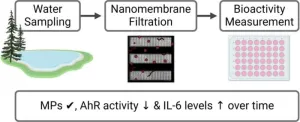
A new study reveals the bioactivity of microplastics in Lake Ontario using cutting-edge nanomembrane filtering technology. Researchers found all samples contained microplastics ranging between 8 and 20 µm. The study highlights varying bioactivity levels, such as aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activity and IL-6 levels, indicating potential health risks. These findings underscore the urgent need for further research to comprehend the impact of microplastics on human health and the environment. This pioneering approach offers fresh insights into tackling the challenges posed by microplastic pollution.
Microplastics are a significant pollutant present in ecosystems worldwide, including oceans, lakes, and rivers. These particles pose potential health risks due to their persistence and complex composition, which includes various toxic chemicals. Prior research has highlighted the widespread presence of microplastics and their potential impact on human health. Based on these challenges, it is crucial to conduct in-depth studies on the bioactivity of microplastics in environmental samples to assess their health risks.
A study (DOI: 10.1016/j.eehl.2024.05.004) conducted by the University of Rochester Medical Center, published in Eco-Environment & Health on 29 May 2024, investigates the bioactivity of microplastics in Lake Ontario using silicon nitride nanomembrane technology. Researchers isolated debris between 8 and 20 µm from water samples collected at different times and locations. By analyzing cell viability, aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activity, and IL-6 levels, the study aims to provide insights into the potential health risks posed by microplastics.
The study utilized innovative nanomembrane filtering technology to isolate and analyze microplastic-containing debris from Lake Ontario. Researchers collected samples from four locations at different times, using silicon nitride nanomembrane filters to isolate debris between 8 and 20 µm. Nile Red staining confirmed the presence of microplastics in all samples. Cell-based assays assessed cell viability, AhR activity, and IL-6 levels, revealing that while microplastics were consistently present, their bioactivity varied over time. The isolated debris showed no impact on cell viability, indicating a lack of cytotoxicity. However, variations in AhR activity and IL-6 levels suggest that the bioactivity of microplastics depends on their physicochemical properties. The study emphasizes the need for more extensive sampling to fully characterize microplastic bioactivity and understand the influence of sample properties.
Dr. Sarah E. Morgan, lead researcher, stated, "Our findings demonstrate the potential health risks posed by microplastics in Lake Ontario. The variability in bioactivity observed highlights the importance of understanding the physicochemical properties of these particles. This study underscores the need for more extensive sampling and analysis to fully assess the health implications of microplastic exposure. The novel nanomembrane filtering technology we employed offers a promising approach for future research in this field."
The implications of this research are far-reaching, offering a new methodology for environmental monitoring and health risk assessment. By enhancing our ability to detect and analyze microplastics, the study paves the way for more targeted strategies to mitigate plastic pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems. Moreover, the insights gained could inform regulatory measures and public health policies aimed at reducing exposure to these pervasive contaminants.
###
References
DOI
10.1016/j.eehl.2024.05.004
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2024.05.004
Funding information
This work was supported by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS R01 ES021492), the University of Rochester Toxicology Training Program (NIEHS T32 ES007026), and the University of Rochester Environmental Health Sciences Center (NIEHS P30 ES001247).
About Eco-Environment & Health
Eco-Environment & Health (EEH) is an international and multidisciplinary peer-reviewed journal designed for publications on the frontiers of the ecology, environment and health as well as their related disciplines. EEH focuses on the concept of "One Health" to promote green and sustainable development, dealing with the interactions among ecology, environment and health, and the underlying mechanisms and interventions. Our mission is to be one of the most important flagship journals in the field of environmental health.
END
Sizing up microplastics: Nanofiltration uncovers environmental bioactivity
2024-08-02
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What gave the first molecules their stability?
2024-08-02
The origins of life remain a major mystery. How were complex molecules able to form and remain intact for prolonged periods without disintegrating? A team at ORIGINS, a Munich-based Cluster of Excellence, has demonstrated a mechanism that could have enabled the first RNA molecules to stabilize in the primordial soup. When two RNA strands combine, their stability and lifespan increase significantly.
In all likelihood, life on Earth began in water, perhaps in a tide pool that was cut off from seawater at low tide but flooded by waves at high tide. Over billions of years, complex molecules like DNA, RNA and proteins ...
Cold antimatter for quantum state-resolved precision measurements
2024-08-02
Why does the universe contain matter and (virtually) no antimatter? The BASE international research collaboration at the European Organisation for Nuclear Research (CERN) in Geneva, headed by Professor Dr Stefan Ulmer from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU), has achieved an experimental breakthrough in this context. It can contribute to measuring the mass and magnetic moment of antiprotons more precisely than ever before – and thus identify possible matter-antimatter asymmetries. BASE has developed a trap, which can cool individual antiprotons much more rapidly ...
Smart aggregates: The future of infrastructure health monitoring
2024-08-02
The proliferation of concrete infrastructure worldwide has been met with growing concerns over its durability and safety. Concrete structures are increasingly subjected to dynamic forces from natural disasters like earthquakes and environmental degradation, such as corrosion. These factors, coupled with the saturation of infrastructure projects, amplify the risks associated with structural failure. Consequently, there is a pressing need for effective structural health monitoring (SHM) systems that can preemptively identify and address these vulnerabilities. The ...
Synthesis of SiOC@C ceramic nanospheres with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption performance
2024-08-02
In recent years, microwave technology has dramatically progressed, marked by the arrival of the 5G era, owing to the advantages of electromagnetic waves in long-distance, wireless, and high-speed transmissions. However, electromagnetic wave pollution problems such as electromagnetic wave interference and electromagnetic wave radiation are becoming increasingly serious. Electromagnetic wave pollution not only affects the normal operation of electronic equipment, greatly threatens the information security of the scientific community, but also endangers human health and is a possible cause of cancer ...
NWSL add lifesavers to the chain of survival in New York City
2024-08-02
NEW YORK CITY, August 2, 2024 — According to American Heart Association data, nine out of every ten people who experience cardiac arrest outside of a hospital die, in part because they do not receive immediate CPR more than half of the time. CPR, especially if performed immediately, can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. That is why the American Heart Association and the National Women’s Soccer League (NWSL) brought cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training to NWSL staff at the New York headquarters office located on Madison ...
Solving the doping problem: Enhancing performance in Organic Semiconductors
2024-08-02
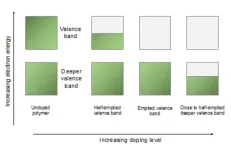
Cavendish physicists have discovered two new ways to improve organic semiconductors. They found a way to remove more electrons from the material than previously possible and used unexpected properties in an environment known as the non-equilibrium state, boosting its performance for use in electronic devices.
“We really wanted to hit the nail and figure out what is happening when you heavily dope polymer semiconductors,’ said Dr Dionisius Tjhe, Postdoctoral Research Associate at the Cavendish Laboratory. Doping is the process of removing or adding electrons into a semiconductor, increasing its ability to ...
More pets relinquished to shelters due to housing insecurity
2024-08-02
Housing policies may be becoming more pet inclusive, but housing insecurity is getting worse, finds a new study that examined the housing issues that led to owners turning their pets over to an animal shelter.
“Over the duration of the study, instances of animals entering shelters due to loss of housing rose, while those due to pet restrictions and landlord conflicts declined,” said the study’s lead author Jennifer Applebaum, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Department of Environmental and Global Health in the University ...
KTU researchers’ eye-tracking study provides valuable insights into learning mathematics
2024-08-02
Eye-tracking allows studying aspects that cannot be seen, for example, the thinking processes of a student solving a mathematical problem. Researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU) are the first in Lithuania to integrate eye-tracking into education and are using the technology to radically improve the teaching of mathematics.
Eye-tracking creates the possibility for researchers to observe a subject’s attention shifts based on where they fix their gaze or how they move it. This helps researchers understand various emotional, thinking and cognitive processes that happen in response to the environment.
“By applying this technology in mathematical education, ...
New approaches and insights on the environment and climate change at the 37th International Geological Congress 2024
2024-08-02
□ Overview
○ Event: The 37th International Geological Congress 2024 (IGC 2024)
○ Date/Venue:: 25 Aug (Sun) - 31 Aug (Sat) 2024, 7 days / BEXCO, Busan, Republic of Korea ※ Hosted in a 4-year cycle across continents
○ Scale: Over 7,000 participants from 121 countries (more than 3,000 scientipic programs, 250 exhibition booths)
○ Theme: The Great Travelers: Voyages to the Unifying Earth
○ Host: International Union of Geologcial Sciences (IUGS)
○ Organizer: IGC 2024 Organizing Committee (The Geological Society Of Korea, Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources, Busan Metropolitan ...
Genetic signatures of domestication identified in pigs, chickens
2024-08-02
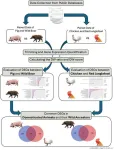
Wild boars and red junglefowl gave rise to common pigs and chickens. These animals’ genes evolved to express themselves differently, leading to signatures of domestication — such as weaker bones and better viral resistance — in pigs and chickens, according to a research team based in Japan.
The findings, published on July 6 in Animals, could provide insight into the genetic changes of the domestication process and highlight target genes for healthier and more productive livestock breeding, the researchers ...