative capability may uncover new mechanisms for rejuvenating stem cell function and extending the healthy lifespan ...
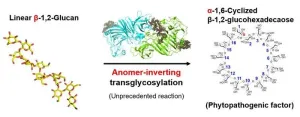
Breakthrough in plant disease: New enzyme could lead to anti-bacterial pesticides
2024-08-01
Plant diseases pose significant challenges to agricultural productivity, presenting formidable hurdles that require urgent attention. Left unchecked, these diseases can spread rapidly, inflicting widespread damage on crops and leading to reduced yields and substantial economic losses. Therefore, accurately identifying the pathogens responsible for these diseases is crucial. This identification allows for targeted interventions that minimize risks and effectively mitigate the agricultural impacts.
Xanthomonas species are notorious plant pathogens that affect a broad spectrum of hosts, including key crops like rice, wheat, and tomatoes. These pathogens augment ...
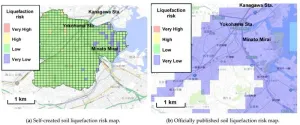
Towards smart cities: Predicting soil liquefaction risk using artificial intelligence
2024-08-01
The development of human societies is concurrent with infrastructural changes, evidenced by rapid urbanization in recent years. We are moving towards the era of 'smart cities' powered by advanced technology—such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things, and big data analytics—for sustainable urban development. However, climate change has been hampering this growth—earthquakes and other natural hazards negatively impact buildings and other structures in their wake.
Soil liquefaction is an example of a natural ...
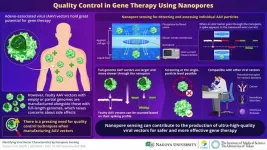
Novel nanosensing technique for quality control of viral vectors in gene therapy
2024-08-01
Over the past few decades, there has been remarkable progress in genetic manipulation technologies, bringing us closer to the point where genes can be modified in vivo. Such tools would open up the way to gene therapy, ushering in a new era in medicine. Thus far, the most promising strategies for gene therapy involve leveraging the existing molecular machinery found in viruses.
In particular, adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have recently garnered significant attention from the scientific community, given their potential to serve as nucleic acid vaccines ...
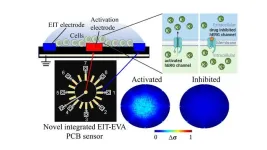
Electrical impedance tomography–extracellular voltage activation technique simplifies drug screening
2024-08-01
When developing new drugs, understanding their effects on ion channels in the body, such as the human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) ion channel found in neurons and heart muscle cells, is critical. Blocking hERG channels can disrupt normal heart rhythm, potentially leading to a fatal condition known as torsade de pointes. Current methods for assessing these effects typically involve invasive procedures like patch-clamp techniques or fluorescence microscopy. These methods alter cell properties and may affect measurement accuracy, requiring specialized equipment ...
Research catalogs greenhouse gas emissions tied to energy use for interbasin water transfers
2024-08-01
Much of the water in the West is transported across vast geographical areas by large infrastructure projects known as interbasin water transfers. Two of these projects in particular make up 85% of all energy-related greenhouse gas emissions associated with U.S. interbasin transfers — one in Arizona and the other in California — according to the new research published this week in the journal Nature Water.
The project in Arizona is known as the Central Arizona Project and in California it’s the State Water Project.
“You hear a lot about these big projects and how much energy they use,” said Avery Driscoll, a doctoral student in ...
Largest study to date finds multiple urinary metals play key role in cardiovascular disease and mortality
2024-08-01
Higher levels of urinary metals such as cadmium, tungsten, uranium, cobalt, copper and zinc are linked to increased cardiovascular disease and mortality in a racially and ethnically diverse U.S. population, according to a new study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. While it is well documented that exposure to certain metals has been associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality, until now the evidence was limited beyond arsenic, cadmium, and lead and for a racially diverse population. The findings are published in the journal Circulation.
When analyzed together, ...
Tipping risks from overshooting 1.5 °C can be minimised if warming is swiftly reversed
2024-08-01
Human-made climate change can lead to a destabilisation of large-scale components of the Earth system such as ice sheets or ocean circulation patterns, the so-called tipping elements. While these components will not tip over night, fundamental processes are put into motion unfolding over tens, hundreds or thousands of years. These changes are of such a serious nature that they should be avoided at all costs, the researchers argue. In their new study, they assessed the risks of destabilisation of at least one ...
Which strains of tuberculosis are the most infectious?
2024-08-01
For some forms of tuberculosis, the chances that an exposed person will get infected depend on whether the individual and the bacteria share a hometown, according to a new study comparing how different strains move through mixed populations in cosmopolitan cities.
Results of the research, led by Harvard Medical School scientists and published Aug. 1 in Nature Microbiology, provide the first hard evidence of long-standing observations that have led scientists to suspect that pathogen, place, and human host ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
[Press-News.org] Judging your own happiness could backfireExperiencing emotions with acceptance is more useful, study finds