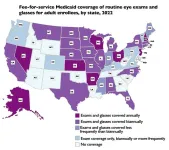
(Press-News.org) A study supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) shows that 6.5 million Medicaid enrollees (12%) lived in states without coverage for routine adult eye exams; and 14.6 million (27%) resided in states without coverage for eyeglasses. The study based on 2022-23 coverage policies, published in Health Affairs, is among the first to provide a comprehensive, state-by-state analysis of adult Medicaid benefits for basic vision services in both fee-for-service and managed care.
Medicaid provides health coverage to millions of Americans, including eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults and people with disabilities. While the federal government establishes overarching rules for Medicaid, each state runs its own program, including determining eligibility and coverage policies. The law allows states to determine coverage of eye exams and eyeglasses for adults. It is important to note that for children, federal law entitles Medicaid-enrolled infants, children, and adolescents to Medicaid coverable, appropriate, and medically necessary services needed to correct and ameliorate health conditions, including vision services.
“Our study clearly shows that there are opportunities to expand coverage of routine vision services at the state level, and based on previous research, we expect more generous coverage would reduce rates of vision impairment, improve quality of life, and promote health equity,” said Brandy Lipton, Ph.D., study author and associate professor of health, society and behavior at the University of California, Irvine.
Exams conducted by an eye care provider are the only way to detect eye diseases early, when treatment has the best chance to prevent vision loss. Exams are also essential to obtain a prescription for glasses to correct refractive error, the leading cause of vision impairment that affects more than 12 million people in the U.S.
The analysis of 2020 Medicaid enrollee data, and 2022-23 coverage policies, shows that state-level coverage for adults varied widely; gaps in coverage included:
In 20 states, fee-for-service Medicaid policies did not cover glasses at all; and in 12 of those states, eye exams were also not covered.
Seven states had no coverage for exams or glasses under both fee-for-service and managed care policies (Arizona, Idaho, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Tennessee, West Virginia, and Wyoming).
Thirty-five states did not cover low vision aids such as magnifiers and loupes.
“Visual impairment can be corrected with glasses in most instances, but not all. Particularly among older adults, lack of coverage for low vision aids may be an important gap,” said Lipton.
Moreover, even in states that had coverage for vision care services, copays and restrictive policies could still be a barrier for enrollees following through on an exam or glasses. Fully two-thirds of states required enrollees to cost share.
Medical Expenditure Panel Survey data show that out-of-pocket expenses for an uninsured adult for an eye exam and glasses can cost around $485, which is more than a third of the monthly income for a single adult living at or below the federal poverty level.
Maine had the most restrictive glasses coverage policy, where glasses were covered only once per lifetime, and only for people who required an unusually strong prescription to correct their vision.
Previous research shows that vision impairment can increase the risk of falls and hip fractures, difficulties performing activities of daily living, social isolation, depression, cognitive impairment and mortality.
“Reducing disparities in vision care is a powerful way to improve quality of life for everyone. This study points to opportunities for expanding coverage to reduce inequities in basic vision care for people with lower incomes,” said Michael F. Chiang, M.D., NEI director.
With the aging of the U.S. population, the number of people with vision impairment from all causes is expected to double by 2050.
The study was funded by NEI grant R01EY033746.
Reference:
Lipton, BJ; Garcia, J; Boudreaux, MH; Axatyan, P; and McInerney, P. “Most state Medicaid programs cover routine eye exams for adults, but coverage of other routine vision services varies.” Published August 5, 2024, Health Affairs. DOI:10.1377/hlthaff.2023.00873
END
Medicaid vision coverage for adults varies widely by state
NIH-funded study finds lack of coverage, copays, restrictive policies barriers to vital eye care for adults
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chemical and nutritional profile of fruit, vegetables and co-produts to improve human health
2024-08-06
A new study emphasizes the vital role of fruits, vegetables, and their co-products in boosting human health and life expectancy. Packed with minerals, vitamins, and dietary fiber, these foods help prevent chronic diseases. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, such as vitamins and carotenoids, combat harmful free radicals.
Interested in more information and in contributing to the topic, visit: bit.ly/46zTKFX
Combining various fruits like oranges, apples, grapes, and blueberries enhances antioxidant effects. Diets rich in these foods can lower blood pressure, reduce heart disease and ...
Better cancer trial representation begins with speaking one’s language
2024-08-06
NEW YORK, NY (July 29, 2024) ---- Underrepresentation of racial and ethnic minority populations in cancer clinical trials persists partly because translation and interpretation services and resources are unavailable or inadequate in the United States, according to a Children’s Oncology Group (COG) study led by Columbia University School of Nursing. The updated study was published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute Cancer Spectrum on July 25, 2024 and will appear in the August 2024 journal issue.
In 2019, 68 million people in the United States were reported to speak a language other than ...
Social and structural factors are key drivers of disparities in obesity rates
2024-08-06
Obesity is an epidemic in the United States. It has been increasing among adults of all races and ethnicities over the last two decades; however, obesity is higher among Non-Hispanic Black adults, Hispanic adults, and American Indian or Alaska Native adults, than their White and Asian counterparts, according to the National Institutes of Health. Adults with lower income also have higher risk of obesity than those with a high income.
A George Mason University College of Public Health team of interprofessional researchers analyzed the last five years ...
New study helps global MNCs weigh the pros and cons of implementing blockchain technology
2024-08-06
Blockchain technology has become one of the most hyped advancements in recent years, but there hasn’t been a clear understanding of the potential trade-offs for its use by multinational corporations (MNCs). A new study published in the Global Strategy Journal provides a better understanding of blockchain merits and drawbacks by focusing on three particular applications of the technology in this sector: financial transactions, collaboration, and data analytics.
The study, “A perspective on three trade-offs of blockchain technology for the global strategy of the MNC,” was authored by Tuuli Hakkarainen of the University of Liverpool, Anatoli Colicev of the University ...
Increased ventilation not effective in reducing influenza virus spread in play-based model, Emory study finds
2024-08-06
Increasing ventilation in child-care settings may not always be effective at preventing flu virus spread, according to a new study published by a team of researchers at Emory University, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, and Virginia Tech.
The spread of flu viruses is commonly studied in animal models that don’t mimic the real-life scenarios of the human experience, making it difficult to evaluate strategies that will be effective in common places where disease spreads rapidly, such as childcare settings. As reported online and in a coming print issue of the journal Proceedings of the National ...
Lonely people tend to have more nightmares, Oregon State University research shows
2024-08-06
CORVALLIS, Ore. – People who are lonely are more apt to have bad dreams, according to a collaboration that included an Oregon State University scientist.
The findings are important because both loneliness and sleep disorders are serious public health issues, said OSU’s Colin Hesse. They are connected to increased risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death.
In a paper published in the Journal of Psychology, Hesse and researchers at the University of Arizona, the University of Tampa and Whitworth University note that stress ...
UC Irvine-led team reveals how TREM2 genetic mutation affects late-onset Alzheimer’s
2024-08-06
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 6, 2024 — Researchers led by the University of California, Irvine have discovered how the TREM2 R47H genetic mutation causes certain brain areas to develop abnormal protein clumps, called beta-amyloid plaques, associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Leveraging single-cell Merfish spatial transcriptomics technology, the team was able to profile the effects of the mutation across multiple cortical and subcortical brain regions, offering first-of-their-kind insights at the single-cell level.
The study, recently published online in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, compared the brains of normal mice and special mouse models that undergo ...
Considering the patient’s perspective in inducible laryngeal obstruction care
2024-08-06
Inducible laryngeal obstruction is a breathing disorder characterized by unwanted vocal fold closure having the potential to restrict breathing at times.
It’s estimated that between 3-12% of patients with dyspnea complaints have inducible laryngeal obstruction.
Patients with inducible laryngeal obstruction are thought to make up to 22% of patients with frequent emergency room visits due to sudden onset dyspnea.
While experts know how to treat the condition, there’s not much formal research about what patients with the disorder experience ...
Living with a killer: How an unlikely mantis shrimp-clam association violates a biological principle
2024-08-06
Media
When clams gamble on living with a killer, sometimes their luck may run out, according to a University of Michigan study.
A longstanding question in ecology asks how can so many different species co-occur, or live together, at the same time and at the same place. One influential theory called the competitive exclusion principle suggests that only one species can occupy a particular niche in a biological community at any one time.
But out in the wild, researchers find many instances of different species that appear to occupy the same ...
Researchers urge united nations to reject growth-driven framework in favor of lower population and consumption
2024-08-06
In a new peer-reviewed article in The Journal of Population and Sustainability, demographic experts are urging the United Nations to reject the current “‘growth’ paradigm which treats Earth and its nonhuman inhabitants as mere resources” and to take the lead in “contracting the large-scale variables of the human enterprise” in order to “forge a path out of multiple environmental and social crises,” and “reverse our advanced state of ecological overshoot.”
Earth Overshoot Day, the date when humanity’s demand on nature’s resources surpasses Earth’s capacity ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
[Press-News.org] Medicaid vision coverage for adults varies widely by stateNIH-funded study finds lack of coverage, copays, restrictive policies barriers to vital eye care for adults