(Press-News.org) A new study led by the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology shows how feeding mice a drug called GSM-15606 provided protection against air pollution-related increases in proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
Senior author Caleb Finch, USC University Professor and holder of the ARCO/William F. Kieschnick Chair in the Neurobiology of Aging at the USC Leonard Davis School, has studied air pollution’s effects on the brain for several years, especially the consequences of exposure to fine particulates found in pollution from automobiles, factories and more. Many studies have shown that air quality has a sizeable impact on risk of Alzheimer and accelerates cognitive decline, he said.
Air pollution is correlated with systemic inflammation and promotes the formation of amyloid plaques, the clumps of aggregated peptide Aβ42 that form between the brain’s nerve cells in Alzheimer’s.
The latest work from Finch’s lab, published August 12 in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, highlights the potential protection offered by a type of drug called a gamma-secretase modulator. The team tested a specific drug called GSM-15606, which was developed by study co-authors Rudolph E. Tanzi of Harvard and Kevin D. Rynearson of the University of California, San Diego.
GSM-15606 was fed to mice over 8 weeks; during that time, the animals were regularly exposed to air pollution in the form of either ambient nanoparticulate matter (nPM) or diesel exhaust particles (DEP). Following air pollution exposure, mice fed GSM-15606 had much lower levels of Aβ42 in the brain than mice exposed to pollution but not the drug.
The results indicate that GSM-15606 may one day have a role as a preventive measure against Alzheimer’s in people living with air pollution, Finch said.
“Because gamma secretase is needed for normal functions body-wide, this drug was designed to modulate, but not inhibit, production of Aβ42,” he said. “This is the first example of a new drug developed to slow Alzheimer’s that may also protect aging individuals from the environmental risk factor of air pollution.”
Along with Finch, study authors included first author Jose A. Godoy-Lugo as well as Max A. Thorwald, Mafalda Cacciottolo, Carla D’Agostino, Ararat Chakhoyan, and Constantinos Sioutas of USC; Rudolph E. Tanzi of Harvard; and Kevin D. Rynearson of the University of California, San Diego. Lab studies were supported by grants to Finch from the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund and NIH (R01-AG051521, P01-AG055367).
END
USC study: Drug protects against air pollution-related Alzheimer’s signs in mice
Mice that had been fed the drug GSM-15606 had lower levels of Aβ42, the largest form of the amyloid beta protein that makes up the telltale plaques seen in brains with Alzheimer’s.
2024-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mild Cognitive Impairment could be going unreported in rural areas of west Michigan, study suggests
2024-08-12
Grand Rapids, Mich., Aug. 12, 2024 – Corewell Health™ and Michigan State University researchers are the first in the state to use de-identified electronic health records of more than 1.5 million patients to analyze incidence rates and risk factors of mild cognitive impairment, or MCI, in rural and urban areas in West Michigan.
Results showed that many cases could be going undetected among those living in rural communities in the area, and researchers now will use the findings to develop AI tools that can detect MCI earlier among patients across the country.
The retrospective study, which included 10 years of historical patient ...
Brain electrical stimulation suppresses appetite. A new frontier in obesity treatment?
2024-08-12
The R&D on neuromodulation technology for the treatment and management of metabolic syndrome conducted by a team led by Dr. Ki-young Shin of Human Care Electro-Medical Device Research Center, Electro-Medical Equipment Research Division of KERI is underway smoothly.
Metabolic syndrome is a complex of multiple metabolic abnormalities, including obesity, high blood pressure, and high triglycerides, often caused by poor diet and lack of exercise. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), one in eight people worldwide is overweight, making obesity treatment ...
Eco-conscious fashionistas hampered by geographical barriers to return clothing
2024-08-12
Eco-conscious consumers are not well-served by clothing companies claiming green credentials, as shoppers’ location has a major impact on the effectiveness of clothing return schemes, a new study reveals.
Environmental circular economy initiatives for activewear companies are limited by where firms and consumers are located, preventing them from being fully effective.
The clothing industry is one of the biggest global polluters, with fast fashion companies creating cheap clothing that gets thrown away after one or two uses and ends up in landfill. According to the European ...
Redefining the computer whiz: research shows diverse skills valued by youth
2024-08-12
FOR A COPY OF THE STUDY AHEAD OF PUBLICATION, PLEASE ENSURE YOU ARE SIGNED UP TO TAYLOR & FRANCIS’ EMBARGO AREA AND THEN VISIT: https://newsroom.taylorandfrancisgroup.com/redefining-the-computer-whiz-research-shows-diverse-skills-valued-by-youth/
New study reveals diverse perceptions of the 'ideal' computer science student among young people.
Researchers at the University of Reading, with colleagues at King's College London, have uncovered a more nuanced view of what makes an 'ideal' computer science student, challenging long-held stereotypes of geeky, clever, ...
Fern becomes first in suborder to be classed as “independent gametophyte”
2024-08-10
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered that the fern Hymenasplenium murakami-hatanakae can become independent gametophytes i.e. live for long periods without a spore-producing sporophyte. They collected specimens from Izu-Oshima Island, Japan, and used DNA analysis to show that this Aspleniineae fern, a suborder encompassing thirty percent of ferns on the planet, was part of this rare class. Studying the species further promises to reveal more about how ferns diversify and adapt.
The “alternation of generations” in plants and algae is the intricate cycle by which they reproduce. Each ...
Study reveals Canadian wildfires are affecting US air quality and raising health concerns
2024-08-09
Climate-driven wildfire events are rapidly transferring harmful particulate matter containing toxic chemicals over long distances, compromising air quality in the New Jersey and New York City areas, according to Rutgers Health research.
Published in Environmental Science & Technology and to be featured on the cover of the journal’s next issue, the study assessed the physical and chemical characteristics of wildfire-related particulate matter and was the first to report this characterization from a climate-driven wildfire event in the densely populated Northeast region.
“Particulate ...
As temperatures break records, many are unaware of symptoms of heat-related illnesses
2024-08-09
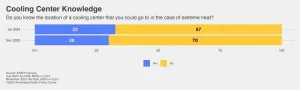
PHILADELPHIA – With NASA data showing that July 22, 2024, was the hottest day on record and indications that July may have been the hottest month, an Annenberg Public Policy Center survey conducted in mid-July found that most people know three of the symptoms of a heat-related illness but do not know the location of their nearest cooling center. At the same time, increasing numbers of people think that heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense and affecting their daily activities.
Knowledge of cooling centers in the case of extreme heat
Although the locations of cooling centers, or indoor air-conditioned facilities such as libraries, ...
Researchers discover new mechanism to cool buildings while saving energy
2024-08-09
With temperatures rising globally, the need for more sustainable cooling options is also growing. Researchers at UCLA and their colleagues have now found an affordable and scalable process to cool buildings in the summer and heat them in the winter.
Led by Aaswath Raman, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering, the research team recently published a study in Cell Reports Physical Science detailing a new method to manipulate the movement ...
New study will provide HIV prevention and treatment for incarcerated people with opioid use disorder
2024-08-09
The University of Massachusetts Amherst and Tufts Medical Center are conducting a study to provide HIV prevention, diagnosis and treatment for people with opioid use disorders who are incarcerated in the Boston area.
The study is funded with a $4.74 million CONNECT grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Elizabeth Evans, professor of community health education in the UMass Amherst School of Public Health and Health Sciences, and Dr. Alysse Wurcel, a ...
Russian invasion of Ukraine could have lasting impacts on global economy, environment
2024-08-09
As the Russian invasion of Ukraine stretches into its third year, international trade has felt the effects as sanctions on Russian exports have expanded. Now researchers have found that the invasion may not only have significant short-term impacts on the global timber markets but may leave lasting effects on the global economy and the environment.
These findings are detailed in a new study which projects the impact of sanctions on Russia and military disruption in Ukraine on the global wood product markets. Researchers compared two projected scenario outcomes based on the Global Forest Products Market model, one ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
[Press-News.org] USC study: Drug protects against air pollution-related Alzheimer’s signs in miceMice that had been fed the drug GSM-15606 had lower levels of Aβ42, the largest form of the amyloid beta protein that makes up the telltale plaques seen in brains with Alzheimer’s.