(Press-News.org) Human-made climate change can lead to a destabilisation of large-scale components of the Earth system such as ice sheets or ocean circulation patterns, the so-called tipping elements. While these components will not tip over night, fundamental processes are put into motion unfolding over tens, hundreds or thousands of years. These changes are of such a serious nature that they should be avoided at all costs, the researchers argue. In their new study, they assessed the risks of destabilisation of at least one tipping element as a result of overshooting 1.5 °C. Their analysis shows how crucial it is for the state of the planet to adhere to the climate objectives of the Paris Agreement. It further emphasises the legacy of today’s climate (in)action for centuries to millennia to come.
“While timescales to 2300 or beyond may seem far away, it is important to map out tipping risks to the best of our abilities. Our results show how vitally important it is to achieve and maintain net-zero greenhouse gas emissions in order to limit these risks for the next hundreds of years and beyond,“ explains co-lead author Tessa Möller, scientist at IIASA and PIK. “Our calculations reveal that following current policies until the end of this century would lead to a high tipping risk of 45 percent of at least one of the four elements tipping by 2300.”
Exceeding 2 °C global warming strongly increases tipping risks
“We see an increase in tipping risk with every tenth of a degree of overshoot above 1.5 °C. But if we were to also surpass 2 °C of global warming, tipping risks would escalate even more rapidly. This is very concerning as scenarios that follow currently implemented climate policies are estimated to result in about 2.6 °C of global warming by the end of this century,” says Annika Ernest Högner from PIK, who co-lead the study.
“Our study confirms that tipping risks in response to overshoots can be minimised if warming is swiftly reversed. Such a reversal of global warming can only be achieved if greenhouse gas emissions reach at least net-zero by 2100. The results underline the importance of the Paris Agreement’s climate objectives to limit warming to well below 2 °C even in case of a temporary overshoot above 1.5 °C,“ says study author Nico Wunderling of PIK.
The four tipping elements analysed in the study are pivotal in regulating the stability of the Earth’s climate system. So far, complex Earth system models are not yet able to comprehensively simulate their non-linear behaviour, feedbacks, and interactions between some of the tipping elements. Therefore, the researchers used a stylised Earth system model to represent the main characteristics and behaviour and thereby systematically include relevant uncertainties in tipping elements and their interactions.
"This analysis of tipping point risks adds further support to the conclusion that we are underestimating risks, and need to now recognise that the legally binding objective in the Paris Agreement of holding global warming to ‘well below 2°C’, in reality means limiting global warming to 1.5°C. Due to insufficient emission reductions, we run an ever increasing risk of a period overshooting this temperature limit, which we need to minimise at all costs, to reduce dire impacts to people across the world,” concludes PIK director and author of the study Johan Rockström.
Article:
Tessa Möller, Annika Ernest Högner, Carl-Friedrich Schleussner, Samuel Bien, Niklas H. Kitzmann, Robin D. Lamboll, Joeri Rogelj, Jonathan F. Donges, Johan Rockström & Nico Wunderling (2024): Achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions critical to limit climate tipping risks. Nature Communications. [DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49863-0]
Weblink to the article, once published:
https://www.nature.com/articles/41467-024-49863-0
END
Tipping risks from overshooting 1.5 °C can be minimised if warming is swiftly reversed
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Which strains of tuberculosis are the most infectious?
2024-08-01
For some forms of tuberculosis, the chances that an exposed person will get infected depend on whether the individual and the bacteria share a hometown, according to a new study comparing how different strains move through mixed populations in cosmopolitan cities.
Results of the research, led by Harvard Medical School scientists and published Aug. 1 in Nature Microbiology, provide the first hard evidence of long-standing observations that have led scientists to suspect that pathogen, place, and human host ...
New AI tool simplifies heart monitoring: Fewer leads, same accuracy
2024-08-01
LA JOLLA, CA—To diagnose heart conditions including heart attacks and heart rhythm disturbances, clinicians typically rely on 12-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs)—complex arrangements of electrodes and wires placed around the chest and limbs to detect the heart’s electrical activity. But these ECGs require specialized equipment and expertise, and not all clinics have the capability to perform them.
Now, a team of scientists and clinicians from Scripps Research has shown that heart conditions can be diagnosed roughly as accurately using just three electrodes and an artificial intelligence (AI) tool. In a ...
Tipping risks from overshooting 1.5°C can be minimized if warming is swiftly reversed
2024-08-01
Current climate policies imply a high risk for tipping of critical Earth system elements, even if temperatures return to below 1.5°C of global warming after a period of overshoot. A new study indicates that these risks can be minimized if warming is swiftly reversed.
Human-made climate change can lead to a destabilization of large-scale components of the Earth system such as ice sheets, ocean circulation patterns, or global biosphere components, the so-called tipping elements. In their new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from IIASA and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) analyzed the risks for four interconnected core climate tipping elements ...
Comprehensive meta-analysis pinpoints what vaccination strategies different countries should adopt
2024-08-01
Vaccines are safe and effective, and help reduce death and illness. But global vaccination rates are suboptimal and have trended downward, leaving humanity more vulnerable to vaccine-preventable diseases such as COVID-19, influenza, measles, polio, and HPV.
Identifying interventions that could increase vaccine coverage could help save lives. A new paper from a team led by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania offers the first comprehensive meta-analysis examining what types of vaccine intervention strategies have the ...
Predicting the future: Easy tool helps estimate fall risks
2024-08-01
Osaka, Japan — An aging society has posed a new global problem, the risk of falling. It is estimated that 1 in 3 adults over the age of 65 falls each year and the resulting injuries are becoming more prevalent.
To tackle this growing issue, Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda and Specially Appointed Professor Tadashi Okano from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine, together with Professor Chisato Hayashi from the University of Hyogo, have developed a formula and assessment tool for estimating fall risks that is simple for older adults to use. The tool was developed using data collected from older adults over a ten-year period from April 2010 to December ...
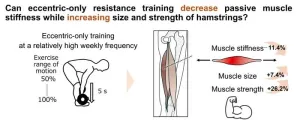
Eccentric-only resistance training can lower passive muscle stiffness
2024-08-01
Resistance, or weight training, is widely recommended in sports and rehabilitation as an effective exercise to increase muscular strength and size. This form of exercise involves applying resistance to muscle contraction to build strength. However, some practitioners believe resistance training can increase passive muscle stiffness over time. Passive muscle stiffness is a key indicator of how muscles behave mechanically when they are stretched without active contraction. Specifically, it refers to the amount of force required to change the muscle length by a given amount during passive stretching. Studies ...
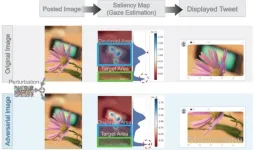
Enhancing automatic image cropping models with advanced adversarial techniques
2024-08-01
Image cropping is an essential task in many contexts, right from social media and e-commerce to advanced computer vision applications. Cropping helps maintain image quality by avoiding unnecessary resizing, which can degrade the image and consume computational resources. It is also useful when an image needs to conform to a predetermined aspect ratio, such as in thumbnails. Over the past decade, engineers around the world have developed various machine learning (ML) models to automatically crop images. These models aim to crop an input image in a way that preserves its most relevant parts.
However, ...
$2.4 million grant helping MCG scientists better understand what happens to our skeleton as we age
2024-08-01
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Aug. 1, 2024) – Figuring out how the tissues in our bones, adrenal glands, muscle and fat “talk” to each other could help scientists better understand what happens to our skeletons with age, when our bones tend to lose mass and become weaker, leaving us at risk for falls and fractures.
“Tissues don’t function in isolation – everything in the body “talks” to everything else to keep people healthy across the lifespan,” explains Meghan McGee-Lawrence, PhD, bone biologist at the Medical College of Georgia at ...
Using AI, USC researchers pioneer a potential new immunotherapy approach for treating glioblastoma
2024-08-01
In an innovative new study of glioblastoma, scientists used artificial intelligence (AI) to reprogram cancer cells, converting them into dendritic cells (DCs), which can identify cancer cells and direct other immune cells to kill them.
Glioblastoma is the most common brain cancer in adults and also the deadliest, with less than 10% of patients surviving five years after their diagnosis. While new approaches such as immunotherapy have revolutionized treatment for other cancers, they have done little for patients with glioblastoma. That is partly because these hard-to-reach brain tumors ...
High blood pressure associated with environmental contamination by tellurium
2024-08-01
The likelihood of developing high blood pressure (hypertension) increases with higher levels of tellurium, a contaminant transferred from mining and manufacturing activities to foods. Improved monitoring of tellurium levels in specific foods could help decrease high blood pressure in the general population. The results of a study examining the relationship between tellurium exposure and hypertension were published in the journal Environment International.
The study was led by Nagoya University in Japan. According to Takumi Kagawa, one of the researchers involved in the ...