(Press-News.org) People with celiac disease must navigate everyday life by avoiding gluten, a protein in wheat, rye and barley which can trigger painful symptoms in the gut, impede the absorption of nutrients and raise the risk of other serious long-term issues.
The autoimmune disorder affects about 1 per cent of the population. Its rate of occurrence has roughly doubled in the past 25 years, but there is no treatment available.
An interdisciplinary team of medical and engineering researchers centred at Canada’s McMaster University and including colleagues from the US, Australia, and Argentina, has spent the last six years working to unlock a significant piece of the puzzle in the search for a cure: how and where the gluten response begins.
It had previously been thought that the inflammatory response to gluten occurred inside the gut wall and exclusively involved immune cells, but In a new paper published today in the journal Gastroenterology, the team has shown there is more to the story.
They found that the inner lining of the upper intestine, called the “epithelium” –composed of a variety of cells that are not classically part of the immune system – also plays an active role in directing the inflammatory response to gluten.
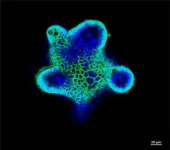
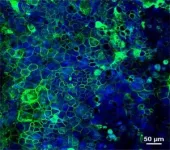
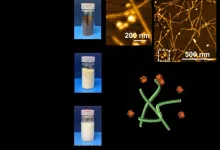
Using microscopic biomaterials in the laboratory, the team created a biologically functioning model of the intestinal epithelium which allowed the researchers to isolate the effects of specific molecules in the epithelial cells of people with celiac disease.
The model allowed the researchers to generate and observe the reactions under controlled conditions, an option that is simply not available in extremely complex gut environments of living beings.
They were able to observe how the molecules alert immune cells to the presence of gluten, and to conclude definitvely that the epithelium plays a crucial role in activating the immune system in celiac disease.
Such a mechanism had been postulated before, but was never proven. Answering this controversial question is expected to advance the development of new drugs.
“The only way we can treat celiac disease today is by fully eliminating gluten from the diet. This is difficult to do, and experts agree that a gluten-free diet is insufficient,” says Elena Verdu, a corresponding author on the paper who is a professor of gastroenterology and director of McMaster’s Farncombe Family Digestive Health Research Institute.
Precisely locating the spark of the immune response could stimulate research into drug delivery to inhibit this newly found role of the epithelium, using drugs already in clinical trials, Verdu says.
“This allowed us to narrow down the specific cause and effect and prove exactly whether and how the reaction takes place,” says Tohid Didar, a corespounding author on the paper and an associate professor at McMaster’s School of Biomedical Engineering who holds the Canada Research Chair in Nano-biomaterials.
Another significant finding from the study is that after detecting gluten, the epithelium sends stronger signals to immune cells if pathogens are also present.
This means that In the future it may be possible to detect the pathogen in a person at risk of developing the disease, and inhibit the interactions with gluten and the gut epithelium to prevent the disease, says the paper’s lead author, Sara Rahmani, a PhD candidate in the Verdu and Didar labs.
END
Researchers crack a key celiac mystery
Where in the body does the gluten reaction begin?
2024-08-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Continuing climate warming trend and pronounced interannual variability in precipitation in the Three Gorges Region in 2022–2023
2024-08-09
The Three Gorges Region of the Yangtze River (TGR) in China has a unique geographical location, complex geomorphological features, and a fragile and sensitive climate. The Three Gorges Project, as a large-scale comprehensive water conservancy hub project in the region, has not only greatly changed the nature, society and economy of the area, but also brought great benefits and created problems, such as environmental and climatic impacts. Therefore, it is of great importance to conduct climate and environmental monitoring in the region.
Recently, a team led by Chen Xianyan, a Professor at ...
Is doping of Spiro-OMeTAD a requirement for efficient and stable perovskite indoor photovoltaics?
2024-08-09
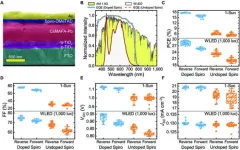
In this work, we study the outdoor and indoor photovoltaic performance of LHP-based devices utilizing Spiro-OMeTAD as the hole-transport material with commonly used dopants such as lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Li-TFSI) or without any dopants. We find out that, despite the expected low performance of devices employing undoped Spiro-OMeTAD layer under 1-Sun illumination (up to 7.7% efficiency), the devices achieve up to 25.6% efficiency under 1000 lux illumination, which is comparable to the doped counterpart devices achieving up to 29.7% efficiency. This is mainly due to the major improvement in fill factor when going towards low-light ...
HKUST engineering researchers enhance perovskite solar cells durability with first-of-its-kind chiral-structured “springy” interface
2024-08-09
A research team led by the School of Engineering of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has constructed an unprecedented chiral-structured interface in perovskite solar cells, which enhances the reliability and power conversion efficiency of this fast-advancing solar technology and accelerates its commercialization.
A perovskite solar cell (PSC) is a type of solar cell that includes perovskite-structured compound materials, which are inexpensive to produce and simple to manufacture. Unlike conventional silicon solar cells that require expensive high-temperature, high-vacuum fabrication processes, perovskites can ...
GSA announces 2024 Award Winners honoring excellence in geoscience
2024-08-09
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America (GSA) is proud to announce the recipients of the 2024 GSA Awards, recognizing outstanding contributions to the geoscience community. Each awardee has demonstrated exceptional dedication, innovation, and impact in their respective fields.
GSA President’s Medal
Kathy Jefferson Bancroftis, a Paiute-Shoshone community leader and environmental protector, is honored for her advocacy and education on water misuse and environmental degradation in the Owens Valley, ...
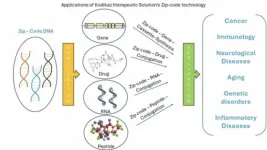
Retrotransposon DNA zip code for myeloma cell internalization
2024-08-09
“GT is a fascinating evolutionary phenomenon observed in lower species and humans, albeit with differing impacts and mechanisms.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 9, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on July 13, 2024, entitled, “Unveiling retrotransposon-derived DNA zip code for myeloma cell internalization.”
The complex interplay between extracellular genetic material and the tumor's genetic landscape presents a significant challenge in grasping cancer evolution, tumor genetic heterogeneity, and treatment response. Earlier research has revealed the role of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in mediating the gene expression among ...
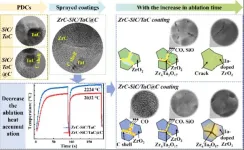
High heat dissipation design improves thermal protection on ultrahigh temperature ablation
2024-08-09
ZrC has drawn wide attention as an anti-ablation coating material for lightweight C/C composites but is limited by the produced porous and loose ZrO2 film. To address this issue, the second phase is introduced to improve the densification of the formed Zr-X-O film. Such as ZrC-SiC/TaC coating, the produced low-melting-point oxides, SiO2 (Tm=1650 °C), Ta2O5 (Tm=1800 °C) and Zr6Ta2O17 (Tm=1900 °C), helped to form a dense oxides film. However, the high service temperature causes heat accumulation and a large thermal stress gradient on the surface of the coatings, which will result in large local defects and accelerate the failure of the coating. To decrease the ablation heat ...
SDGs Design International Awards 2024: Let’s create sustainable design for FOOD!
2024-08-09
Fukuoka, Japan—The SDGs Design International Awards 2024 are calling for students worldwide to submit their original ideas for using design to achieve Sustainable Development Goals.
First organized in 2019 and led by Faculty of Design, Kyushu University, the awards aim to demonstrate the power of design in solving social problems and to elevate society's expectations for design.
Now in its sixth year, this year’s theme is “Let’s Create Sustainable Design for FOOD." ...
Upcycling spent coffee grounds by isolating Mannan-rich Holocellulose nanofibers
2024-08-09
Along with all the coffee we drink every day, over 6 million tons of spent coffee grounds are produced annually worldwide. Some of these grounds are reused as biofuel but the rest are disposed of in landfills. Over the last decade, research has focused on how to reuse these grounds. The primary focus has been on the polysaccharides from the cellulose and hemicellulose in the ground up coffee bean’s cell walls. Polysaccharides are used in composites, biopolymers, food packaging, construction materials and cellulose nanofibers (CNFs). CNFs specifically, which are cellulose reduced to nanoparticle size, 3 to 5 ...
Long-term coral reef monitoring continues to deliver crucial insights
2024-08-09
As the effects of a changing climate and other ecological insults compound, many coral reefs face severe perturbations and a generally poor prognosis for recovery. In an article published in BioScience's new "Perspective and Insight" category, Dr. Peter J. Edmunds of California State University, Northridge, argues for the continued monitoring of coral reefs, even when the seascapes they inhabit are in a significantly degraded state.
Drawing from his ongoing 37-year study in the US Virgin Islands, Edmunds argues that "only consistent, rigorous, and detail-oriented ...
AACR CEO Dr. Margaret Foti selected as the 2024 Beacon Award Winner for her significant impact in the fight against cancer
2024-08-09
Rockville, MD (8/9/2024) – The AIM-HI Accelerator Fund today announces Margaret Foti, PhD, MD (hc), Chief Executive Officer of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), is selected unanimously by the 2024 Blue Ribbon Selection Committee as the recipient of the 2024 Beacon Award for Women Leaders in Oncology, from a pool of outstanding global nominees.
The Beacon Award for Women Leaders in Oncology was established in 2022 by the AIM-HI Accelerator Fund and sponsored by the National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR). The Beacon Award recognizes outstanding women leaders in health and life sciences who have significantly impacted cancer ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Researchers crack a key celiac mysteryWhere in the body does the gluten reaction begin?