(Press-News.org) Mayonnaise continues to help researchers better understand the physics behind nuclear fusion.
“We’re still working on the same problem, which is the structural integrity of fusion capsules used in inertial confinement fusion, and Hellmann’s Real Mayonnaise is still helping us in the search for solutions,” says Arindam Banerjee, the Paul B. Reinhold Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics at Lehigh University and Chair of the MEM department in the P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science.
In simple terms, fusion reactions are what power the sun. If the process could be harnessed on earth, scientists believe it could offer a nearly limitless and clean energy source for humanity. However, replicating the sun’s extreme conditions is an incredibly complex challenge. Researchers across science and engineering disciplines, including Banerjee and his team, are examining the problem from a multitude of perspectives.
Inertial confinement fusion is a process that initiates nuclear fusion reactions by rapidly compressing and heating capsules filled with fuel, in this case, isotopes of hydrogen. When subjected to extreme temperatures and pressure, these capsules melt and form plasma, the charged state of matter that can generate energy.
“At those extremes, you’re talking about millions of degrees Kelvin and gigapascals of pressure as you’re trying to simulate conditions in the sun,” says Banerjee. “One of the main problems associated with this process is that the plasma state forms these hydrodynamic instabilities, which can reduce the energy yield.”
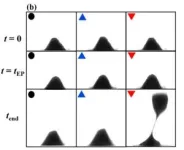
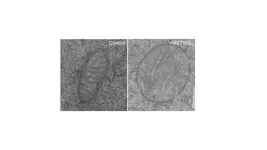
In their first paper on the topic back in 2019, Banerjee and his team examined that problem, known as Rayleigh-Taylor instability. The condition occurs between materials of different densities when the density and pressure gradients are in opposite directions, creating an unstable stratification.
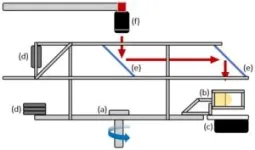
“We use mayonnaise because it behaves like a solid, but when subjected to a pressure gradient, it starts to flow,” he says. Using the condiment also negates the need for high temperatures and pressure conditions, which are exceedingly difficult to control.
Banerjee’s team used a custom-built, one-of-a-kind rotating wheel facility within Banerjee’s Turbulent Mixing Laboratory to mimic the flow conditions of the plasma. Once the acceleration crossed a critical value, the mayo started to flow.
One of the things they figured out during that initial research was that before the flow became unstable, the soft solid, i.e., the mayo, went through a couple of phases.
“As with a traditional molten metal, if you put a stress on mayonnaise, it will start to deform, but if you remove the stress, it goes back to its original shape,” he says. “So there’s an elastic phase followed by a stable plastic phase. The next phase is when it starts flowing, and that’s where the instability kicks in.”
Understanding this transition between the elastic phase and the stable plastic phase is critical, he says, because knowing when the plastic deformation starts might tip off researchers as to when the instability would occur, Banerjee says. Then, they’d look to control the condition in order to stay within this elastic or stable plastic phase.
In their latest paper, published in Physical Review E, the team (including former graduate student and first author of the study, Aren Boyaci '24 PhD, now working at Rattunde AG as a Data Modeling Engineer in Berlin, Germany), looked at the material properties, the perturbation geometry (amplitude and wavelength), and the acceleration rate of the materials that undergo Rayleigh-Taylor instability.
“We investigated the transition criteria between the phases of Rayleigh-Taylor instability, and examined how that affected the perturbation growth in the following phases,” Boyaci says. “We found the conditions under which the elastic recovery was possible, and how it could be maximized to delay or completely suppress the instability. The experimental data we present are also the first recovery measurements in the literature.”
The finding is an important one as it could inform the design of the capsules in such a way that they never become unstable.
There is, however, the looming question of how the team’s data fit into what happens in actual fusion capsules, the property values of which are orders of magnitude different from the soft solids used in their experiments.
“In this paper, we have non-dimensionalized our data with the hope that the behavior we are predicting transcends these few orders of magnitude,” says Banerjee. “We’re trying to enhance the predictability of what would happen with those molten, high-temperature, high-pressure plasma capsules with these analog experiments of using mayonnaise in a rotating wheel.”
Ultimately, Banerjee and his team are part of a global effort to turn the promise of fusion energy into reality.
“We’re another cog in this giant wheel of researchers,” he says. “And we’re all working towards making inertial fusion cheaper and therefore, attainable.”
Related Links
Physical Review E: "Transition to plastic regime for Rayleigh-Taylor instability in soft solids"
Faculty Profile: Arindam Banerjee
Lehigh News (May 8, 2019): "Behold the Mayo: Researchers Reveal 'Instability Threshold' of Elastic-Plastic Material..."
Video: The Rotating Wheel Rayleigh Taylor Instability Experiment END
Lehigh University researchers dig deeper into stability challenges of nuclear fusion—with mayonnaise
Condiment is a key ingredient in ongoing research on the phases of Rayleigh-Taylor instability, which could inform the design of future inertial confinement fusion processes for clean energy
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Texas Tech professor receives grant for printable semiconductors research
2024-08-06
Minxiang “Glenn” Zeng, an assistant professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Texas Tech University, has been awarded a $250,000 grant from the Launching Early-Career Academic Pathways in the Mathematical and Physical Sciences (LEAPS-MPS) award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to further his research about printable semiconductors and electronics under extreme environments.
The grant supports Zeng’s work in understanding and controlling the thermal degradation pathways of printed metal chalcogenides, which are semiconductor materials including selenides, tellurides and sulfides. His goal is to develop strategies to enhance the thermal stability ...
Digital Olfaction Society 2024: Revolutionizing scent digitization and global transfer
2024-08-06
The 8th Annual Meeting of the Digital Olfaction Society (DOS) will take place on December 5-6, 2024, in Tokyo, Japan, and Online. The DOS meeting is uniquely aimed at digitizing scents, transferring them, and re-creating them in different parts of the world. The two-day event includes one day dedicated to talks and another day for demonstrations. Under the slogan "Olfaction to Digital Olfaction", the congress will explore the latest advances in olfaction science and digital olfaction technologies, highlighting their transformative impact across multiple fields.
The first day of the congress will focus on olfaction science, scent-based diagnosis and treatment ...
New York City’s fireworks display prompts temporary surge of air pollution
2024-08-06
In 2023, roughly 60,000 firework shells exploded above Manhattan’s East River as part of Macy’s Fourth of July show. The resulting air pollutant levels were many times higher in the hours after the display than those seen when smoke from a Canadian wildfire had blanketed the area a month before.
This is according to the results of a new study, led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, which measured air quality just before and after the Independence Day event, one of the largest in the United States. Tiny particles of hazardous metals and organic compounds peaked at 3,000 micrograms per cubic meter at an air sampling site ...
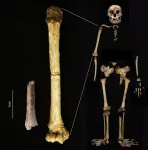
Smallest arm bone in human fossil record sheds light on the dawn of Homo floresiensis
2024-08-06
A paper out today in Nature Communications reports the discovery of extremely rare early human fossils from the Indonesian island of Flores, including an astonishingly small adult limb bone.
Dated to about 700,000 years old, the new findings shed light on the evolution of Homo floresiensis, the so-called ‘Hobbits’ of Flores whose remains were uncovered in 2003 at Liang Bua cave in the island’s west by a team co-led by Australian-New Zealand archaeologist Professor Mike Morwood (1950–2013).
Archaeological evidence suggests these diminutive, small-brained humans inhabited Liang Bua ...
Type 2 diabetes and fracture risk in older women
2024-08-06
About The Study: The results from this study suggest that the higher fracture risk among older women with type 2 diabetes may be due to impaired physical function and not skeletal characteristics.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Mattias Lorentzon, MD, PhD, email mattias.lorentzon@medic.gu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25106)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and ...
AI for early detection of pediatric eye diseases using mobile photos
2024-08-06
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the artificial intelligence (AI) model demonstrated strong performance in accurately identifying myopia, strabismus, and ptosis using only smartphone images. These results suggest that such a model could facilitate the early detection of pediatric eye diseases in a convenient manner at home.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Lin Li, MD, PhD (jannetlee130@gmail.com), and Jie Xu, DHM (xujie@pjlab.org.cn).
To access the embargoed ...
Demographic representation of generative AI images of physicians
2024-08-06
About The Study: This study identifies demographic biases in artificial intelligence (AI)-generated images of physicians with disproportionate representation of white and male physicians and concerning underrepresentation of other races and ethnicities (Asian and Latino) and female physicians in some platforms. This bias has the potential to reinforce stereotypes and undermine diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives within health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sang Won Lee, MSc, email sangwon_lee@hms.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
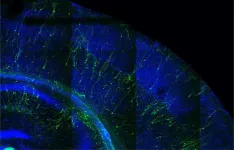
When faster is not better: New study links premature development of human neurons to brain developmental disorders
2024-08-06
Leuven, 7 August 2024—The mechanisms underlying intellectual disabilities or autism remain largely unknown. Researchers in the labs of Prof. Pierre Vanderhaeghen and Prof. Vincent Bonin at the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain & Disease Research and NERF have discovered that mutations in a gene called SYNGAP1 disrupt the prolonged development of human neurons, which is thought to be essential for normal cognitive function. Their work has interesting implications for our understanding and treatment ...
Meteorin-like protein drains energy from T cells, limiting immune system’s power to fight cancer
2024-08-06
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL AUG. 6 AT 11 A.M. ET**
A protein called Meteorin-like (METRNL) in the tumor microenvironment saps energy from T cells, thereby severely limiting their ability to fight cancer, according to new research directed by investigators at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. Finding ways to block the effects of METRNL signaling on tumor-infiltrating T cells may allow these immune cells to regain the energy necessary to eliminate tumors.
A report about the work was published Aug. 6 in the journal Immunity.
METRNL ...
Live longer, die healthier
2024-08-06
Everyone wants to live to a ripe old age, but no one wants to be decrepit. Now, University of Connecticut researchers have demonstrated a treatment that could lengthen life—and vigor—up to the very end.
Even as human lifespans have lengthened over the past century, most people in old age suffer a serious health decline in the last decade of life. Chronic illnesses such as cancer, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease may begin, followed by frailty. Many interventions can prolong life, but not necessarily good health. And nobody wants to spend the last ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Night lights can structure ecosystems
A parasitic origin for the ribosome?
A gold-standard survey of the American mood
Tool for identifying children at risk of speech disorders
How Japanese medical trainees view artificial intelligence in medicine
MambaAlign fusion framework for detecting defects missed by inspection systems
Children born with upper limb difference show the incredible adaptability of the young brain
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
Fast-paced lives demand faster vision: ecology shapes how “quickly” animals see time
Global warming and heat stress risk close in on the Tour de France
New technology reveals hidden DNA scaffolding built before life ‘switches on’
New study reveals early healthy eating shapes lifelong brain health
Trashing cancer’s ‘undruggable’ proteins
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
[Press-News.org] Lehigh University researchers dig deeper into stability challenges of nuclear fusion—with mayonnaiseCondiment is a key ingredient in ongoing research on the phases of Rayleigh-Taylor instability, which could inform the design of future inertial confinement fusion processes for clean energy