(Press-News.org) About The Study: This qualitative study found that semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products. Two websites evaluated were sent FDA warning letters for unlawful sale of unapproved and misbranded semaglutide. U.S. poison centers have reported a 1500% increase in calls related to semaglutide, highlighting the need for enhanced pharmacovigilance including for online sourcing harms.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tim K. Mackey, MAS, PhD, email tkmackey@ucsd.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.28280)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.28280?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=080224
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Safety and risk assessment of no-prescription online semaglutide purchases
JAMA Network Open
2024-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Glycated hemoglobin A1c time in range and dementia in older adults with diabetes
2024-08-02
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that for older adults with diabetes, maintaining hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) stability in individualized target ranges over time is associated with a lower risk of Alzheimer disease and related dementias. Lower HbA1c time in range may identify patients at increased risk of Alzheimer disease and related dementias.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paul R. Conlin, MD, email paul.conlin@va.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
Mast cells trap and use living neutrophils during allergic reactions
2024-08-02
Inflammation is the body's response to harmful stimuli, characterized by heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of tissue function. When balanced, inflammation protects the body by clearing harmful agents and initiating tissue repair. However, excessive inflammation can cause tissue destruction and disease. Key players in this process are various immune cells, which work together during inflammation. The type of immune cells involved often varies depending on the harmful stimulus, influencing the outcome of the inflammatory response.
Immune cell trapping during allergic responses
Mast cells, residing in tissues and critical for initiating ...
Exploding popularity of Ozempic and Wegovy among privately insured patients may worsen disparities
2024-08-02
A new USC study suggests that publicly insured individuals who are most likely to benefit from new drugs for diabetes and obesity are less likely to get them than those with private insurance.
Prescription fills for the drug best known as Ozempic or Wegovy — semaglutide — increased by more than 400% between January 2021 and December 2023, according to research out today in JAMA Health Forum.
Approved first for type 2 diabetes, then for weight loss, studies show that semaglutide also improves blood pressure and reduces cardiovascular disease — problems that plague millions of Americans. Yet the lion’s share of prescriptions ...
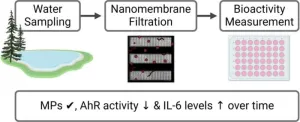
Sizing up microplastics: Nanofiltration uncovers environmental bioactivity
2024-08-02
A new study reveals the bioactivity of microplastics in Lake Ontario using cutting-edge nanomembrane filtering technology. Researchers found all samples contained microplastics ranging between 8 and 20 µm. The study highlights varying bioactivity levels, such as aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activity and IL-6 levels, indicating potential health risks. These findings underscore the urgent need for further research to comprehend the impact of microplastics on human health and the environment. This pioneering approach offers fresh insights into tackling the challenges posed by microplastic pollution.
Microplastics ...
What gave the first molecules their stability?
2024-08-02
The origins of life remain a major mystery. How were complex molecules able to form and remain intact for prolonged periods without disintegrating? A team at ORIGINS, a Munich-based Cluster of Excellence, has demonstrated a mechanism that could have enabled the first RNA molecules to stabilize in the primordial soup. When two RNA strands combine, their stability and lifespan increase significantly.
In all likelihood, life on Earth began in water, perhaps in a tide pool that was cut off from seawater at low tide but flooded by waves at high tide. Over billions of years, complex molecules like DNA, RNA and proteins ...
Cold antimatter for quantum state-resolved precision measurements
2024-08-02
Why does the universe contain matter and (virtually) no antimatter? The BASE international research collaboration at the European Organisation for Nuclear Research (CERN) in Geneva, headed by Professor Dr Stefan Ulmer from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU), has achieved an experimental breakthrough in this context. It can contribute to measuring the mass and magnetic moment of antiprotons more precisely than ever before – and thus identify possible matter-antimatter asymmetries. BASE has developed a trap, which can cool individual antiprotons much more rapidly ...
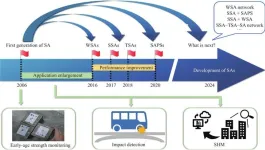
Smart aggregates: The future of infrastructure health monitoring
2024-08-02
The proliferation of concrete infrastructure worldwide has been met with growing concerns over its durability and safety. Concrete structures are increasingly subjected to dynamic forces from natural disasters like earthquakes and environmental degradation, such as corrosion. These factors, coupled with the saturation of infrastructure projects, amplify the risks associated with structural failure. Consequently, there is a pressing need for effective structural health monitoring (SHM) systems that can preemptively identify and address these vulnerabilities. The ...
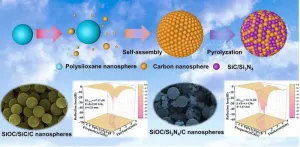
Synthesis of SiOC@C ceramic nanospheres with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance
2024-08-02
In recent years, microwave technology has dramatically progressed, marked by the arrival of the 5G era, owing to the advantages of electromagnetic waves in long-distance, wireless, and high-speed transmissions. However, electromagnetic wave pollution problems such as electromagnetic wave interference and electromagnetic wave radiation are becoming increasingly serious. Electromagnetic wave pollution not only affects the normal operation of electronic equipment, greatly threatens the information security of the scientific community, but also endangers human health and is a possible cause of cancer ...
NWSL add lifesavers to the chain of survival in New York City
2024-08-02
NEW YORK CITY, August 2, 2024 — According to American Heart Association data, nine out of every ten people who experience cardiac arrest outside of a hospital die, in part because they do not receive immediate CPR more than half of the time. CPR, especially if performed immediately, can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. That is why the American Heart Association and the National Women’s Soccer League (NWSL) brought cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training to NWSL staff at the New York headquarters office located on Madison ...
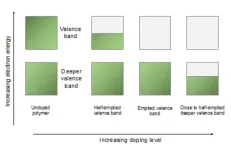
Solving the doping problem: Enhancing performance in Organic Semiconductors
2024-08-02
Cavendish physicists have discovered two new ways to improve organic semiconductors. They found a way to remove more electrons from the material than previously possible and used unexpected properties in an environment known as the non-equilibrium state, boosting its performance for use in electronic devices.
“We really wanted to hit the nail and figure out what is happening when you heavily dope polymer semiconductors,’ said Dr Dionisius Tjhe, Postdoctoral Research Associate at the Cavendish Laboratory. Doping is the process of removing or adding electrons into a semiconductor, increasing its ability to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
[Press-News.org] Safety and risk assessment of no-prescription online semaglutide purchasesJAMA Network Open