(Press-News.org)
Rome, 7 August 2024 -- Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are one of the most recent open mysteries of modern astrophysics. Within a few milliseconds, these powerful events release an immense amount of energy, among the highest observable in cosmic phenomena. FRBs were discovered just over ten years ago and mostly arise from extragalactic sources. Their origin, however, is still uncertain and there are huge ongoing efforts by the astrophysics community around the world to understand the physical processes behind them.
In very few cases, the rapid flash that characterises FRBs coincides with a persistent emission, which is also observed in the radio band. A new study led by the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) has recorded the weakest persistent radio emission ever detected for an FRB so far. The subject of the study is FRB20201124A, a fast radio burst discovered in 2020, whose source is located about 1.3 billion light-years away from us. Along with INAF researchers, the collaboration involves the Universities of Bologna, Trieste and Calabria, in Italy, and the international participation of research institutes and universities in China, the United States, Spain and Germany.
The observations were performed with the most sensitive radio telescope in the world, the Very Large Array (VLA) in the United States. The data enabled scientists to verify the theoretical prediction that a plasma bubble is at the origin of the persistent radio emission of fast radio bursts. The results are published today in the journal Nature.
“We were able to demonstrate through observations that the persistent emission observed along with some fast radio bursts behaves as expected from the nebular emission model, i.e. a ‘bubble’ of ionised gas that surrounds the central engine” explains Gabriele Bruni, INAF researcher in Rome and lead author of the new paper. “In particular, through radio observations of one of the bursts that is nearest to us, we were able to measure the weak persistent emission coming from the same location as the FRB, extending the radio flux range explored so far for these objects by two orders of magnitude”.
This research also helps narrow down the nature of the engine powering these mysterious radio flashes. According to the new data, the phenomenon is based on a magnetar (a strongly magnetised neutron star) or a high-accretion X-ray binary, i.e. a binary system consisting of a neutron star or black hole, accreting material from a companion star at very intense rates. In fact, winds produced by the magnetar or the X-ray binary would be able to “blow” the plasma bubble giving rise to the persistent radio emission. There is therefore a direct physical relationship between the engine of FRBs and the bubble, which is located in its immediate vicinity.
The motivation for this observing campaign came from another work led by Luigi Piro of INAF, who is also a co-author of the new paper. In their earlier work, the researchers had identified the persistent emission in this FRB’s host galaxy, but they had not yet measured the position with sufficient precision to associate the two phenomena. “In this new work, we conducted a campaign at higher spatial resolution with the VLA, along with observations in different bands with the NOEMA interferometer and the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GranTeCan), which allowed us to reconstruct the general picture of the galaxy and discover the presence of a compact radio source – the FRB plasma bubble – immersed in the star-forming region” adds Piro. “In the meantime, the theoretical model on the nebula had also been published, allowing us to test its validity and, finally, to confirm the model itself.”
Most of the work focussed on excluding that the persistent radio emission comes from a star-forming region, and is therefore not physically linked to the FRB source. For this purpose, the NOEMA observations in the millimetre band measured the amount of dust, which is a tracer of “obscured” star-forming regions, whereas GranTeCan optical observations measured emission from ionised hydrogen, which is also a tracer of the star formation rate.
“Optical observations were an important element to study the FRB region at a spatial resolution similar to that of radio observations” notes co-author Eliana Palazzi from INAF in Bologna. “Mapping hydrogen emission at such a great level of detail allowed us to derive the local star formation rate, which we found to be too low to justify continuous radio emission.”
Most FRBs do not exhibit persistent emission. Until now, this type of emission had only been associated with two FRBs – both, however, with such a low brightness that did not allow to verify the proposed model. FRB20201124A, instead, is located at a large but not excessive distance, which made it possible to measure the persistent emission despite its low brightness. Understanding the nature of the persistent emission allows researchers to add a piece to the puzzle about the nature of these mysterious cosmic sources.
For further information:
The paper “A nebular origin for the persistent radio emission of fast radio bursts”, by Gabriele Bruni, Luigi Piro, Yuan-Pei Yang, Salvatore Quai, Bing Zhang, Eliana Palazzi, Luciano Nicastro, Chiara Feruglio, Roberta Tripodi, Brendan O'Connor, Angela Gardini, Sandra Savaglio, Andrea Rossi, A. M. Nicuesa Guelbenzu, Rosita Paladino, is published in the journal Nature.
END
One of the academic world’s largest international meetings addressing topics in microbial ecology, the 19th International Symposium on Microbial Ecology (ISME), will take place in Cape Town, South Africa in August.
More than 1 500 scientists from over 50 countries worldwide will convene at the Cape Town International Convention Centre (CT-ICC) from 18 to 23 August 2024. This will be the first time that this prestigious meeting is held on the African continent.
Prof. Thulani Makhalanyane, chair of the ISME organising committee and professor of microbiology at Stellenbosch University (SU), ...
Recent advancements highlight the intricate interplay between the heart and brain, underscoring their profound influence on each other, especially concerning central nervous system (CNS) neurological disorders. In light of this, a new special issue aims to explore therapeutic targets that impact both cardiac and cerebral functions. By focusing on these targets, the issue seeks to provide an in-depth understanding of the complex relationship between these vital organs.
For more information and to contribute ...
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that highly experienced human resources leader and author Claire Fox has been appointed to the role of Chief People Officer.
Claire joins the Digital Science Executive Team at a time of growth for the company, with its continued mission to drive progress for all through research and innovation.
Based in London, UK, Claire has more than 20 years’ HR experience, initially in national, European and global HR leadership roles in the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) sector at Unilever. She then moved into international development, with senior leadership roles including ...
SAN DIEGO – AUGUST 7, 2024 – West Health and UC San Diego Health announced today that nearly three million older adults in California now have access to specialized care for medical emergencies, making the state the nation’s leader in accredited geriatric emergency departments (GEDs). Nearly half of the state’s seniors now have access to a GED compared to about 30% of seniors nationwide.
UC San Diego Health and West Health collaborated and collectively engaged more than 650 ...
Anyone who has picnicked on the beach has experienced the unpleasant crunch of a sandwich with a surprise helping of sand. But for primates, the tolerance for sand may depend on whether their energy is better spent reproducing and fighting rivals or on protecting their teeth from a mouthful of grit, according to a new Dartmouth study.
Social rank may determine whether animals prioritize immediate energy consumption over long-term health, or vice versa, the researchers report in the journal eLife. They observed the eating habits of long-tailed ...
Los Angeles, California – August 6, 2024 - In a significant leap forward for healthcare equity and accessibility, researchers at the University of Victoria and the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) have developed a revolutionary system that combines remote health monitoring and drug delivery using 3D-printed hollow microneedles. This innovative approach, detailed in a recent study published in Advanced Healthcare Materials, promises to transform healthcare delivery, particularly for those in underserved or remote regions.
The ...
A blood test can help predict which preterm babies will go onto develop chronic lung disease, allowing for earlier diagnosis and more targeted treatments, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology found that changes in certain blood proteins, alongside gestational age, birth weight and sex, strongly predicated bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) within 72 hours of life.
BPD usually occurs when a baby’s lungs are damaged by respiratory support and the long-term ...
New research from a team of genome scientists and DNA damage response experts breaks new ground in understanding the function of a protein currently limited in clinical trials for cancer treatments.
Led by Haichao Zhao, PhD, in the Yan Lab at UNC Charlotte, the new research shows how ATM-mediated signaling is induced by DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs) for DNA damage repair – illuminating the distinct mechanisms of SSB-induced ATM kinase and shedding an important light on APE1 function.
In the new study, published today in Nature Communications, ...
SOUTHFIELD, MI, Aug. 7, 2024 - New Corewell Health™ research suggests an MRI scan can help predict whether patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer (cancer confined to the entire prostate) may have more aggressive cancer in five years. Knowing this could potentially help doctors determine if treatment is needed up front vs. using a method called active surveillance where the disease is closely monitored over time. The study, recently published in the Journal of Urology, is the first to evaluate this risk group.
Currently, there has been a growing trend to manage low-risk prostate cancer patients with active ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
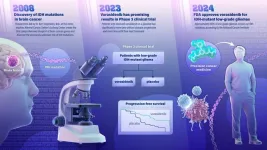
A new drug for treatment of a type of brain cancer, called IDH-mutant low-grade glioma, was approved Aug. 6 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The promising new drug stems from a 2008 genetic discovery made at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The drug, called vorasidenib, is a targeted cancer therapy that works by inhibiting the activity of a mutated gene called IDH, slowing the growth of the cancer. The gene was identified by Bert Vogelstein, M.D., and team at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center’s ...