(Press-News.org) August 6, 2024 — Thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (TOPLL) is a rare condition associated with ectopic bone formation in the thoracic spine. A long-term follow-up study from Japan shows significant and lasting improvement in outcomes with posterior decompression and fixation surgery for patients with T-OPLL, reports The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Surgical treatment of T-OPLL is effective in improving neurological function, quality of life, and pain management over an extended period," according to the new research by Hiroaki Nakashima, MD, PhD, and colleagues of Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine.
New evidence on long-term outcomes of surgery for T-OPLL
Patients with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament have ectopic bone growth in the spinal column, resulting in neurological signs and symptoms. Most cases involve the cervical spine. Although thoracic involvement is less common, it is prone to delayed diagnosis and often goes undetected until severe symptoms develop. Japan has the highest prevalence of T-OPLL.
Studies of operatively treated T-OPLL have reported better outcomes when spinal decompression is combined with fixation. To assess the long-term outcomes of this procedure, the researchers analyzed follow-up data on 51 patients undergoing posterior decompression and corrective fixation surgery for T-OPLL.
The patients, who had an average age of 51.6 years, underwent surgery at the study center between 2001 and 2014, with follow-up of at least 10 years. Severity was assessed using the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score. Other assessments included back and leg pain, quality of life (QoL), and radiographic outcomes.
'Long-term stability and structural improvements' after decompression and fixation
The average JOA score improved significantly from 3.7 preoperatively to 7.9 at two years postoperatively, remaining stable thereafter. These scores indicated “sustained neurological and functional improvement from surgery over the long term,” the researchers write.
Decompression and fixation also yielded lasting improvement in patient-reported outcomes, including QoL (EQ-5D score). Numeric rating scale pain scores decreased from 5.4 preoperatively to 3.5 at 10 years for back pain and from 4.0 to 3.0 for leg pain. Radiographic outcomes included reduction in Cobb angles for T1-T12 in sagittal plane and kyphosis.
Eleven patients had progression of ossification, largely within the first five years. A total of 14 patients experienced postoperative complications, including six within the first 30 days postoperatively and eight thereafter. Perioperative complications included lower limb paralysis, infection, and hematoma, whereas later complications were mainly adjacent vertebral fractures. A total of four patients underwent an additional surgical procedure during follow-up.
The study provides new long-term follow-up data on the outcomes of decompression and fixation for T-OPLL, including persistent gains in clinical and patient-reported outcomes. Although some patients developed distal junctional failure or required reoperation, "these complications and interventions did not substantially detract from the overall QoL improvement," Dr. Nakashima and coauthors conclude. "The imaging results showed minimal progression of ossification beyond two years postoperatively, contributing to the long-term stability and structural improvements observed in the patients."
Read Article: Ten Year Follow-Up of Posterior Decompression and Fixation Surgery for Thoracic Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health.
###
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in information, software solutions and services for professionals in healthcare; tax and accounting; financial and corporate compliance; legal and regulatory; corporate performance and ESG. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2023 annual revenues of €5.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 21,400 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, YouTube and Instagram.
END
Good outcomes 10 years after surgery for ectopic bone in thoracic spine
Decompression and fixation yields long-term benefits in T-OPLL, reports Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
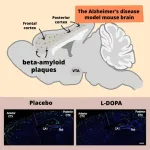
Dopamine treatment alleviates symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-06
A new way to combat Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by Takaomi Saido and his team at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan. Using mice with the disease, the researchers found that treatment with dopamine could alleviate physical symptoms in the brain as well as improve memory. Published in the scientific journal Science Signaling on August 6, the study examines dopamine’s role in promoting the production of neprilysin, an enzyme that can break down the harmful plaques in the brain that are the ...
Do your supplements contain potentially hepatoxic botanicals?
2024-08-06
Millions of Americans consume supplements that contain potentially hepatoxic botanical ingredients, according to a study from University of Michigan researchers.
Over a 30-day period, 4.7% of the adults surveyed in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2017 to 2020 took herbal and dietary supplements containing at least one of the botanicals of interest: turmeric; green tea; ashwagandha; black cohosh; garcinia cambogia; and red yeast rice containing products.
The resulting paper, “Estimated Exposure ...
No room for nuance in polarized political climate: SFU study
2024-08-06
Sometimes you just can’t win, and that goes double for people navigating the increasingly polarized political landscape in the United States.
Having nuanced opinions of politics in the U.S. turns out to be a very lonely, and unpopular, road, according to a recent study from a research team that includes assistant professor Aviva Phillipp-Muller from Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the study found that people who express ambivalence about political topics – ranging from COVID-19 mask mandates, immigration and the death ...
What happens to your brain when you drink with friends?
2024-08-06
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 6, 2024) – Grab a drink with friends at happy hour and you’re likely to feel chatty, friendly and upbeat. But grab a drink alone and you may experience feelings of depression. Researchers think they now know why this happens.
“Social settings influence how individuals react to alcohol, yet there is no mechanistic study on how and why this occurs,” said Kyung-An Han, Ph.D., a biologist at The University of Texas at El Paso who uses fruit flies to study alcoholism.
Now, Han and a team of UTEP faculty and students have taken a key step in understanding the neurobiological process behind social drinking and how it boosts ...
University of Houston researchers create new treatment and vaccine for flu and various coronaviruses
2024-08-06
A team of researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered two new ways of preventing and treating respiratory viruses. In back-to-back papers in Nature Communications, the team - from the lab of Navin Varadarajan, M.D. Anderson Professor of William A. Brookshire Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering - reports the development and validation of NanoSTING, a nasal spray, as a broad-spectrum immune activator for controlling infection against multiple respiratory viruses; and the development of NanoSTING-SN, a pan-coronavirus nasal vaccine, that can protect against infection and disease by all members of the coronavirus family.
NanoSTING ...
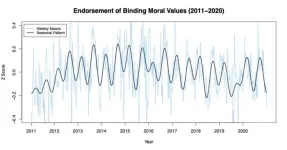
People's moral values change with the seasons
2024-08-06
A new UBC study has revealed regular seasonal shifts in people’s moral values.
The finding has potential implications for politics, law and health—including the timing of elections and court cases, as well as public response to a health crisis.
The research published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) analyzed survey responses from more than 230,000 people in the U.S. over 10 years and revealed that people’s embrace of certain moral ...
Researchers reveal atomic-scale details of catalysts’ active sites
2024-08-06
The chemical and energy industries depend upon catalysts to drive the reactions used to create their products. Many important reactions use heterogeneous catalysts — meaning that the catalysts are in a different phase of matter than the substances they are reacting with, such as solid platinum reacting with gases in an automobile’s catalytic converter.
Scientists have investigated the surface of well-defined single crystals, illuminating the mechanisms underlying many chemical reactions. However, there is much more to be learned. For heterogeneous catalysts, their 3D atomic structure, their chemical composition and the nature of ...
The prescription for a healthier democracy
2024-08-06
When we’re sick, the first step on the road to recovery is a visit to the doctor’s office.
It turns out the same may also be true for breathing life into America’s democracy.
A Rutgers University–New Brunswick study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum finds that physicians can play a crucial role in strengthening political inclusion of marginalized groups by aiding patients in voter registration.
“Hospitals aren’t the first place we think of when it comes to voter registration,” said Katherine McCabe, an associate professor of American politics at Rutgers University-New Brunswick and lead ...
New substrate material for flexible electronics could help combat e-waste
2024-08-06
Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a rapidly growing global problem, and it’s expected to worsen with the production of new kinds of flexible electronics for robotics, wearable devices, health monitors, and other new applications, including single-use devices.
A new kind of flexible substrate material developed at MIT, the University of Utah, and Meta has the potential to enable not only the recycling of materials and components at the end of a device’s useful life, but also the scalable manufacture of more ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists probe molecular cause of COVID-19 related diarrhea, revealing potential treatments
2024-08-06
Working with human stem cells that form a kind of “mini intestine-in-a-dish,” Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have found several molecular mechanisms for COVID-19-related diarrhea, suggesting potential ways to control it.
Details of the experiments in a model of human intestinal tissue, called enteroids, are described on July 30 in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Along with the unpleasant aches, fever, sore throat, cough, respiratory distress and other symptoms that may accompany COVID-19 infection, up to half of people who get the virus will experience diarrhea. Some 30% of them will go on to develop ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] Good outcomes 10 years after surgery for ectopic bone in thoracic spineDecompression and fixation yields long-term benefits in T-OPLL, reports Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery