(Press-News.org) A new UBC study has revealed regular seasonal shifts in people’s moral values.
The finding has potential implications for politics, law and health—including the timing of elections and court cases, as well as public response to a health crisis.
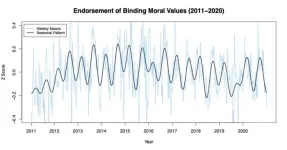
The research published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) analyzed survey responses from more than 230,000 people in the U.S. over 10 years and revealed that people’s embrace of certain moral values fluctuates depending on the time of year. The seasonal patterns also emerged in smaller data samples from Canada and Australia.
“People’s endorsement of moral values that promote group cohesion and conformity is stronger in the spring and fall than it is in the summer and winter,” said Ian Hohm, the study’s first author and a doctoral student in UBC’s psychology department. “Moral values are a fundamental part of how people make decisions and form judgments, so we think this finding might just be the tip of the iceberg in that it has implications for all sorts of other downstream effects.”
Since 2009, a website established by social psychology researchers has been collecting survey data that measures participants’ endorsement of five moral values:
Loyalty: Valuing devotion to one’s group and maintaining strong group bonds.
Authority: Respecting and following leadership and established rules.
Purity: Emphasizing cleanliness, sanctity and upholding tradition.
Care: Prioritizing kindness and preventing harm to others.
Fairness: Ensuring equal treatment for everyone.
Loyalty, authority and purity are referred to by researchers as “binding” values because they encourage conformity to group norms. They also align closely with modern political conservatism. Care and fairness may be considered more liberal values, with their focus on individual rights and welfare. All have been shown by research to guide people’s judgments about right and wrong.
The researchers found that respondents endorsed the “binding” values more strongly in spring and fall, but not as much in summer and winter—a pattern that was remarkably consistent over 10 years.
They also found evidence that the summer decrease in endorsement of binding moral values was more pronounced in areas with more extreme seasonal climate differences.
Anxiety a possible explanation
The study observed a potential link between these seasonal moral shifts and levels of anxiety, using large-scale data on seasonal anxiety provided by Dr. Brian O’Shea, a co-author of the paper and assistant professor of psychology at the University of Nottingham.
“We noticed that anxiety levels peak in the spring and autumn, which coincides with the periods when people endorse binding values more strongly,” said Dr. Mark Schaller, the study’s senior author and a professor of psychology at UBC. “This correlation suggests that higher anxiety may drive people to seek comfort in the group norms and traditions upheld by binding values.”
Implications for politics, law, health, social relations
The findings have wide-reaching implications, with potential examples including:
Elections: The timing of elections could have an impact on outcomes, as shifts in moral values influence political opinions and behaviours.
Legal judgments: The timing of trials and legal decisions could be influenced by seasonal variations in moral values, because those who endorse “binding” values tend to be more punitive of those who commit crimes and violate social norms.
Disease response: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the extent to which people followed social distancing guidelines and were vaccinated was influenced by their moral values. Knowing these values change with the seasons could help tailor more effective health campaigns.
Intergroup prejudice: Seasonal changes in moral values might affect how people view outsiders or those who don’t conform to group norms.
The research team plans to delve deeper into the connections between anxiety and moral values and to investigate how these seasonal patterns influence prejudices and legal judgments.
Interview language(s): English
END
People's moral values change with the seasons
Seasonality of moral values has potential implications for politics, law and health—including the timing of elections and court cases
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers reveal atomic-scale details of catalysts’ active sites
2024-08-06
The chemical and energy industries depend upon catalysts to drive the reactions used to create their products. Many important reactions use heterogeneous catalysts — meaning that the catalysts are in a different phase of matter than the substances they are reacting with, such as solid platinum reacting with gases in an automobile’s catalytic converter.
Scientists have investigated the surface of well-defined single crystals, illuminating the mechanisms underlying many chemical reactions. However, there is much more to be learned. For heterogeneous catalysts, their 3D atomic structure, their chemical composition and the nature of ...
The prescription for a healthier democracy
2024-08-06
When we’re sick, the first step on the road to recovery is a visit to the doctor’s office.
It turns out the same may also be true for breathing life into America’s democracy.
A Rutgers University–New Brunswick study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum finds that physicians can play a crucial role in strengthening political inclusion of marginalized groups by aiding patients in voter registration.
“Hospitals aren’t the first place we think of when it comes to voter registration,” said Katherine McCabe, an associate professor of American politics at Rutgers University-New Brunswick and lead ...
New substrate material for flexible electronics could help combat e-waste
2024-08-06
Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a rapidly growing global problem, and it’s expected to worsen with the production of new kinds of flexible electronics for robotics, wearable devices, health monitors, and other new applications, including single-use devices.
A new kind of flexible substrate material developed at MIT, the University of Utah, and Meta has the potential to enable not only the recycling of materials and components at the end of a device’s useful life, but also the scalable manufacture of more ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists probe molecular cause of COVID-19 related diarrhea, revealing potential treatments
2024-08-06
Working with human stem cells that form a kind of “mini intestine-in-a-dish,” Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have found several molecular mechanisms for COVID-19-related diarrhea, suggesting potential ways to control it.
Details of the experiments in a model of human intestinal tissue, called enteroids, are described on July 30 in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Along with the unpleasant aches, fever, sore throat, cough, respiratory distress and other symptoms that may accompany COVID-19 infection, up to half of people who get the virus will experience diarrhea. Some 30% of them will go on to develop ...
New open-source platform for high-resolution spatial transcriptomics
2024-08-06
Leuven, 6 August 2024 - A team of researchers from the lab of Prof. Stein Aerts (VIB-KU Leuven) presents Nova-ST, a new spatial transcriptomics technique that promises to transform gene expression profiling in tissue samples. Nova-ST will make large-scale, high-resolution spatial tissue analysis more accessible and affordable, offering significant benefits for researchers. The research was published in Cell Reports Methods.
Transcriptomics is the study of gene expression in a cell or a population of cells, but it usually does not include spatial information about where those genes were active. This hurdle limited our understanding of complex ...
Targeted cancer therapy: initial high concentration may slow down selection for resistance
2024-08-06
BUFFALO, NY- August 6, 2024 – On July 28, 2024, Mikhail V. Blagosklonny M.D., Ph.D., from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center published a new editorial in Volume 16, Issue 14 of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), entitled, “Targeted cancer therapy: the initial high concentration may slow down the selection for resistance.”
“Unfortunately, any targeted therapy is, always, started with low levels of the drug in the organism, selecting for drug resistance. One should propose that initial drug levels must be maximized, ...
Lehigh University researchers dig deeper into stability challenges of nuclear fusion—with mayonnaise
2024-08-06
Mayonnaise continues to help researchers better understand the physics behind nuclear fusion.
“We’re still working on the same problem, which is the structural integrity of fusion capsules used in inertial confinement fusion, and Hellmann’s Real Mayonnaise is still helping us in the search for solutions,” says Arindam Banerjee, the Paul B. Reinhold Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics at Lehigh University and Chair of the MEM department in the P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science.
In simple terms, fusion reactions are what power the sun. If the process could ...
Texas Tech professor receives grant for printable semiconductors research
2024-08-06
Minxiang “Glenn” Zeng, an assistant professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Texas Tech University, has been awarded a $250,000 grant from the Launching Early-Career Academic Pathways in the Mathematical and Physical Sciences (LEAPS-MPS) award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to further his research about printable semiconductors and electronics under extreme environments.
The grant supports Zeng’s work in understanding and controlling the thermal degradation pathways of printed metal chalcogenides, which are semiconductor materials including selenides, tellurides and sulfides. His goal is to develop strategies to enhance the thermal stability ...
Digital Olfaction Society 2024: Revolutionizing scent digitization and global transfer
2024-08-06
The 8th Annual Meeting of the Digital Olfaction Society (DOS) will take place on December 5-6, 2024, in Tokyo, Japan, and Online. The DOS meeting is uniquely aimed at digitizing scents, transferring them, and re-creating them in different parts of the world. The two-day event includes one day dedicated to talks and another day for demonstrations. Under the slogan "Olfaction to Digital Olfaction", the congress will explore the latest advances in olfaction science and digital olfaction technologies, highlighting their transformative impact across multiple fields.
The first day of the congress will focus on olfaction science, scent-based diagnosis and treatment ...
New York City’s fireworks display prompts temporary surge of air pollution
2024-08-06
In 2023, roughly 60,000 firework shells exploded above Manhattan’s East River as part of Macy’s Fourth of July show. The resulting air pollutant levels were many times higher in the hours after the display than those seen when smoke from a Canadian wildfire had blanketed the area a month before.
This is according to the results of a new study, led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, which measured air quality just before and after the Independence Day event, one of the largest in the United States. Tiny particles of hazardous metals and organic compounds peaked at 3,000 micrograms per cubic meter at an air sampling site ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] People's moral values change with the seasonsSeasonality of moral values has potential implications for politics, law and health—including the timing of elections and court cases