(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — August 12, 2024 – Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) is launching the next phase of an electric vehicle (EV) battery consortium dedicated to understanding performance of energy storage systems. The Electrified Vehicle and Energy Storage Evaluation-II (EVESE-II) consortium builds on more than a decade of SwRI-led, precompetitive research with companies across the mobility sector.
“We are proud to serve the EV industry by bringing together manufacturers, suppliers and battery designers and developers with materials scientists to address a variety of challenges,” said Dr. Andre Swarts, an SwRI staff engineer in SwRI’s Automotive Propulsion Systems Department.
The consortium will host a kickoff meeting on August 15 where potential members can learn more about EVESE research and SwRI’s electrified powertrain activities. Visit https://evese.swri.org to register for free virtual or in-person attendance at SwRI in San Antonio.
EVESE-II will continue battery cell research established during the first phase of EVESE while expanding its focus on module and pack research. “Cell research will remain at the heart of the program with a focus on test repeatability, cell aging and fast charging research as well as exploring emerging cell chemistries with increased energy capacities,” Swarts said.
Performance and abuse testing at various scales will provide critical data and insights to improve thermal management and safety performance by the application of different technologies. Immersion cooling is the technology that entails submerging battery cells or packs into a dielectric fluid that dissipates heat more effectively than air-cooling.
“The emphasis on immersion cooling came out of past EVESE work, which underscored its ability to enhance thermal management and mitigate thermal runaway,” said Dr. Swapnil Salvi, an SwRI research engineer in SwRI’s Automotive Propulsion Systems Department. “SwRI has developed a substantial portfolio of test capabilities over the past few years to support these research activities.” For more information, visit Battery Immersion Cooling Testing & Research. In addition, EVESE-II will explore new frontiers in charging technology, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) systems and advanced in-situ battery health diagnostics and improved understanding, all supported by advanced modeling and simulation.
Consortium members will select from proposed topics or suggest new ones with the final work scope determined by mutual agreement. Members are entitled to all consortium data, with confidentiality restrictions in place to protect sensitive information. Member benefits and deliverables include monthly and final reports and regular remote and in-person meetings with updates on regulatory, market and technology trends. Other benefits include access to SwRI internal research data, test rigs and methodologies as well as royalty-free licenses to patents that result from consortium activities.
SwRI is home to several consortia dedicated to advancing a variety of powertrain technologies spanning electric, internal combustion and fuel cell technologies.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/industry/battery-testing-research/electrified-vehicle-energy-storage-evaluation-ii-evese-ii.
END
SwRI launches Electrified Vehicle and Energy Storage Evaluation-II battery consortium
EVESE-II consortium advances research of EV battery cells, modules, packs, and applications
2024-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Possible explanation for link between diabetes and Alzheimer's
2024-08-12
People with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive problems. A new study led by Umeå University, Sweden, shows that the reason may be that people with type 2 diabetes have more difficulty getting rid of a protein that may cause the disease.
"The results may be important for further research into possible treatments to counteract the risk of people with type 2 diabetes being affected by Alzheimer's," says Olov Rolandsson, senior professor at the Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine at Umeå University, research leader and first author of the study.
The substances ...
Surf spots are global ally in climate fight, study finds
2024-08-12
Surf Spots are Global Ally in Climate Fight, Study Finds
Nearly 90 million metric tonnes of planet-warming carbon found surrounding surf breaks across the world; U.S., Australia, Indonesia, Brazil identified as conservation priorities
ARLINGTON, Va. (Aug. 12, 2024) – A first-of-its-kind study, published today in Conservation Science and Practice, has found that the forests, mangroves and marshes surrounding surf breaks store almost 90 Mt (million metric tonnes) of climate-stabilizing “irrecoverable carbon,” making these coastal locations ...
Taking a ‘one in a million’ shot to tackle dopamine-linked brain disorders
2024-08-12
Dopamine, a powerful brain chemical and neurotransmitter, is a key regulator of many important functions such as attention, experiencing pleasure and reward, and coordinating movement. The brain tightly regulates the production, release, inactivation and signaling of dopamine via a host of genes whose identity and link to human disease continue to expand.
Brain disorders associated with altered dopamine signaling include substance use disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. The complexity of the human brain and its ...
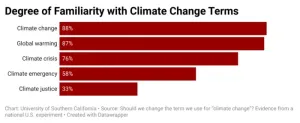
Just say “climate change” – not “climate emergency”
2024-08-12
The terms “climate change” and “global warming” are not only more familiar to people than some of their most common synonyms, but they also generate more concern about the warming of the Earth, according to a USC study published today in the journal Climatic Change.
The study began by looking at how familiar people are with the terms “global warming,” “climate change,” “climate crisis,” “climate emergency,” and “climate justice.” ...
Mature forests vital in frontline fight against climate change
2024-08-12
Mature forests have a key role to play in the fight against climate change – extracting carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and locking it into new wood, a new study reveals.
Researchers discovered that older trees responded to increased atmospheric levels of CO2 by increasing production of woody biomass – countering existing theories that mature woodland has no capacity to respond to elevated CO2 levels.
The experts found exposure to elevated levels of the greenhouse gas (ambient ...
Balancing technology and governance are key to achieving climate goals
2024-08-12
Despite advancements in clean energy, global CO2 emissions continue to rise. IIASA researchers contributed to a new international study that underscores the importance of integrating technological advancements with robust institutional capacities to formulate effective climate policies.
The Paris Agreement's goal to limit global warming to 1.5°C demands rapid reductions in CO2 emissions and heightened attention to non-CO2 greenhouse gases. Despite advancements in clean energy, global CO2 ...
Align or die
2024-08-12
A previously unknown mechanism of active matter self-organization essential for bacterial cell division follows the motto ‘dying to align’: Misaligned filaments ‘die’ spontaneously to form a ring structure at the center of the dividing cell. The study, led by the Šarić group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), was published in Nature Physics. The work could find applications in developing synthetic self-healing materials.
How does matter, lifeless by definition, self-organize and make us alive? One of the hallmarks of life, self-organization, is the spontaneous formation ...
Breakthrough heart MRI technique accurately predicts heart failure risk in general population
2024-08-12
New research looking at more than 39,000 UK biobank participants found those with higher heart pressure estimated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) were five times more likely to develop heart failure
Key risk factors discovered for increased heart pressure include age over 70, high blood pressure, obesity, alcohol consumption and male gender
Breakthrough by University of East Anglia and Queen Mary University of London suggests that heart MRI could potentially replace invasive diagnostic tests
Peer-reviewed – Observational Study - People
MRI scans could replace invasive heart tests, as new research shows they can reliably estimate pressures ...
Global study predicts increases in cancer cases and deaths among men, with widening disparities based on age and countries’ economic status
2024-08-12
In an analysis of 30 cancer types among men, investigators uncovered substantial disparities in cancer cases and deaths by age and countries’ economic status—disparities that are projected to widen by 2050. The study is published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Men face higher rates of cancer and cancer-related deaths than women, likely due to various factors including lower participation in cancer prevention activities; underuse of screening and treatment options; increased exposure to cancer risk factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and occupational exposure to carcinogens; and biological ...
USC study: Drug protects against air pollution-related Alzheimer’s signs in mice
2024-08-12
A new study led by the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology shows how feeding mice a drug called GSM-15606 provided protection against air pollution-related increases in proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
Senior author Caleb Finch, USC University Professor and holder of the ARCO/William F. Kieschnick Chair in the Neurobiology of Aging at the USC Leonard Davis School, has studied air pollution’s effects on the brain for several years, especially the consequences of exposure to fine particulates found in pollution from automobiles, factories and more. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] SwRI launches Electrified Vehicle and Energy Storage Evaluation-II battery consortiumEVESE-II consortium advances research of EV battery cells, modules, packs, and applications