(Press-News.org) Everyone gets sleepy at work from time to time, especially after a big lunch. But for people whose jobs involve driving or working with heavy machinery, drowsiness can be extremely dangerous — if not outright deadly. Drowsy driving contributes to hundreds of fatal vehicle accidents in the U.S. each year, and the National Safety Council has cited drowsiness as a critical hazard in construction and mining.
To help protect drivers and machine operators from the dangers of drifting off, engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have created prototype earbuds that can detect the signs of drowsiness in the brain.
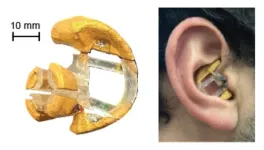
The earbuds detect brain waves in the same way as an electroencephalogram (EEG), a test that doctors use to measure electrical activity in the brain. While most EEGs detect brain waves using a series of electrodes attached to the head, the earbuds do so using built-in electrodes that are designed to make contact with the ear canal.
The electrical signals detected by the ear buds are smaller than those picked up by a traditional EEG. However, in a new study, the researchers show that their Ear EEG platform is sensitive enough to detect alpha waves, a pattern of brain activity that increases when you close your eyes or start to fall asleep.
“I was inspired when I bought my first pair of Apple's AirPods in 2017. I immediately thought, ‘What an amazing platform for neural recording,’” said study senior author Rikky Muller, an associate professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences at UC Berkeley. “We believe that this technology has many potential uses, and that classifying drowsiness is a good indicator that the technology can be used to classify sleep and even diagnose sleep disorders.”
Using an earbud as an EEG electrode poses a variety of practical challenges. In order to obtain an accurate EEG, electrodes need to make good contact with the skin. This is relatively easy to achieve in traditional EEGs, which use flat metal electrodes stuck to the scalp. However, it is much trickier to design an earbud that will fit snugly — and comfortably — in a wide variety of ear sizes and shapes.
When Muller’s team started working on the project, other groups developing Ear EEG platforms were either using wet electrode gels to ensure a good seal between the earbud and the ear canal, or creating custom-molded earpieces for each individual user. She and her team wanted to design a model that was dry and user generic, so that anyone could stick them in their ears and get reliable readings.
“My personal goal was to try to make a device that could be used every day by someone who would really benefit from it,” said Ryan Kaveh, a UC Berkeley postdoctoral scholar and co-first author of the study. “In order to do that, I knew that it would have to be reusable, fit a variety of people, and [be] easy to manufacture.”
Kaveh co-led the study with graduate student Carolyn Schwendeman and collaborated with Ana Arias’s lab at UC Berkeley to design the final earpiece in three sizes: small, medium and large. The earpiece incorporates multiple electrodes in a cantilevered design that applies gentle outward pressure to the ear canal and uses flexible electronics to ensure a comfortable fit. The signals are read out through a custom, low-power, wireless electronic interface.
In a 2020 paper, the researchers showed that these earpieces can detect a number of physiological signals, including eye blinks, alpha brain waves and the auditory steady-state response, which is the brain’s response to hearing a steady pitch. In the new study, they improved the earpiece design and incorporated machine learning to demonstrate how the earpieces could be used in a real-world application.
As part of the experiment, they asked nine volunteers to wear the earpieces while doing a series of boring tasks in a darkened room. Every so often, the volunteers were asked to rate their level of drowsiness, and their response times were measured.
“We found that even when the signal quality from the earpieces seemed worse, we could still classify the onset of drowsiness with the same level of accuracy as much more complicated, bulky systems,” Kaveh said. The earpieces also retain their accuracy when categorizing drowsiness in brand-new users, a characteristic of devices that could work 'out of the box'.
Muller, who developed the Ear EEG with the support of the Bakar Fellowship and the Bakar Prize, is continuing to refine the design and explore other potential applications of the device, which can also record signals beyond EEG, such as heart beats, eye movements and jaw clenches.
“Wireless earbuds are something we already wear all the time,” Muller said. “That’s what makes Ear EEG such a compelling approach to wearables. It doesn’t require anything extra.”
This study was supported in part by the Ford University Research Program and a Bakar Spark Award.
END
Dozing at the wheel? Not with these fatigue-detecting earbuds
UC Berkeley researchers have created earpieces that identify brain activity associated with relaxation and drowsiness
2024-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
FDA approves new therapy for glioma patients for first time in decades
2024-08-07
Boston – Vorasidenib has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with Grade 2 gliomas with IDH1 or IDH2 mutations.
Based on evidence from the INDIGO clinical trial, a global phase 3, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial, vorasidenib more than doubled progression-free survival and delayed the need for treatment with radiation and chemotherapy for patients with Grade 2 IDH-mutant glioma after surgery to remove the tumor. INDIGO was the first phase 3 clinical trial of a molecularly targeted therapy for IDH-mutant glioma.
“The INDIGO trial ...
Think about banning kitchen worktop favourite to ward off incurable lung disease, urge doctors
2024-08-07
It may now be time to ban artificial stone—a firm favourite for kitchen worktops in the UK— to ward off the incurable lung disease caused by its manufacturing and fitting, say a team of doctors in the journal Thorax after treating the first 8 cases of artificial stone silicosis reported in the UK.
Silicosis is caused by breathing in crystalline silica dust, and millions of people around the world are at risk of developing it as a result of their jobs in mining, quarrying, stone-cutting ...
Follow Australia’s lead and ban artificial stone, researchers urge European governments
2024-08-07
The UK and the European Union should follow Australia’s lead and ban the kitchen worktop favourite and cause of irreversible and rapidly progressive lung disease—artificial stone siliicosis—urge researchers in an editorial, published online in Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
And until a ban comes into force, all possible control measures should be legally enforced to minimise workers’ exposure to the harmful crystalline silica dust generated during its manufacture and fitting, insist the authors.
Artificial stone (also known as engineered stone) is widely used for surfaces ...
Reducing child poverty in England would significantly boost child health and narrow health inequalities
2024-08-07
Renewed efforts to reduce child poverty in England between now and 2033, such as removing the 2-child limit on child benefit, would significantly boost several aspects of child health and narrow health inequalities across the country, finds research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Tackling it would substantially cut the number of infant deaths and children in care, as well as rates of childhood nutritional anaemia and emergency admissions, with the most deprived regions, especially ...
Cut ties with Coca Cola in interests of athletes, spectators, and the planet, IOC urged
2024-08-07
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) should cut its ties with Coca Cola in the best interests of athletes, spectators, and the planet, urge Trish Cotter and Sandra Mullin of the international public health organisation, Vital Strategies, in an editorial to be published shortly in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.*
The company’s sponsorship forces athletes to implicitly endorse unhealthy sugary drinks and provides Coca Cola with elite access to political and corporate leaders to exert its influence, insist the authors.
Coca Cola has sponsored the Olympic Games for almost 100 years, they note. And there’s ...
Bloomberg Philanthropies makes founding gift to Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine
2024-08-07
Today, Bloomberg Philanthropies announced a gift of $5 million in seed funding to support the creation of the Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine (XOCOM), a newly established medical school in New Orleans founded by Xavier University of Louisiana and Ochsner Health.
Earlier this year, Xavier University of Louisiana, a historically Black college and university (HBCU) with a strong track record of sending graduates into the medical field, and Ochsner Health, the Gulf South’s leading not-for-profit health system with a long academic ...
Domestication causes smaller brian size in dogs than in the wolf, but such an evolutionary change is not unusual in wild animals
2024-08-07
A recent study by László Zsolt Garamszegi from the Institute of Ecology and Botany, Centre for Ecological Research, Hungary, and Niclas Kolm from the Department of Zoology, Stockholm University, Sweden, challenges the long-held notion that domestication is the primary driver of reduced brain size in domesticated animals, specifically dogs. The study employs a phylogenetic comparative method to analyze whether the domesticated dog (Canis familiaris) exhibits a uniquely small brain relative to its body size compared to other canid species.
The prevailing belief has been that domestication leads to a significant ...
Gestational diabetes does not increase risk of breast cancer, large Danish study finds
2024-08-07
*Note this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association of the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2024, Madrid, 9-13 September). Please credit the meeting if using this material*
Women who develop gestational diabetes are not more likely to go on to be diagnosed with breast cancer, according to a study of almost three-quarters of a million mothers to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September).
Gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that can develop during ...
Chemical and nutritional profile of fruit, vegetables and co-products to improve human health
2024-08-06
New studies emphasize the vital role of fruits, vegetables, and their co-products in boosting human health and life expectancy. Packed with minerals, vitamins, and dietary fiber, these foods help prevent chronic diseases. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, such as vitamins and carotenoids, combat harmful free radicals.
To get more information and to contribute to the research, visit: bit.ly/46zTKFX
Combining various fruits like oranges, apples, grapes, and blueberries enhances antioxidant effects. Diets ...
Attitudes such as distrust of government can cause swine farmers to resist animal biosecurity: UVM study finds
2024-08-06
A new University of Vermont study published today in Nature: Scientific Reports examines the social and psychological aspects of farmers’ decisions about whether or not to implement biosecurity measures on pig farms. This is the first study to look at human behavior in biosecurity adoption among swine producers.
Through survey data and simulations, the scientists found that it is largely farmers’ attitudes, which have the biggest impact on farmers’ decision-making strategies regarding implementing farm biosecurity. Farmer’s attitudes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
[Press-News.org] Dozing at the wheel? Not with these fatigue-detecting earbudsUC Berkeley researchers have created earpieces that identify brain activity associated with relaxation and drowsiness