(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have made unexpected progress toward developing a new optical memory that can quickly and energy-efficiently store and access computational data. While studying a complex material composed of manganese, bismuth and tellurium (MnBi2Te4), the researchers realized that the material’s magnetic properties changed quickly and easily in response to light. This means that a laser could be used to encode information within the magnetic states of MnBi2Te4.
“This really underscores how fundamental science can enable new ways of thinking about engineering applications very directly,” said Shuolong Yang, assistant professor of molecular engineering and senior author of the new work. “We started with the motivation to understand the molecular details of this material and ended up realizing it had previously undiscovered properties that make it very useful.”
In a paper published in Science Advances, Yang and colleagues showed how the electrons in MnBi2Te4 compete between two opposing states – a topological state useful for encoding quantum information and a light-sensitive state useful for optical storage.
Solving a topological puzzle
In the past, MnBi2Te4 has been studied for its promise as a magnetic topological insulator (MTI), a material that behaves like an insulator on its interior but conducts electricity on its outer surfaces. For an ideal MTI in the 2D limit, a quantum phenomenon emerges in which an electric current flows in a two-dimensional stream along its edges. These so-called “electron freeways” have the potential to encode and carry quantum data.
While scientists have predicted that MnBi2Te4 should be able to host such an electron freeway, the material has been hard to work with experimentally.
“Our initial goal was to understand why it has been so hard to get these topological properties in MnBi2Te4,” said Yang. “Why is the predicted physics not there?”
To answer that question, Yang’s group turned to cutting-edge spectroscopy methods that let them visualize the behavior of the electrons within MnBi2Te4 in real time on ultrafast time scales. They used time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy developed in the Yang lab, and collaborated with Xiao-Xiao Zhang’s group at the University of Florida to perform time-resolved magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) measurements, which allows the observation of magnetism.
“This combination of techniques gave us direct information on not only how electrons were moving, but how their properties were coupled to light,” explained Yang.
Two opposing states
When the researchers analyzed their spectroscopy results, it was clear why MnBi2Te4 was not acting as a good topological material. There was a quasi-2D electronic state, which was competing with the topological state for electrons.
“There is a completely different type of surface electrons that replace the original topological surface electrons,” said Yang. “But it turns out that this quasi-2D state actually has a different, very useful property.”
The second electronic state had a tight coupling between magnetism and external photons of light — not useful for sensitive quantum data but the exact requirements for an efficient optical memory.
To further explore this potential application of MnBi2Te4, Yang’s group is now planning experiments in which they use a laser to manipulate the material’s properties. They believe that an optical memory using MnBi2Te4 could be orders of magnitude more efficient than today’s typical electronic memory devices.
Yang also pointed out that a better understanding of the balance between the two electron states on the surface of MnBi2Te4 could boost its ability to act as an MTI and be useful in quantum data storage.
“Perhaps we could learn to tune the balance between the original, theoretically predicted state and this new quasi-2D electronic state,” he said. “This might be possible by controlling our synthesis conditions.”
END
New material for optically-controlled magnetic memory discovered
PME researchers were carrying out basic research on a magnetic topological insulator when they realized it had the potential to build optical storage devices.
2024-08-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Detroit research team to investigate fear of falling in MS patients
2024-08-09
DETROIT — Taylor Takla, a Ph.D. candidate in the translational neuroscience program in Wayne State University’s School of Medicine, recently received a two-year, $96,812 F31 grant from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study fear of falling in those with multiple sclerosis (MS).
The grant, “Investigating Fear of Falling in Multiple Sclerosis: An Interplay of Neural, Motor, Cognitive, and Psychological Factors,” aims to address a major public health concern in persons with MS that results in increased falls, decreased physical activity and ...
A new mechanism for shaping animal tissues
2024-08-09
A key question that remains in biology and biophysics is how three-dimensional tissue shapes emerge during animal development. Research teams from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden, Germany, the Excellence Cluster Physics of Life (PoL) at the TU Dresden, and the Center for Systems Biology Dresden (CSBD) have now found a mechanism by which tissues can be “programmed” to transition from a flat state to a three-dimensional shape. To accomplish this, the researchers looked at the development of the fruit fly Drosophila and its ...
New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversity
2024-08-09
New ancient marine crocodile from time of dinosaurs provides insight into the groups lifestyle and diversity
A newly discovered species of marine crocodile from 135 million years ago described from Germany
An international team of scientists, including researchers from Germany and the UK, have described a new species of ancient marine crocodile, Enalioetes schroederi. Enalioetes lived in the shallow seas that covered much of Germany during the Cretaceous Period, approximately 135 million years ago.
This ...
CMU researchers outline promises, challenges of understanding AI for biological discovery
2024-08-09
Machine learning is a powerful tool in computational biology, enabling the analysis of a wide range of biomedical data such as genomic sequences and biological imaging. But when researchers use machine learning in computational biology, understanding model behavior remains crucial for uncovering the underlying biological mechanisms in health and disease.
In a recent article in Nature Methods, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University's School of Computer Science propose guidelines that outline pitfalls and opportunities for using interpretable ...
Japan SciCom Forum 2024 comes to Fukuoka on October 22-23
2024-08-09
On October 22 and 23, the sixth Japan SciCom Forum Conference (JSF 2024) will be held at Kyushu University's Ito Campus. Fukuoka will become the third city, following Tokyo and Okinawa, to welcome specialists in science communication from Japan and around the world.
JSF 2024 will bring together a diverse group of science communicators, writers, researchers, and journalists, along with experts from overseas. The conference is open to anyone involved in sharing research findings internationally, as well as those interested in science communication, public outreach, and engagement.
This year's JSF will explore a wide range of topics, including ...
Organic farms certified by peers display higher product diversity
2024-08-09
In Brazil, a study compared two systems of organic product certification implemented in São Paulo state. One system involves conventional certification by auditors accredited by the Ministry of Agriculture and the National Institute of Metrology, Quality and Technology (INMETRO). The other is peer-to-peer certification.
The study, reported in an article published in the journal Organic Agriculture, suggests that peer-to-peer certification adds the virtue of agrobiodiversity to organic farming in light of the significantly larger number of products offered by farms with this type of certification. “This ...
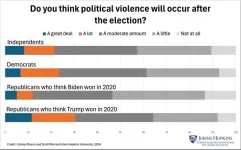
Republicans who believe Trump won in 2020 expect significant chaos in November
2024-08-09
Republicans who believe Donald Trump won the 2020 election are anticipating a much more chaotic election cycle this year than other GOP, Democratic, and independent voters, according to new polling data from the SNF Agora Institute at Johns Hopkins University.
Among Republican respondents who believe President Joe Biden did not lawfully win the 2020 election, about 31% think that either “a lot” or “a great deal” of political violence will occur after the 2024 election—compared to 24% of Democratic voters, 21% of independents and just 12% of GOP voters who acknowledge Biden’s victory four years ago, the poll found.
In ...
Memory problems in old age linked to a key enzyme, study in mice finds
2024-08-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Everyone has moments of forgetfulness from time to time, especially as we get older. But older adults don’t just have difficulty remembering new information. They also have a harder time modifying those memories when new details emerge. Yet, little is known about the mechanisms behind memory updating and how those mechanisms go awry with age.
A team of researchers from Penn State has identified an enzyme that contributes to age-related impairments in memory updating. When blocked, older mice were better able to incorporate new information and performed similarly ...
National study shows how internal medicine chief residency has changed over 20 years
2024-08-09
New research shows how the chief resident position in academic internal medicine residency programs has evolved over the past 20 years, revealing how the position has changed, the types of careers these individuals pursue, and improvement in gender representation.
These findings, published this summer by the American Journal of Medicine, stem from a 20-year multicenter study that involved the University of Colorado Internal Medicine Residency Program. CU Department of Medicine faculty member William Turbyfill, MD, was among the study’s site investigators.
Turbyfill, who practices in the Veterans Affairs ...
VA’s Disrupted Care National Project discovers vascular surgery rates still decreasing since COVID-19 pandemic
2024-08-09
White River Junction, VT – Recently published findings from the VA Disrupted Care National Project (DCNP) revealed the number of vascular surgeries performed across the United States continued to decline even after large drops during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A multi-institutional team of researchers, led by the White River Junction VA Medical Center, analyzed 21,031 vascular surgeries of three common procedures from 2019 to 2023 using Medicare claim data. There was a dramatic drop of 47% at the beginning of the pandemic, but while rates of care recovered partially another ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] New material for optically-controlled magnetic memory discoveredPME researchers were carrying out basic research on a magnetic topological insulator when they realized it had the potential to build optical storage devices.