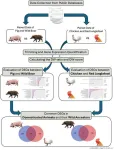
(Press-News.org) Wild boars and red junglefowl gave rise to common pigs and chickens. These animals’ genes evolved to express themselves differently, leading to signatures of domestication — such as weaker bones and better viral resistance — in pigs and chickens, according to a research team based in Japan.
The findings, published on July 6 in Animals, could provide insight into the genetic changes of the domestication process and highlight target genes for healthier and more productive livestock breeding, the researchers said.
“Through domestication, these animals have been brought under human control and have been selectively bred for specific traits useful to humans, such as faster growth rates, improved meat quality and increased litter size,” said corresponding author Hidemasa Bono, professor at Hiroshima University (HU). Bono is associated with the Laboratory of Genome Informatics in the HU Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life and the Laboratory of Bio-DX in the Genome Editing Innovation Center.
“This process has significantly altered the animals’ behavior, morphology and physiological functions. … While the selection for traits beneficial to humans has occurred, excessive selective breeding has led to health issues in domesticated animals and decreased their reproductive capacity. To address these issues, it is crucial to understand the changes in gene expression between domesticated animals and their wild ancestors.”
By comparing how genes are expressed in pairs of pigs and wild boars, as well as pairs of chickens and red junglefowl, the researchers said they aimed to elucidate common patterns of such changes. Using data from publicly available databases, they compared 240 genes in pigs and 206 in chickens and found 10 were up-regulated — meaning they were expressed more compared to their wild ancestor partners. They also found seven genes were up-regulated in wild boars and red junglefowl, which have a total of 206 genes and 200 genes, respectively.
“Notably, domesticated animals exhibited higher expression of genes related to viral resistance and bone weakness, whereas their wild ancestors showed higher expression of genes associated with stress response and energy metabolism,” said first author Motoki Uno, a graduate student in the Laboratory of Genome Informatics at HU’s Graduate School of Integrated Sciences for Life.
“Our analysis revealed that genes commonly up-regulated in pigs and chickens are involved in the immune response, olfactory learning, epigenetic regulation, cell division and the extracellular matrix, which is the molecular structure that gives support to cells and tissues in an organism. In contrast, genes up-regulated in wild boar and red junglefowl are related to stress response, cell proliferation, cardiovascular function, neural regulation and energy metabolism.”
According to the researchers, these changes may have come about because domesticated animals are typically kept at high densities in confined spaces, such as chickens in a coop. This closeness can foster more vulnerability to infection as viruses spread, compared to their wild ancestor counterparts. In contrast, wild boars and red junglefowl are exposed to more stressors in nature, such as avoiding predators and finding food, which could account for the up-regulated genes related to cardiovascular function, neural regulation and energy metabolism.
“These findings provide valuable insights into the genetic basis of the domestication process and highlight potential candidate genes for breeding applications,” Bono said. “Moving forward, we aim to contribute to sustainable breeding through the improvement of analytical methods and the integration of various biological data.”
The Center of Innovation for Bio-Digital Transformation and the Japan Science and Technology Agency funded this research.
###
About Hiroshima University
Since its foundation in 1949, Hiroshima University has striven to become one of the most prominent and comprehensive universities in Japan for the promotion and development of scholarship and education. Consisting of 12 schools for undergraduate level and 4 graduate schools, ranging from natural sciences to humanities and social sciences, the university has grown into one of the most distinguished comprehensive research universities in Japan. English website: https://www.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/en
END
Genetic signatures of domestication identified in pigs, chickens
2024-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Megamonas bacterium found to influence obesity risk
2024-08-02
A recent study published in Cell Host & Microbe identifies a potential obesity-linked bacterium, Megamonas, from a large-scale cohort of obese individuals in China. This research suggests potential strategies for future obesity management by illustrating how the bacterium degrades intestinal myo-inositol, enhances lipid absorption, and contributes to obesity.
The study is jointly conducted by Ruijin Hospital affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, BGI Research, and BGI Genomics Institute of Intelligent Medical Research (IIMR).
"Through a large-scale study of intestinal ...
Scientists find a human “fingerprint” in the upper troposphere’s increasing ozone
2024-08-02
Ozone can be an agent of good or harm, depending on where you find it in the atmosphere. Way up in the stratosphere, the colorless gas shields the Earth from the sun’s harsh ultraviolet rays. But closer to the ground, ozone is a harmful air pollutant that can trigger chronic health problems including chest pain, difficulty breathing, and impaired lung function.
And somewhere in between, in the upper troposphere — the layer of the atmosphere just below the stratosphere, where most aircraft cruise — ozone contributes to warming the planet as a potent greenhouse gas.
There are signs that ozone is continuing to rise in the upper troposphere despite efforts to reduce its ...
Researchers develop promising therapy treatment that can kill glioblastoma cells in newly discovered brain pathway
2024-08-02
A new pathway that is used by cancer cells to infiltrate the brain has been discovered by a team of Canadian and American research groups led by the Singh Lab at McMaster University. The research also reveals a new therapy that shows promise in blocking and killing these tumors.
The research, published in Nature Medicine on Aug. 2, 2024, offers new hope and potential treatments for glioblastoma, the most aggressive form of brain cancer. With existing treatments like surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy, the tumors often return, and
patient survival is limited to only a few months. With this new treatment, ...
York researchers make breakthrough in bid to develop vaccines and drugs for neglected tropical disease
2024-08-02
Scientists have developed a new, safe and effective way to infect volunteers with the parasite that causes leishmaniasis and measure the body’s immune response, bringing a vaccine for the neglected tropical disease a step closer.
The breakthrough, by a team from the University of York and Hull York Medical School, is described in the journal Nature Medicine and lays the foundations for vaccine development and for testing new preventative measures.
Controlled human infection studies, where volunteers are exposed to small amounts of ...
Combined effects of plastic pollution and seawater flooding amplify threats to coastal plant species
2024-08-02
Two of the planet’s more pressing environmental stressors have the potential to alter the growth and reproductive output of plants found right along the world’s coastlines, a new study suggests.
The research, published in the journal Environmental Pollution, is one of the first to examine the combined effects of seawater flooding and microplastic pollution on coastal plants.
It showed that both stressors had some effects on the species tested, with microplastics impacting the plants’ reproduction while flooding caused greater tissue death.
However, being exposed to both microplastics ...
Sea level changes shaped early life on Earth, fossil study reveals
2024-08-02
A newly developed timeline of early animal fossils reveals a link between sea levels, changes in marine oxygen, and the appearance of the earliest ancestors of present-day animals.
The study reveals clues into the forces that drove the evolution of the earliest organisms, from which all major animal groups descended.
A team from the University of Edinburgh studied a compilation of rocks and fossils from the so-called Ediacaran-Cambrian interval – a slice of time 580–510 million years ago. This period witnessed an explosion of biodiversity according to fossil records, the causes of which have ...
'Screaming Woman' mummy may have died in agony 3,500 years ago
2024-08-02
In 1935, the Metropolitan Museum of New York led an archaeological expedition to Egypt. In Deir Elbahari near Luxor, the site of ancient Thebes, they excavated the tomb of Senmut, the architect and overseer of royal works – and reputedly, lover – of the famed queen Hatschepsut (1479-1458 BCE). Beneath Senmut's tomb, they found a separate burial chamber for his mother Hat-Nufer and other, unidentified relatives.
Here, they made an uncanny discovery: a wooden coffin holding the mummy of an elderly woman, wearing a black wig and two scarab rings in silver and gold. But what struck the archaeologists was the ...
Healthy AI: Sustainable artificial intelligence for healthcare
2024-08-02
Similar to other sectors around the world, the light speed development of artificial intelligence (AI) has made its way into healthcare, particularly the radiology field. As such, AI-based diagnostic systems are flourishing, with hospitals quickly adopting the technology to assist radiologists. In contrast, there are concerns about the environmental impact of increasingly complex AI models and the need for more sustainable AI solutions.
Therefore, Associate Professor Daiju Ueda of Osaka Metropolitan University’s ...
First full 2-D spectral image of aurora borealis from a hyperspectral camera
2024-08-02
Auroras are natural luminous phenomena caused by the interaction of electrons falling from the sky and the upper atmosphere. Most of the observed light consists of emission lines of neutral or ionized nitrogen and oxygen atoms and molecular emission bands, and the color is determined by the transition energy levels, molecular vibrations and rotations. There is a variety of characteristic colors of auroras, such as green and red, but there are multiple theories about the emission process by which they appear in different types of auroras, and to understand the colors of auroras, the light must be broken down. ...
Turkey vultures fly faster to defy thin air
2024-08-02
Mountain hikes are invigorating. Crisp air and clear views can refresh the soul, but thin air presents an additional challenge for high-altitude birds. ‘All else being equal, bird wings produce less lift in low density air’, says Jonathan Rader from the University of North Carolina (UNC) at Chapel Hill, USA, making it more difficult to remain aloft. Yet this doesn’t seem to put them off. Bar-headed geese, cranes and bar-tailed godwits have recorded altitude records of 6000 m and more. So how do they manage to take to the air when thin air offers ...