(Press-News.org) Recent research has uncovered significant genetic and epigenetic variations in blueberry cultivars, particularly between northern highbush (NHB) and southern highbush (SHB) blueberries. The study highlights gene introgression's role in SHB's adaptation to subtropical climates and identifies key genes, such as VcTBL44, associated with fruit firmness. These findings offer valuable insights and resources for future blueberry breeding.
Blueberries, part of the Vaccinium genus, are renowned for their nutritional benefits and increasing global demand. However, cultivation faces challenges like climate adaptability and fruit quality. Modern blueberries have a short domestication history, primarily through interspecific hybridization. These challenges necessitate deeper research into the genetic and epigenetic factors influencing blueberry traits.
Researchers from Peking University and Jilin Agricultural University, in collaboration with international experts, have made significant strides in blueberry genetic research. Published (DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae138) in the prestigious journal Horticulture Research on May 14, 2024, their study presents a comprehensive analysis of blueberry genomic variation, marking a pivotal moment in agricultural science.
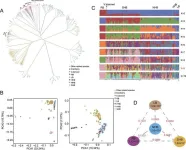
The study involved whole-genome re-sequencing and bisulfite sequencing on various blueberry cultivars to understand their genetic and epigenetic differences. Researchers identified significant gene introgression from V. darrowii and V. ashei into southern highbush (SHB), aiding its subtropical adaptation. They discovered the VcTBL44 gene, crucial for regulating fruit firmness in SHB. Additionally, they found significant differences in DNA methylation patterns between northern highbush (NHB) and SHB, particularly in CHH-DMRs associated with transposon regulation. These findings offer a comprehensive understanding of the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms that have improved blueberry cultivars, providing valuable resources for future breeding programs aimed at enhancing fruit quality and climate resilience.
Dr. Haiyue Sun, a leading researcher in the study, stated, "Our research provides a detailed genetic and epigenetic map of blueberries, offering crucial insights for breeding programs. The identification of key genes like VcTBL44 paves the way for developing cultivars with improved fruit quality and climate adaptability."
The insights from this study have significant implications for blueberry breeding. The genetic and epigenetic resources identified can develop new cultivars more resilient to climate changes and superior in fruit quality. This research enhances our understanding of blueberry genetics and provides practical tools for breeders to meet the growing consumer demand for high-quality blueberries.
###
References
DOI
10.1093/hr/uhae138
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1093/hr/uhae138
Funding information
This work was supported by funds from the State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research, the Project of Science and Technology Development of Jilin Province, China (20220508099RC), the Project of Development and Reform Commission of Jilin Province, China (2023C035-4) and startup funds from the School of Advanced Agricultural Sciences at Peking University.
About Horticulture Research
Horticulture Research is an open access journal of Nanjing Agricultural University and ranked number one in the Horticulture category of the Journal Citation Reports ™ from Clarivate, 2022. The journal is committed to publishing original research articles, reviews, perspectives, comments, correspondence articles and letters to the editor related to all major horticultural plants and disciplines, including biotechnology, breeding, cellular and molecular biology, evolution, genetics, inter-species interactions, physiology, and the origination and domestication of crops.
END
Blueprint for blueberry improvement: genetic and epigenetic discoveries
2024-08-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The heightened importance of EZH2 in cancer immunotherapy
2024-08-09
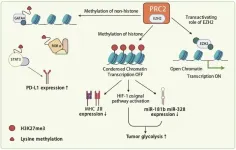
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is a catalytic subunit of the Polycomb-repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which plays a crucial role in transcriptional repression through the methylation of histone H3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3). This epigenetic modification leads to chromatin compaction and gene silencing. EZH2 is frequently overexpressed in a variety of cancers, including head and neck, breast, prostate, bladder, colorectal, lung, pancreatic, melanoma, and lymphoma. Mutations in the EZH2 gene are also prevalent in several hematological malignancies, such as B-lymphomas and follicular lymphomas. The dual role of EZH2 as both a tumor suppressor and oncogene depending on the cancer type ...
Researchers expose vulnerability of speech emotion recognition models to adversarial attacks
2024-08-09
Recent advancements in speech emotion recognition have highlighted the significant potential of deep learning technologies across various applications. However, these deep learning models are susceptible to adversarial attacks. A team of researchers at the University of Milan systematically evaluated the impact of white-box and black-box attacks on different languages and genders within speech emotion recognition. The research was published May 27 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The ...
Classical music lifts our mood by synchronizing our “extended amygdala”
2024-08-09
Whether Bach, Beethoven, or Mozart, it’s widely recognized that classical music can affect a person’s mood. In a study published August 9 in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports, scientists in China use brainwave measurements and neural imaging techniques to show how Western classical music elicits its positive effects on the brain. Their goal is to find more effective ways to use music to activate the brain in those who otherwise don’t respond, such as people with treatment-resistant depression.
“Our research integrates the fields of neuroscience, psychiatry, and ...
New technology uses light to engrave erasable 3D images
2024-08-09
Imagine if physicians could capture three-dimensional projections of medical scans, suspending them inside an acrylic cube to create a hand-held reproduction of a patient's heart, brain, kidneys, or other organs. Then, when the visit is done, a quick blast of heat erases the projection and the cube is ready for the next scan.
A new report in the journal Chem by researchers at Dartmouth and Southern Methodist University (SMU) outlines a technical breakthrough that could enable such scenarios, and others with widespread utility.
The study introduces a technique that uses a specialized ...
How did mental health parity laws affect new moms?
2024-08-09
Pregnant and postpartum women with depression and anxiety have a slightly better chance of getting psychotherapy these days, a new study finds. And they are paying less of their own money when they do.
The changes in care and cost happened mainly after the Affordable Care Act took effect in 2014, and to a lesser extent after the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act, or MHPAEA, took effect in 2010, the analysis shows.
Both laws aimed at reducing insurance-related barriers to mental health care.
Even so, only about 10% of women with private insurance ...
Universal free school meals and school and student outcomes
2024-08-09
About The Study: In this systematic review, universal free school meals were associated with increased meal participation, no or slight improvements in attendance, and decreased obesity prevalence and suspension rates; certainty of evidence was moderate for lunch participation and low or very low for other outcomes. Studies did not report several important outcomes, such as diet quality and food security, suggesting the need for more high-quality research encompassing policy-relevant indicators.
Corresponding Author: To ...
Researchers crack a key celiac mystery
2024-08-09
People with celiac disease must navigate everyday life by avoiding gluten, a protein in wheat, rye and barley which can trigger painful symptoms in the gut, impede the absorption of nutrients and raise the risk of other serious long-term issues.
The autoimmune disorder affects about 1 per cent of the population. Its rate of occurrence has roughly doubled in the past 25 years, but there is no treatment available.
An interdisciplinary team of medical and engineering researchers centred at Canada’s McMaster University and including colleagues from the US, Australia, and Argentina, has spent the ...
Continuing climate warming trend and pronounced interannual variability in precipitation in the Three Gorges Region in 2022–2023
2024-08-09
The Three Gorges Region of the Yangtze River (TGR) in China has a unique geographical location, complex geomorphological features, and a fragile and sensitive climate. The Three Gorges Project, as a large-scale comprehensive water conservancy hub project in the region, has not only greatly changed the nature, society and economy of the area, but also brought great benefits and created problems, such as environmental and climatic impacts. Therefore, it is of great importance to conduct climate and environmental monitoring in the region.
Recently, a team led by Chen Xianyan, a Professor at ...
Is doping of Spiro-OMeTAD a requirement for efficient and stable perovskite indoor photovoltaics?
2024-08-09
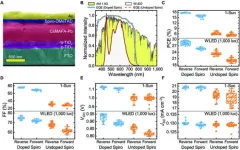
In this work, we study the outdoor and indoor photovoltaic performance of LHP-based devices utilizing Spiro-OMeTAD as the hole-transport material with commonly used dopants such as lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Li-TFSI) or without any dopants. We find out that, despite the expected low performance of devices employing undoped Spiro-OMeTAD layer under 1-Sun illumination (up to 7.7% efficiency), the devices achieve up to 25.6% efficiency under 1000 lux illumination, which is comparable to the doped counterpart devices achieving up to 29.7% efficiency. This is mainly due to the major improvement in fill factor when going towards low-light ...
HKUST engineering researchers enhance perovskite solar cells durability with first-of-its-kind chiral-structured “springy” interface
2024-08-09
A research team led by the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has constructed an unprecedented chiral-structured interface in perovskite solar cells, which enhances the reliability and power conversion efficiency of this fast-advancing solar technology and accelerates its commercialization.
A perovskite solar cell (PSC) is a type of solar cell that includes perovskite-structured compound materials, which are inexpensive to produce and simple to manufacture. Unlike conventional silicon solar cells that require expensive high-temperature, high-vacuum fabrication processes, perovskites can ...