(Press-News.org) New study reveals a significant sex bias in pain management at emergency departments, showing that female patients are consistently less likely to receive pain medication prescriptions compared to male patients with similar complaints. This bias persists across different ages, pain levels, and physician sex, indicating a systemic issue. Female patients' pain scores are less frequently recorded, and they spend more time in the emergency department than male patients. The findings highlight the need for urgent policy interventions and training for healthcare professionals to address and counteract these biases, ensuring equal pain treatment for all patients.
A new study led by Prof. Shoham Choshen-Hillel and Mika Guzikevits from the Hebrew University, Dr. Alex Gileles-Hillel from Hebrew University- Hadassah Medical Center, Dr. Tom Gordon-Hecker from Ben-Gurion University, and an international team of researchers from Hebrew University, Hadassah Medical Center, the University of Missouri, and Marshall University has uncovered a concerning sex bias in pain management decisions at emergency rooms. The research, published in the journal PNAS, analyzed over 21,000 patient records across the United States and Israel and found that female patients are consistently less likely to receive pain medication prescriptions compared to male patients with similar complaints.
The study revealed that female patients are prescribed fewer pain relief medications than male patients, even after considering the levels of pain reported and other variables such as age, medical history, and the type of complaint. This suggests a systemic issue where women's pain may not be taken as seriously or treated as aggressively as men's pain.
By analyzing electronic health records from American and Israeli healthcare systems, the researchers present evidence that a female patient discharged from the emergency department is less likely to receive treatment for a pain complaint compared to a male patient. Specifically, datasets from emergency departments in the US and Israel, with a total sample size of 21,851 discharge notes, revealed that female patients are less likely to receive a prescription for any type of analgesic medication, both opioids and non-opioids, compared to male patients.
Female patients with pain complaints are less likely to receive analgesics for every pain score and at every age group and receive less analgesics from both male and female physicians. In addition, female patients stay an additional 30 minutes at the emergency department, and their pain score is 10% less likely to be recorded by triage nurses. In a controlled experiment involving 109 nurses, pain was rated as less intense if the patient was said to be female rather than male, suggesting that the bias is driven by gender stereotypes. According to the authors, the under-treatment of females’ pain bears immediate implications for the healthcare system and broad implications for society’s attitude toward female pain.
Interestingly, the study found that this disparity in prescribing pain medication exists regardless of whether the treating physician is male or female. Both male and female doctors are less likely to prescribe pain medication to women, indicating that the bias is pervasive and not limited to one sex of healthcare providers.
The research also highlighted that nurses are 10% less likely to record pain scores for female patients compared to male patients. This lack of documentation can contribute to underestimating the severity of women's pain and result in inadequate treatment. Additionally, the study found that female patients spend an average of 30 minutes longer in the emergency department than male patients. This delay could be due to a variety of factors, including potentially being taken less seriously when they report pain or symptoms.
In a controlled experiment, nurses judged female patients' pain as less intense than male patients' pain when presented with identical clinical scenarios. This suggests that there may be a subconscious bias in how healthcare professionals perceive and assess pain based on the patient's sex..
"Our research reveals a troubling bias in how women's pain is perceived and treated in emergency care settings," said Prof. Choshen-Hillel. "This under-treatment of female patients' pain could have serious implications for women's health outcomes, potentially leading to longer recovery times, complications, or chronic pain conditions."
Recommendations: The study argues that these findings reflect a systemic under-treatment of women's pain in medical settings. The researchers call for urgent policy interventions to address this bias and ensure equal pain treatment regardless of sex. They recommend training programs for healthcare professionals to recognize and counteract sex biases and suggest that pain management protocols should be revisited and standardized to ensure fair and adequate treatment for all patients.
END
Sex bias in pain management at emergency departments new study reveals
2024-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Child Mind Institute paper reveals next frontier in reproducible brain imaging for neuroscience discovery
2024-08-05
New York, NY (August 5, 2024) — The Child Mind Institute has released a paper detailing their pioneering study in the journal Nature Human Behaviour titled, "Moving Beyond Processing and Analysis-Related Variation in Resting State Functional Brain Imaging." The research identifies significant challenges in the reproducibility and standardization of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) used to understand brain function and behavior — and proposes concrete solutions to move the field towards results that translate into real world impact.
Along with a diverse team of international collaborators, ...
Hospital pneumonia diagnoses are uncertain, revised more than half the time, study finds
2024-08-05
Pneumonia diagnoses are marked by pronounced uncertainty, an AI-based analysis of over 2 million hospital visits has found.
More than half the time, a pneumonia diagnosis made in the hospital will change from a patient’s entrance to their discharge—either because someone who was initially diagnosed with pneumonia ended up with a different final diagnosis, or because a final diagnosis of pneumonia was missed when a patient entered the hospital (not including cases of hospital-acquired pneumonia).
The study describing the new results publishes August 6th in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Barbara Jones, MD, MSCI, pulmonary and critical care physician ...
Cancer screening estimated to cost $43 billion a year in the United States
2024-08-05
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 5 August 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Researchers receive 9.5 million grant to study relationship between polyphenol intake, Alzheimer’s prevention, and the brain-gut-microbiome system
2024-08-05
UCLA Health researchers, in collaboration with researchers from the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland, have received $9.5 million award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) with support from European funding agencies — The Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) and the Public Health Agency Health & Social Care (HSC) — to study the effects of polyphenols on cognitive health and the brain-gut microbiome system.
The proposal, named MAEVE, stands for “Microbiota mediated flavonoid metabolites for cognitive health.”
In this interdisciplinary and multicenter study funded through the Tripartite US-Ireland Research & Development Partnership Program, ...
UH astronomers uncover risks to planets that could host life
2024-08-05
A groundbreaking study has revealed that red dwarf stars can produce stellar flares that carry far-ultraviolet (far-UV) radiation levels much higher than previously believed. This discovery suggests that the intense UV radiation from these flares could significantly impact whether planets around red dwarf stars can be habitable. Led by current and former astronomers from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (IfA), the research was recently published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
“Few stars have been thought to generate ...
An overlooked side-effect of the housing crisis may be putting Californians at increased risk from climate disasters
2024-08-05
In a new article for the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, UC Santa Cruz researchers laid out the foundation for their highly-anticipated upcoming study of how lack of affordable housing in urban areas of California may be driving increased development in and near wildlands, leading to more severe climate change impacts.
Since the 1990s, California has led the nation in the growth of Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) development, with more than one in three households in the state now located immediately next to or within ...
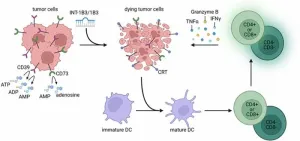
INT-1B3 miR-193a-3p mimic boosts t cell immunity and induces tumor cell death
2024-08-05
BUFFALO, NY- August 5, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 12, 2024, entitled, “INT-1B3, an LNP formulated miR-193a-3p mimic, promotes anti-tumor immunity by enhancing T cell mediated immune responses via modulation of the tumor microenvironment and induction of immunogenic cell death.”
In this study, researchers Chantal L. Duurland, Thijs de Gunst, Harm C. den Boer, Marion T.J. van den Bosch, Bryony J. Telford, Rogier M. Vos, Xiaolei Xie, Mingfa Zang, Fang Wang, Yingying Shao, Xiaoyu ...
Wayne State University professor receives NSF grant to study quantum tunneling
2024-08-05
DETROIT — A Wayne State University professor recently received a three-year, $626,467 grant from the National Science Foundation’s Division of Physics. The project, “Probing Nonadiabatic Strong Field Ionization with Phase-Resolved Attoclock,” will research a quantum mechanical process known as quantum tunneling.
Wen Li, Ph.D., professor of chemistry in Wayne State’s College of Liberal Arts and Sciences and his research team propose a new technique they have developed to study the process of quantum tunneling, a quantum mechanical phenomenon in which an object such as an electron or atom passes through ...
Adding metastasis-directed radiation therapy boosts progression-free survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer
2024-08-05
Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center demonstrated that adding metastasis-directed radiation therapy to standard-of-care chemotherapy improved progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with oligometastatic pancreatic cancer. Findings from the multicenter EXTEND trial, published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, were first presented at the 2024 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
At a median follow-up of 17.3 months, PFS was 10.3 months in patients who received metastasis-directed therapy (MDT) ...
New method tracks how psychedelics affect neurons in minutes
2024-08-05
Researchers at the University of California, Davis have developed a rapid, noninvasive tool to track the neurons and biomolecules activated in the brain by psychedelic drugs. The protein-based tool, which is called Ca2+-activated Split-TurboID, or CaST, is described in research published in Nature Methods.
There has been mounting interest in the value of psychedelic-inspired compounds as treatments for brain disorders including depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and substance use disorder. Psychedelic ...