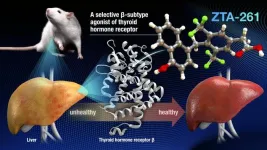
Scientists at Nagoya University in Japan have made a significant breakthrough in treating lipid disorders. They have developed a new compound, ZTA-261, which selectively binds to the thyroid hormone receptor beta (THRβ). THRβ plays an important role in the regulation of lipid metabolism, which affects lipid levels in the blood. Mice administered the drug showed decreased lipid levels in the liver and blood, with fewer side effects in the liver, heart, and bones compared to existing compounds. These findings, published in Communications Medicine, suggest that ZTA-261 is an effective treatment for lipid disorders such as dyslipidemia.
Approximately one in ten people is classified as obese or overweight, often due to abnormalities in lipid metabolism. Abnormal levels of lipids in the blood, known as dyslipidemia, lead to an increased risk of chest pain, heart attack, and stroke.
There is growing interest in developing treatments for dyslipidemia that leverage the properties of thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones increase overall metabolism through binding to two types of receptors: alpha (THRα) and beta (THRβ). The brain, heart, and muscle contain the α-subtype, whereas the liver and pituitary gland primarily express the β-subtype.
Treatments that rely on THR activation face challenges due to the side effects of thyroid hormones. Although THRα regulates cardiovascular functions, excess levels of thyroid hormone lead to adverse effects in nearby organs such as heart enlargement and muscle and bone wasting. On the other hand, activation of THRβ influences lipid metabolism without these severe side effects.
As a result, THRβ has become a desirable target for treating metabolic disorders such as dyslipidemia. However, common treatments, such as the natural thyroid hormone T3, show almost no selectivity between the α and β receptors, making it difficult to avoid the severe side effects caused by binding to THRα.
To address this problem, a research team, including Masakazu Nambo, Taeko Ohkawa, Ayato Sato, Cathleen Crudden, and Takashi Yoshimura from Nagoya University's WPI-ITbM, developed ZTA-261, a thyroid hormone derivative drug with a similar structure. To test its efficacy, they compared it with GC-1, another thyroid hormone derivative, and the natural thyroid hormone T3 in a mouse model.
They found that ZTA-261 had almost 100 times higher selectivity for THRβ than THRα. In comparison, GC-1 showed only a 20-fold difference in affinity, showing ZTA-261's superior selectivity. This was confirmed by the significant increase in heart weight and bone damage indicators in T3-treated mice but not in those treated with ZTA-261.
“Our findings suggest that ZTA-261 is much less toxic than T3 and even less toxic than GC-1, which is known as a THRβ-selective compound,” Ohkawa said. “I find it amazing that the difference in THR beta-selectivity between ZTA-261 and GC-1—100 times selectivity vs. 20 times selectivity—truly has this big an impact on heart and bone toxicity.”
As many drugs have been discontinued in preclinical trials because of their toxicity in the liver, the researchers checked for potential liver toxicity by measuring alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in the blood. Their findings confirmed the safety of the drug, finding no significant differences in ALT levels between mice treated with ZTA-261 and those treated with saline. Although these results are promising,more studies, including human trials, will be necessary before considering ZTA-261 for clinical use. However,this breakthrough represents a significant step forward in the development of safer treatments for lipid disorders.
“ZTA-261 has extremely high affinity and selectivity for THRβ among the thyroid hormone derivatives developed to date,” Nambo explained. “In the process of synthesizing a variety of derivatives, we have found that precise molecular design is crucial for both selectivity and affinity. We believe that this study will provide new and important insights into drug discovery.”
Written by Matthew COSLETT. Science writer at Nagoya University International Communications office.
About the World Premier International Research Center Initiative (WPI)
The WPI program was launched in 2007 by Japan’s Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) to foster globally visible research centers boasting the highest standards and outstanding research environments. Numbering more than a dozen and operating at institutions throughout the country, these centers are given a high degree of autonomy, allowing them to engage in innovative modes of management and research. The program is administered by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
See the latest research news from the centers at the WPI News Portal: https://www.eurekalert.org/newsportal/WPI
Main WPI program site: www.jsps.go.jp/english/e-toplevel
About the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM)
The Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) at Nagoya University in Japan is committed to advance the integration of synthetic chemistry, plant/animal biology and theoretical science, all of which are traditionally strong fields in the university. The aim of ITbM is to develop transformative bio-molecules, innovative functional molecules capable of bringing about fundamental change to biological science and technology. Research at ITbM is carried out in a “Mix-Lab” style, where international young researchers from various fields work together side-by-side in the same lab, enabling interdisciplinary interaction. Through these endeavors, ITbM will create “transformative bio-molecules” that will dramatically change the way of research in chemistry, biology and other related fields to solve urgent problems, such as environmental issues, food production and medical technology that have a significant impact on the society.
ITbM website: http://www.itbm.nagoya-u.ac.jp/
END