(Press-News.org)
“These findings indicate that renalase-1 is a potential antigen for TCR recognition in melanoma and could be considered as a target for immunotherapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 8, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on August 5, 2024, entitled, “Chemical complementarity of tumor resident, T-cell receptor CDR3s and renalase-1 correlates with increased melanoma survival.”
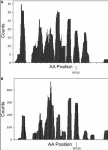
As mentioned in the Abstract of this study, overexpression of the secretory protein renalase-1 negatively impacts the survival of melanoma and pancreatic cancer patients, while inhibition of renalase-1 signaling drives tumor rejection by promoting T-cell activation.
Thus, researchers Saif Zaman, Fred S. Gorelick, Andrea Chrobrutskiy, Boris I. Chobrutskiy, Gary V. Desir, and George Blanck from Yale School of Medicine, Veteran’s Administration Healthcare System, Oregon Health and Science University Hospital, Morsani College of Medicine, and H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, investigated the chemical complementarity between melanoma-resident, T-cell receptor (TCR) complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) amino acid sequences (AAs) and the renalase-1 protein.
“In this study, we asked whether the RNLS protein could potentially be a tumor antigen by examining chemical complementarity between melanoma tumor-resident TCR CDR3s and the AA sequence of RNLS.”
The results suggest that there could be biologically relevant antigenic interaction between RNLS epitopes and T-cell receptors (TCRs).
“We hypothesize that RNLS protein could be recognized by TCRs, leading to local immune responses against melanoma, similar to what we have previously demonstrated with wildtype cancer antigens in the melanoma and glioblastoma settings.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28633
Correspondence to: George Blanck
Email: gblanck@usf.edu
Keywords: RNLS, melanoma, T-cell receptor CDR3s, chemical complementarity
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Reddit
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
END
Key Takeaways
-Fusion has the potential to provide abundant clean energy
-One to two-year awards range from $100,000 to $500,000
In a continuing effort to forge and fund public-private partnerships to accelerate fusion research, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today awarded $4.6 million in 17 awards to U.S. businesses via the Innovation Network for Fusion Energy (INFUSE) program.
The goal of INFUSE is to accelerate fusion energy development in the private sector by reducing impediments to collaboration between business ...
Following the Mediterranean diet versus the traditional Western diet might make you feel like you’re under less stress, according to new research conducted by a team from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The findings suggest that people can lower their perception of how much stress they can tolerate by following a Mediterranean diet, said Lina Begdache, associate professor of health and wellness studies.
“Stress is recognized to be a precursor to mental distress, and research, including our own, has demonstrated that the Mediterranean diet lowers ...
A recent study investigates the intricate mechanisms of sugar import in developing seeds of Camellia oleifera. By identifying key sugar transporters and analyzing their roles, the research provides significant insights into the molecular regulation of seed development. The findings highlight how these transporters, working alongside sucrose-metabolizing enzymes, facilitate efficient sugar import and partitioning. This study not only advances our understanding of seed development in Camellia oleifera but also suggests potential strategies to enhance seed yield and quality in this important ...
Ann Arbor, August 8, 2024 – Media coverage of shootings by police typically involve urban incidents, giving the impression that the issue is unique to cities. However, national data built from the Gun Violence Archive tells a different story, showing a higher rate of shootings by police in rural and suburban areas than in cities during 2015-2020. A new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, reports on the first nationwide, descriptive analysis of where, how often, and under ...
SAN ANTONIO, Aug. 8, 2024 – A drug effective in treating breast cancer shows new promise in addressing breast cancer with brain metastases or recurrent glioblastoma, as reported by results of a prospective window-of-opportunity trial at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio).
The window trial, in which patients agreed to receive a novel treatment before undergoing surgery, found that the drug Sacituzumab Govitecan was well-tolerated and showed signs of effectiveness for those whose breast cancer had progressed to brain tumors.
About half of all women with ...
About The Article: This Viewpoint from the National Center for Health Statistics reports the leading causes of death in the U.S. from 2019 to 2023, including the emergence of COVID-19 and shifts in other top causes as pandemic deaths decreased.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Farida Bhuiya Ahmad, MPH, email hhi0@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.15563)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Scientists have made a significant breakthrough in agricultural biotechnology by using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit the potato genome, resulting in plants with increased resistance to both biotic and abiotic stresses. This innovation could lead to a new era of sustainable farming, where crops are naturally fortified against diseases and harsh environmental conditions, ensuring a stable food supply in the face of climate change and other global challenges.
The global food system is under increasing pressure due to the compounding effects of climate change, which exacerbates the prevalence of pests and diseases in crops. Potatoes, being the third most important food crop worldwide, are ...
A recent review in the journal Sustainable Microbiology discusses how the use of biocides can promote well-being - but must only be used when there are clear benefits.
Biocide use should be restricted to applications where there are tangible benefits but also not unnecessarily restricted where genuine benefits can be demonstrated, the new review suggests.
The article ‘Sustainable application of biocides to promote hygiene and minimise antimicrobial resistance’ by scientists at the University of Manchester, UK, is published in Sustainable Microbiology, an Applied Microbiology International publication.
Contribution to sustainability
“We aimed to present ...
Amazonians are as genetically different from Andeans as Europeans are from East Asians when it comes to genetic variants that affect the response to certain drugs, according to a commentary published August 8 in the journal Cell. These genetic variations can affect what side effects an individual experiences and influence drug dosage recommendations. Taking the genetic diversity within indigenous groups as an example, the scientists highlight the need to address the diversity gap in genomics research.
Historically, Native American populations have been viewed as ...
Physicians at an academic medical center completed surveys about climate change-focused educational modules related to health and sustainability in healthcare offered through an existing biannual quality incentive program.
Most respondents thought that the modules were relevant or very relevant to their lives and clinical practices, and that their knowledge on these topics increased after completing the modules.
Perceptions of the modules’ relevance varied by physicians’ demographics and specialties.
An educational program emphasizing the relationship that climate change has with health and health care environmental sustainability was well-received by physicians, according ...