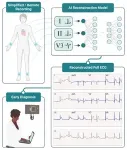
(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—To diagnose heart conditions including heart attacks and heart rhythm disturbances, clinicians typically rely on 12-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs)—complex arrangements of electrodes and wires placed around the chest and limbs to detect the heart’s electrical activity. But these ECGs require specialized equipment and expertise, and not all clinics have the capability to perform them.
Now, a team of scientists and clinicians from Scripps Research has shown that heart conditions can be diagnosed roughly as accurately using just three electrodes and an artificial intelligence (AI) tool. In a study published on August 1, 2024, in npj Digital Medicine, the scientists report that their AI algorithm can recreate full 12-lead ECGs with data from only three ECG leads. Moreover, clinicians can identify heart attacks with nearly the same accuracy when they review the AI-generated ECGs as compared to original 12-lead ECGs.
“This opens up the door to patients being able to get really high-quality, time-sensitive clinical data without traveling to somewhere that has a 12-lead ECG,” says cardiologist Evan Muse, MD, PhD, the lead of cardiovascular genomics at Scripps Research Translational Institute, assistant professor of Molecular Medicine at Scripps Research and co-senior author of the new paper. “It likely means not only increased access to ECG technology, but decreased costs and improved patient safety.”
To build the new AI tool, the team used data from more than 600,000 12-lead ECGs that had been collected from patients. About half of those ECGs had normal health rhythms, while the rest had a variety of heart conditions. Giorgio Quer, PhD, director of artificial intelligence at Scripps Research Translational Institute, assistant professor of Digital Medicine at Scripps Research and co-senior author of the paper, then began testing which combinations of just two or three electrodes could be used for AI to fully recreate the 12-lead data.
“We knew that leads are somehow related. Deep learning algorithms allowed us to process a very large dataset and understand these relationships among the leads, enabling the reconstruction of the full 12-lead. We started out hoping to get a full reconstruction from just limb leads, because those are the easiest for non-specialists to set up,” says Quer. “But we found that we got much better data when we added a chest lead as well.”
The researchers then took a set of 238 ECGs, with half showing signs of a heart attack. They showed cardiologists either the original 12-lead ECG or an ECG reconstructed by AI using data from the three selected leads. The cardiologists could not identify which was which, and they also correctly identified heart attack indicators 81.4 percent of the time in the AI-generated ECGs—very close to the 84.6 percent accuracy of original 12-lead ECGs.
“It was important to us that we not only show that this algorithm works at a technical level, but that the data generated by the algorithm can be accurately interpreted by cardiologists,” says Quer.
The researchers say that before the algorithm can be used for clinical decision making, prospective studies will be needed with different patient populations and in different clinical settings. However, if the tool continues to perform well, it could open the door to ECGs being carried out in new settings with less specialized equipment and clinicians—and for patients, that means faster diagnoses and treatments.
“This is an optimal case for AI—taking a few leads of the (12-lead) electrocardiogram—to make it remarkably informative, which has big practical implications for patients in the future,” says Eric Topol, MD, director and founder of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and executive vice president of Scripps Research.
The research is part of a growing portfolio of work that expands the use of AI tools in screening for and diagnosing heart conditions. In 2023, Quer’s group reported that a single ECG patch worn for two weeks could help determine which patients were most at risk of atrial fibrillation.
“This new work is just one example of how we can use AI to enable things that we could never do in the past,” says Quer.
In addition to Quer, Muse, and Topol, authors of the study, “AI-Enhanced Reconstruction of the 12-Lead Electrocardiogram via 3-Leads with Accurate Clinical Assessment,” are Amitabh Pandey and Matteo Gadaleta of Scripps Research.
This work was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health (UM1TR004407 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and R21AG072349 from the National Institute on Aging).
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr-Skaggs, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
END
New AI tool simplifies heart monitoring: Fewer leads, same accuracy
Scripps Research scientists showed that, with help from an AI tool, cardiologists can diagnose heart attacks using a simpler, easier and more accessible electrocardiogram technology.
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tipping risks from overshooting 1.5°C can be minimized if warming is swiftly reversed
2024-08-01
Current climate policies imply a high risk for tipping of critical Earth system elements, even if temperatures return to below 1.5°C of global warming after a period of overshoot. A new study indicates that these risks can be minimized if warming is swiftly reversed.
Human-made climate change can lead to a destabilization of large-scale components of the Earth system such as ice sheets, ocean circulation patterns, or global biosphere components, the so-called tipping elements. In their new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from IIASA and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) analyzed the risks for four interconnected core climate tipping elements ...
Comprehensive meta-analysis pinpoints what vaccination strategies different countries should adopt
2024-08-01
Vaccines are safe and effective, and help reduce death and illness. But global vaccination rates are suboptimal and have trended downward, leaving humanity more vulnerable to vaccine-preventable diseases such as COVID-19, influenza, measles, polio, and HPV.
Identifying interventions that could increase vaccine coverage could help save lives. A new paper from a team led by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania offers the first comprehensive meta-analysis examining what types of vaccine intervention strategies have the ...
Predicting the future: Easy tool helps estimate fall risks
2024-08-01
Osaka, Japan — An aging society has posed a new global problem, the risk of falling. It is estimated that 1 in 3 adults over the age of 65 falls each year and the resulting injuries are becoming more prevalent.
To tackle this growing issue, Associate Professor Hiromitsu Toyoda and Specially Appointed Professor Tadashi Okano from Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine, together with Professor Chisato Hayashi from the University of Hyogo, have developed a formula and assessment tool for estimating fall risks that is simple for older adults to use. The tool was developed using data collected from older adults over a ten-year period from April 2010 to December ...
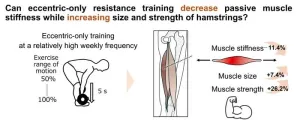
Eccentric-only resistance training can lower passive muscle stiffness
2024-08-01
Resistance, or weight training, is widely recommended in sports and rehabilitation as an effective exercise to increase muscular strength and size. This form of exercise involves applying resistance to muscle contraction to build strength. However, some practitioners believe resistance training can increase passive muscle stiffness over time. Passive muscle stiffness is a key indicator of how muscles behave mechanically when they are stretched without active contraction. Specifically, it refers to the amount of force required to change the muscle length by a given amount during passive stretching. Studies ...
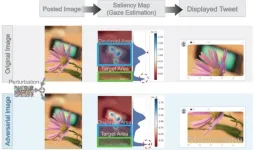
Enhancing automatic image cropping models with advanced adversarial techniques
2024-08-01
Image cropping is an essential task in many contexts, right from social media and e-commerce to advanced computer vision applications. Cropping helps maintain image quality by avoiding unnecessary resizing, which can degrade the image and consume computational resources. It is also useful when an image needs to conform to a predetermined aspect ratio, such as in thumbnails. Over the past decade, engineers around the world have developed various machine learning (ML) models to automatically crop images. These models aim to crop an input image in a way that preserves its most relevant parts.
However, ...
$2.4 million grant helping MCG scientists better understand what happens to our skeleton as we age
2024-08-01
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Aug. 1, 2024) – Figuring out how the tissues in our bones, adrenal glands, muscle and fat “talk” to each other could help scientists better understand what happens to our skeletons with age, when our bones tend to lose mass and become weaker, leaving us at risk for falls and fractures.
“Tissues don’t function in isolation – everything in the body “talks” to everything else to keep people healthy across the lifespan,” explains Meghan McGee-Lawrence, PhD, bone biologist at the Medical College of Georgia at ...
Using AI, USC researchers pioneer a potential new immunotherapy approach for treating glioblastoma
2024-08-01
In an innovative new study of glioblastoma, scientists used artificial intelligence (AI) to reprogram cancer cells, converting them into dendritic cells (DCs), which can identify cancer cells and direct other immune cells to kill them.
Glioblastoma is the most common brain cancer in adults and also the deadliest, with less than 10% of patients surviving five years after their diagnosis. While new approaches such as immunotherapy have revolutionized treatment for other cancers, they have done little for patients with glioblastoma. That is partly because these hard-to-reach brain tumors ...
High blood pressure associated with environmental contamination by tellurium
2024-08-01
The likelihood of developing high blood pressure (hypertension) increases with higher levels of tellurium, a contaminant transferred from mining and manufacturing activities to foods. Improved monitoring of tellurium levels in specific foods could help decrease high blood pressure in the general population. The results of a study examining the relationship between tellurium exposure and hypertension were published in the journal Environment International.
The study was led by Nagoya University in Japan. According to Takumi Kagawa, one of the researchers involved in the ...
Pursuing the middle path to scientific discovery
2024-08-01
In electronic technologies, key material properties change in response to stimuli like voltage or current. Scientists aim to understand these changes in terms of the material’s structure at the nanoscale (a few atoms) and microscale (the thickness of a piece of paper). Often neglected is the realm between, the mesoscale — spanning 10 billionths to 1 millionth of a meter.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, in collaboration with Rice University and DOE’s Lawrence ...
Salk awarded $3.6 million by the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine to advance research on brain aging
2024-08-01
LA JOLLA (July 31, 2024)—The Salk Institute was awarded $3.6 million by the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), one of the world’s largest institutions dedicated to regenerative medicine. Salk Professor Rusty Gage will lead the new CIRM-funded Shared Resources Laboratory focused on stem cell-based models of aging and neurodegeneration.
The award is part of CIRM’s latest round of funding to address challenges in the regenerative medicine field. The state agency dedicated $27 million to help establish six new Shared Resources ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] New AI tool simplifies heart monitoring: Fewer leads, same accuracyScripps Research scientists showed that, with help from an AI tool, cardiologists can diagnose heart attacks using a simpler, easier and more accessible electrocardiogram technology.