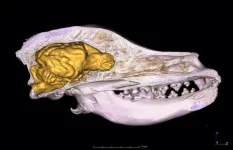
(Press-News.org) A recent study by László Zsolt Garamszegi from the Institute of Ecology and Botany, Centre for Ecological Research, Hungary, and Niclas Kolm from the Department of Zoology, Stockholm University, Sweden, challenges the long-held notion that domestication is the primary driver of reduced brain size in domesticated animals, specifically dogs. The study employs a phylogenetic comparative method to analyze whether the domesticated dog (Canis familiaris) exhibits a uniquely small brain relative to its body size compared to other canid species.
The prevailing belief has been that domestication leads to a significant reduction in brain size due to relaxed selection pressures, such as reduced need for foraging, mating competition, and predator avoidance. This phenomenon is thought to be a result of the decreased necessity for metabolically costly brain tissue in a domesticated environment. While domesticated dogs show a substantial decrease in brain size compared to their wild ancestor, the grey wolf (Canis lupus), this study aimed to determine if this reduction is exceptional when viewed in a broader phylogenetic context.
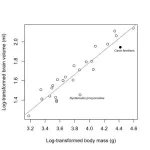
Garamszegi and Kolm analyzed brain and body size data for 25 canid species, including ancient dog breeds that are genetically closer to the ancestral domesticated dog. Their phylogenetic predictions and allometric regressions showed that the reduction in brain size in domesticated dogs is not an unambiguous evolutionary singularity. The observed brain size in dogs fell within the expected range for most ancient breeds used in the study, suggesting that domestication is not uniquely influential in reducing brain size among canids.
Interestingly, the study found that the common raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides), which hibernates, is a more pronounced outlier in terms of brain size reduction. Hibernation, associated with prolonged periods of low metabolic activity and food scarcity, is hypothesized to constrain brain size evolution due to the high energy demands of large brains. The raccoon dog's significantly smaller brain size supports this hypothesis, highlighting that factors other than domestication, such as ecological adaptations like hibernation, can also drive reductions in brain size.
The study concludes that while domestication does contribute to brain size reduction in dogs, it should not be overemphasized as a uniquely powerful evolutionary force. The findings suggest that other ecological and evolutionary pressures can similarly affect brain size and can mediate extreme variations in non-domesticated species as well. A more balanced and less human-focused perspective could refine our understanding of the complex interplay between domestication and brain size evolution in mammals. The work of Garamszegi and Kolm might change how we interpret the evolutionary role of domestication.
END
Domestication causes smaller brian size in dogs than in the wolf, but such an evolutionary change is not unusual in wild animals
2024-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gestational diabetes does not increase risk of breast cancer, large Danish study finds
2024-08-07
*Note this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association of the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2024, Madrid, 9-13 September). Please credit the meeting if using this material*
Women who develop gestational diabetes are not more likely to go on to be diagnosed with breast cancer, according to a study of almost three-quarters of a million mothers to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September).
Gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that can develop during ...
Chemical and nutritional profile of fruit, vegetables and co-products to improve human health
2024-08-06
New studies emphasize the vital role of fruits, vegetables, and their co-products in boosting human health and life expectancy. Packed with minerals, vitamins, and dietary fiber, these foods help prevent chronic diseases. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, such as vitamins and carotenoids, combat harmful free radicals.
To get more information and to contribute to the research, visit: bit.ly/46zTKFX
Combining various fruits like oranges, apples, grapes, and blueberries enhances antioxidant effects. Diets ...
Attitudes such as distrust of government can cause swine farmers to resist animal biosecurity: UVM study finds
2024-08-06
A new University of Vermont study published today in Nature: Scientific Reports examines the social and psychological aspects of farmers’ decisions about whether or not to implement biosecurity measures on pig farms. This is the first study to look at human behavior in biosecurity adoption among swine producers.
Through survey data and simulations, the scientists found that it is largely farmers’ attitudes, which have the biggest impact on farmers’ decision-making strategies regarding implementing farm biosecurity. Farmer’s attitudes ...
Scientists reach consensus for fasting terminology
2024-08-06
Dr. Eric Ravussin of Pennington Biomedical Research Center in Baton Rouge was one of 38 scientists from five continents to present the first international consensus on fasting terminology and key definitions. Published in Cell Metabolism, the recent study reflects the increasing popularity of diets tied to fasting and a significant increase in scientific studies of fasting. While the application of fasting is rapidly growing, there was previously no globally established terminology.
The panel was the first to bring ...
C-Path welcomes new advisory members to Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency consortium
2024-08-06
TUCSON, Ariz., August 6, 2024 — Critical Path Institute’s (C-Path) Critical Path for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (CPA-1) consortium today announced the addition of several key advisory members. The new members, recognized experts in their respective fields and patient advocacy organizations, will contribute their significant expertise to the consortium’s mission to accelerate drug development for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD), a rare genetic disorder.
Joining the consortium are:
Alpha-1 Foundation
COPD Foundation
Global ...
Drug bypasses suppressive immune cells to unleash immunotherapy
2024-08-06
By recruiting the immune system to combat tumor cells, immunotherapy has improved survival rates, offering hope to millions of cancer patients. However, only about one in five people responds favorably to these treatments.
With a goal of understanding and addressing immunotherapy’s limitations, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis have found that the immune system can be its own worst enemy in the fight against cancer. In a new study in mice, a subset of immune cells – type 1 regulatory T cells, or Tr1 cells – did its normal job of preventing the immune system from overreacting but did so while inadvertently restraining immunotherapy’s ...
Treatment with smoke can favor seed germination in the Cerrado
2024-08-06
For thousands of years, plants have evolved in the presence of wildfires in the Cerrado, Brazil’s savanna-like biome. Scientists at São Paulo State University (UNESP) studied the effect of smoke on seed germination for 44 plant species typical of the Cerrado, as reported in an article published in Plant Ecology, where they stress that their findings could be used to optimize the restoration of degraded areas.
The study was conducted by PhD candidate Gabriel Schmidt Teixeira Motta under the supervision of Rosana Marta Kolb, a professor at UNESP.
“Previous studies focused on the effect of smoke on only a few ...
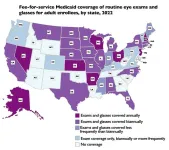
Medicaid vision coverage for adults varies widely by state
2024-08-06
A study supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) shows that 6.5 million Medicaid enrollees (12%) lived in states without coverage for routine adult eye exams; and 14.6 million (27%) resided in states without coverage for eyeglasses. The study based on 2022-23 coverage policies, published in Health Affairs, is among the first to provide a comprehensive, state-by-state analysis of adult Medicaid benefits for basic vision services in both fee-for-service and managed care.
Medicaid provides health coverage to millions of Americans, including eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly ...
Chemical and nutritional profile of fruit, vegetables and co-produts to improve human health
2024-08-06
A new study emphasizes the vital role of fruits, vegetables, and their co-products in boosting human health and life expectancy. Packed with minerals, vitamins, and dietary fiber, these foods help prevent chronic diseases. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, such as vitamins and carotenoids, combat harmful free radicals.
Interested in more information and in contributing to the topic, visit: bit.ly/46zTKFX
Combining various fruits like oranges, apples, grapes, and blueberries enhances antioxidant effects. Diets rich in these foods can lower blood pressure, reduce heart disease and ...
Better cancer trial representation begins with speaking one’s language
2024-08-06
NEW YORK, NY (July 29, 2024) ---- Underrepresentation of racial and ethnic minority populations in cancer clinical trials persists partly because translation and interpretation services and resources are unavailable or inadequate in the United States, according to a Children’s Oncology Group (COG) study led by Columbia University School of Nursing. The updated study was published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute Cancer Spectrum on July 25, 2024 and will appear in the August 2024 journal issue.
In 2019, 68 million people in the United States were reported to speak a language other than ...