(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA – With NASA data showing that July 22, 2024, was the hottest day on record and indications that July may have been the hottest month, an Annenberg Public Policy Center survey conducted in mid-July found that most people know three of the symptoms of a heat-related illness but do not know the location of their nearest cooling center. At the same time, increasing numbers of people think that heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense and affecting their daily activities.
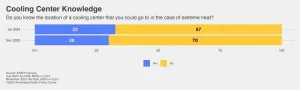
Knowledge of cooling centers in the case of extreme heat
Although the locations of cooling centers, or indoor air-conditioned facilities such as libraries, community and senior centers, schools are publicized by city governments on hot days, many of those surveyed report being unaware of where to find one. Two-thirds of respondents (67%) say they do not know the location of a cooling center to which they could go to in case of extreme heat, a number statistically unchanged from last November. “Communities must do a better job of making the public, especially the most vulnerable, aware of these centers,” said Ken Winneg, managing director of survey research at APPC.
More today see link between extreme heat and climate change.
When compared with an APPC survey in November 2023, significantly more people now say that climate change is increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses, respiratory diseases, and insect-borne diseases. Two-thirds (67%) hold this view vs. just under 6 in 10 (58%) in November 2023.
More people indicate that heat waves in the United States are becoming more frequent and intense than in the past. About two-thirds (65%) believe heat waves are becoming more frequent and intense. Fifty-eight percent (58%) felt this way in November 2023, when we last asked the question. About a quarter (24%) believe heat waves are about as frequent and intense as they have always been, statistically unchanged from our earlier survey.
At the same time, the proportion of people who say extreme heat has often or frequently affected their typical daily activities in the past year has increased significantly. Forty-three percent (43%) say extreme outdoor heat has often (22%) or frequently (21%) affected their daily activities, an 8-point increase compared with November 2023 (35% in total said either “often” or “frequently”).
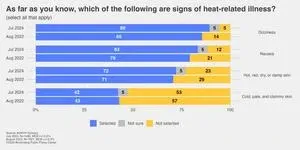
Signs of heat-related illnesses
Notably, most people also know three of the telltale signs of heat-related illnesses:
Dizziness (89% compared to 86% in August 2022)
Nausea (83% compared to 79% in August 2022)
Hot, red, dry, or damp skin (72%, statistically unchanged from August 2022)
Cold, pale, and clammy skin (42%, statistically unchanged from August 2022).
Public understands some extreme heat risks better than others
Thinking about the next 10 years, just under 6 in 10 (58%) think that people in their community will be more likely to experience heat stroke caused by extreme heat waves. This is significantly higher than in November 2023 when just over half (52%) said they thought people in their community would be more likely to experience heat stroke caused by extreme heat waves in the next 10 years.
However, only 3 in 10 (30%) know that a pregnant person in the U.S. who is exposed to extreme heat is more likely to deliver their baby early than a pregnant person who is not exposed to extreme heat. About a quarter (23%) incorrectly say that a pregnant person in the U.S. is either less or just as likely to deliver a baby early. Forty-seven percent (47%) are unsure which is correct.
Broad awareness that heat-related deaths are most common among seniors
Two-thirds (67%) know that heat-related deaths are most common among older adults, aged 65 or older, slightly but significantly higher than in August 2022 (62%).
Preventing heat-related illnesses
Nearly all (92%) know that drinking water is better to prevent heat-related illnesses than drinking sugary drinks.
APPC’s ASAPH survey
The survey data come from the 20th wave of a nationally representative panel of 1,496 U.S. adults, first empaneled in April 2021, conducted for the Annenberg Public Policy Center by SSRS, an independent market research company. This wave of the Annenberg Science and Public Health Knowledge (ASAPH) survey was fielded July 11-18, 2024, and has a margin of sampling error (MOE) of ± 3.6 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. All figures are rounded to the nearest whole number and may not add to 100%. Combined subcategories may not add to totals in the topline and text due to rounding.
Download the topline and methodology statement.
The policy center has been tracking the American public’s knowledge, beliefs, and behaviors regarding vaccination, Covid-19, mpox, flu, maternal health, climate change, and other consequential health issues through this Annenberg Science and Public Health (ASAPH) knowledge survey panel for over three years. In addition to Winneg, the APPC team includes senior data analyst Laura Gibson; research analyst Shawn Patterson Jr. and Patrick E. Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Health and Risk Communication Institute.
The Annenberg Public Policy Center was established in 1993 to educate the public and policy makers about communication’s role in advancing public understanding of political, science, and health issues at the local, state, and federal levels.
END
As temperatures break records, many are unaware of symptoms of heat-related illnesses
Increasing numbers link extreme heat to climate change
2024-08-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover new mechanism to cool buildings while saving energy
2024-08-09
With temperatures rising globally, the need for more sustainable cooling options is also growing. Researchers at UCLA and their colleagues have now found an affordable and scalable process to cool buildings in the summer and heat them in the winter.
Led by Aaswath Raman, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering, the research team recently published a study in Cell Reports Physical Science detailing a new method to manipulate the movement ...
New study will provide HIV prevention and treatment for incarcerated people with opioid use disorder
2024-08-09
The University of Massachusetts Amherst and Tufts Medical Center are conducting a study to provide HIV prevention, diagnosis and treatment for people with opioid use disorders who are incarcerated in the Boston area.
The study is funded with a $4.74 million CONNECT grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Elizabeth Evans, professor of community health education in the UMass Amherst School of Public Health and Health Sciences, and Dr. Alysse Wurcel, a ...
Russian invasion of Ukraine could have lasting impacts on global economy, environment
2024-08-09
As the Russian invasion of Ukraine stretches into its third year, international trade has felt the effects as sanctions on Russian exports have expanded. Now researchers have found that the invasion may not only have significant short-term impacts on the global timber markets but may leave lasting effects on the global economy and the environment.
These findings are detailed in a new study which projects the impact of sanctions on Russia and military disruption in Ukraine on the global wood product markets. Researchers compared two projected scenario outcomes based on the Global Forest Products Market model, one ...
Investigating a critical factor for promoting drug-context associations and relapse
2024-08-09
Most people wouldn’t think twice after seeing sugar spilled on a counter. But for someone with a history of cocaine use, this visual cue could trigger powerful associations with their past drug use and a compulsive urge to seek the drug.
Certain circuits within the brain help to form natural associations between one’s experiences and the context in which those experiences occur. These associations play a critical role in the orchestration of adaptive learning. When addictive substances are introduced, this coupling mechanism can be hijacked so that ...
New material for optically-controlled magnetic memory discovered
2024-08-09
Researchers at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have made unexpected progress toward developing a new optical memory that can quickly and energy-efficiently store and access computational data. While studying a complex material composed of manganese, bismuth and tellurium (MnBi2Te4), the researchers realized that the material’s magnetic properties changed quickly and easily in response to light. This means that a laser could be used to encode information ...
Detroit research team to investigate fear of falling in MS patients
2024-08-09
DETROIT — Taylor Takla, a Ph.D. candidate in the translational neuroscience program in Wayne State University’s School of Medicine, recently received a two-year, $96,812 F31 grant from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study fear of falling in those with multiple sclerosis (MS).
The grant, “Investigating Fear of Falling in Multiple Sclerosis: An Interplay of Neural, Motor, Cognitive, and Psychological Factors,” aims to address a major public health concern in persons with MS that results in increased falls, decreased physical activity and ...
A new mechanism for shaping animal tissues
2024-08-09
A key question that remains in biology and biophysics is how three-dimensional tissue shapes emerge during animal development. Research teams from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden, Germany, the Excellence Cluster Physics of Life (PoL) at the TU Dresden, and the Center for Systems Biology Dresden (CSBD) have now found a mechanism by which tissues can be “programmed” to transition from a flat state to a three-dimensional shape. To accomplish this, the researchers looked at the development of the fruit fly Drosophila and its ...
New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversity
2024-08-09
New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversity
A newly discovered species of marine crocodile from 135 million years ago described from Germany
An international team of scientists, including researchers from Germany and the UK, have described a new species of ancient marine crocodile, Enalioetes schroederi. Enalioetes lived in the shallow seas that covered much of Germany during the Cretaceous Period, approximately 135 million years ago.
This ...
CMU researchers outline promises, challenges of understanding AI for biological discovery
2024-08-09
Machine learning is a powerful tool in computational biology, enabling the analysis of a wide range of biomedical data such as genomic sequences and biological imaging. But when researchers use machine learning in computational biology, understanding model behavior remains crucial for uncovering the underlying biological mechanisms in health and disease.
In a recent article in Nature Methods, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science propose guidelines that outline pitfalls and opportunities for using interpretable ...
Japan SciCom Forum 2024 comes to Fukuoka on October 22-23
2024-08-09
On October 22 and 23, the sixth Japan SciCom Forum Conference (JSF 2024) will be held at Kyushu University's Ito Campus. Fukuoka will become the third city, following Tokyo and Okinawa, to welcome specialists in science communication from Japan and around the world.
JSF 2024 will bring together a diverse group of science communicators, writers, researchers, and journalists, along with experts from overseas. The conference is open to anyone involved in sharing research findings internationally, as well as those interested in science communication, public outreach, and engagement.
This year's JSF will explore a wide range of topics, including ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] As temperatures break records, many are unaware of symptoms of heat-related illnessesIncreasing numbers link extreme heat to climate change